Replacing components of the h, S transmitter – RKI Instruments 65-2330RK User Manual
Page 15
65-2330RK H
2
S Transmitter • 11
Replacing Components of the H
2
S Transmitter
This section includes a procedure to replace the H
2
S plug-in sensor, the entire detector
assembly, the hydrophobic membrane, and the amplifier. In most cases, it is not necessary
to replace the entire detector assembly.
Replacing the Plug-In H
2
S Sensor
CAUTION: The sensor contains electrolyte which is a dilute acid. Do not disassemble the sensor
when replacing it with a new one. If sensor electrolyte comes in contact with your
skin, wash affected area thoroughly with soap and water.
1.
Turn off the controller.
2.
Turn off or unplug power to the controller.
3.
Unscrew the detector housing cap from the detector housing body. Make sure not to
lose the cap gasket.
4.
Unplug and remove the H
2
S sensor.
5.
Carefully plug the replacement sensor into the four-socket pattern that is located in
the detector housing.
6.
Make sure the cap gasket is in place and screw the detector housing cap back onto the
detector housing body.
7.
Turn on or plug in power to the controller.
8.
Turn on the controller and place into normal operation.
CAUTION:
Allow the replacement sensor to warm up for 5 minutes before you continue with the
next step.
