Operation & leakage tests, Operation: general, Mechanical release (caging) of the bendix – Bendix Commercial Vehicle Systems EverSure Spring Brake with No Touch Technology User Manual
Page 4: Eversure, Spring brake
4
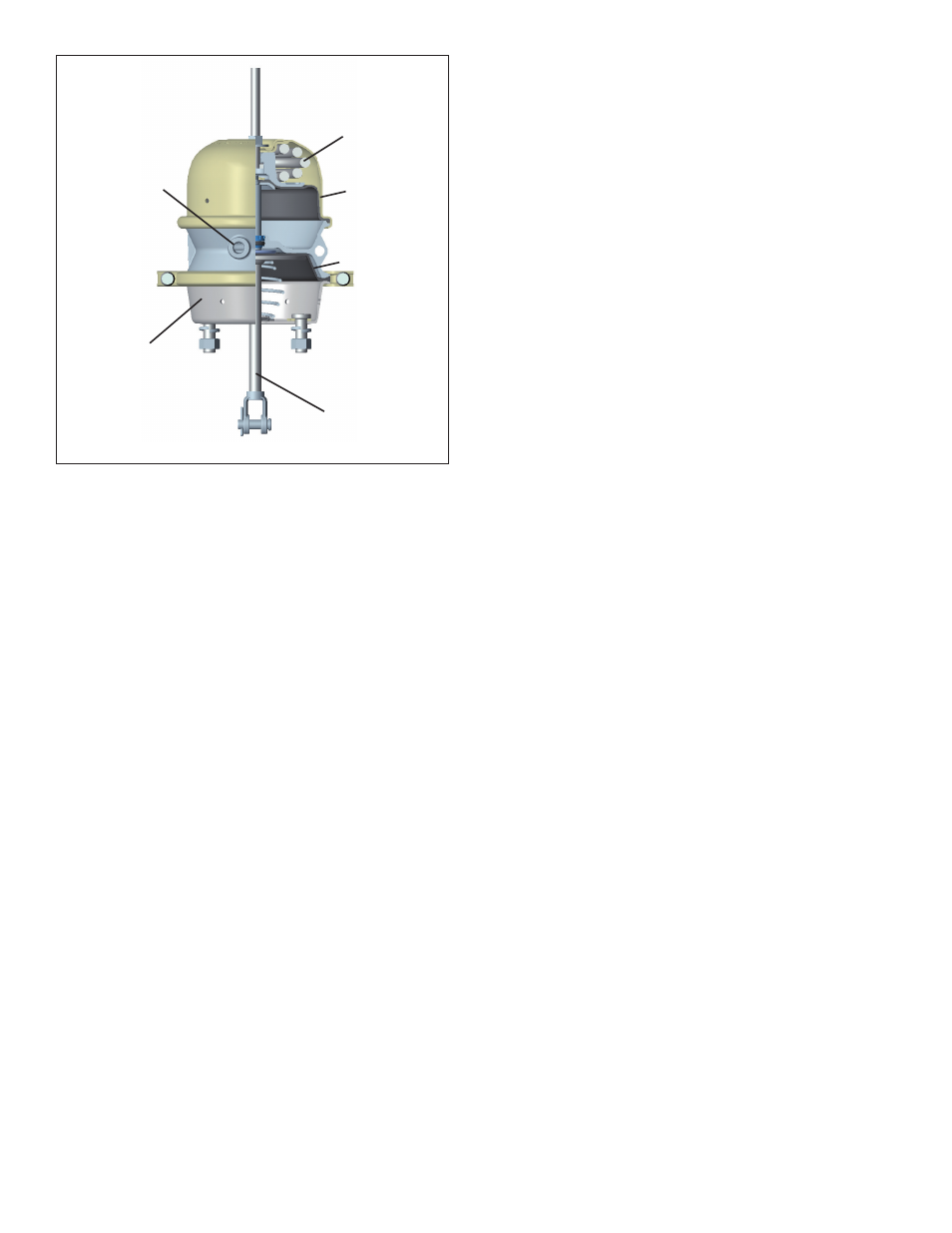
FIGURE 3 - SPRING BRAKE CUT-AWAY VIEW
PARKING/
EMERGENCY
PORT
(MARKED “12”)
NON-PRESSURE
HOUSING
PUSH ROD
DIAPHRAGM
DIAPHRAGM
MAIN SPRING
4. OPERATION & LEAKAGE TESTS
4.1. OPERATING TEST
4.1.1. Apply the brakes and observe that the push rods
move out promptly and without binding.
4.1.2. Release brakes and observe that the push rods
return to the released position promptly and without
binding.
4.1.3. Check push rod travel. Push rod travel should be as
short as possible without brakes dragging. Adjust travel
of push rod at slack adjuster if necessary.
4.1.4. If the orange stroke indication mark on the push rod
is visible, consult the slack adjuster service instructions
and verify the proper slack adjuster function.
4.2. LEAKAGE TEST
4.2.1. Make and hold a full brake application.
4.2.2. Using soap solution, coat the clamping ring(s). If
leakage is detected, tighten the clamping ring only enough
to stop leakage. DO NOT OVERTIGHTEN as this can
distort sealing surface or clamping ring. Coat the area
around push rod hole (loosen boot if applicable). Minimal
leakage is permitted (100 SCCM). If abnormal leakage is
detected, the diaphragm must be replaced.
4.2.3. Using a soap solution, check the hose fitting for
leakage. A one-inch bubble in one minute is acceptable.
5. OPERATION: GENERAL
The Bendix
®
EverSure
™
Spring Brake is made up of the
service chamber and the piggyback spring brake chamber.
The Bendix EverSure Spring Brake provides service
braking, parking, and emergency braking.
The spring brake can be mounted with the mounting bolts
in either a vertical or horizontal plane on standard mounting
stud centers. Two air hoses are used: the service air hose
(the connector is marked “11”); and the parking/emergency
air hose (the connector is marked “12”).
Controlled air pressure enters the service chamber through
the inlet port and acts upon the diaphragm, moving the
push plate and rod assembly forward.
When the service chamber is used to actuate cam-type
brake foundation assemblies, the yoke (which is welded
to, or threaded on, the push rod) is connected to a slack
adjuster, which in turn is connected to the brake cam shaft.
This forward motion of the push rod rotates the slack
adjuster, cam shaft and cam applying the vehicle brakes.
The greater air pressure admitted to the service chamber,
the greater the force applied by the push rod. Conversely,
the less pressure applied to the service chamber, the less
force applied by the push rod. Push rod force is determined
by multiplying the delivered air pressure by the effective
diaphragm area. For example, if 60 psi is admitted to a
Type 30 service chamber, the lineal force on the end of
the push rod is approximately 1,800 lbs.
When air pressure is released from the brake chamber, the
push rod return spring – in combination with the brake shoe
return spring – returns the diaphragm, push plate and rod
assembly, slack adjuster and brake cam to their released
positions releasing the brakes.
When the driver operates the parking brake, air is
exhausted from the chamber. The main spring is allowed
to extend, which forces the push rod and the emergency
diaphragm forward. This forces the service diaphragm
and service push rod forward, which applies the brakes.
When the air pressure in the Bendix EverSure Spring Brake
chamber drops to below approximately 78 psi, the main
spring overcomes chamber pressure and forces the push
rod and emergency diaphragm forward.
6. MECHANICAL RELEASE (CAGING) OF
THE BENDIX
®
EVERSURE
™
SPRING BRAKE
NOTE: The Bendix
®
EverSure
™
Spring Brake Chamber
is not shipped caged. It must be caged prior to any work
being done.
6.0.1. This procedure will be made much easier if air
pressure (100-120 psi; 6.6-8.0 bar) is used to collapse
the power spring by applying air to the port marked “12”,
before turning the release bolt nut with a hand wrench or
simply by hand.
6.0.2. Remove the dust cap from the keyhole in the center
of the spring brake chamber. See Figure 1.
6.0.3. Remove the release tool assembly from the side
pocket of the spring brake chamber.
6.0.4. Insert the release tool (T-bolt) through the release
tool keyhole and into the power spring piston plate.
6.0.5. Turn the release tool one quarter turn clockwise.
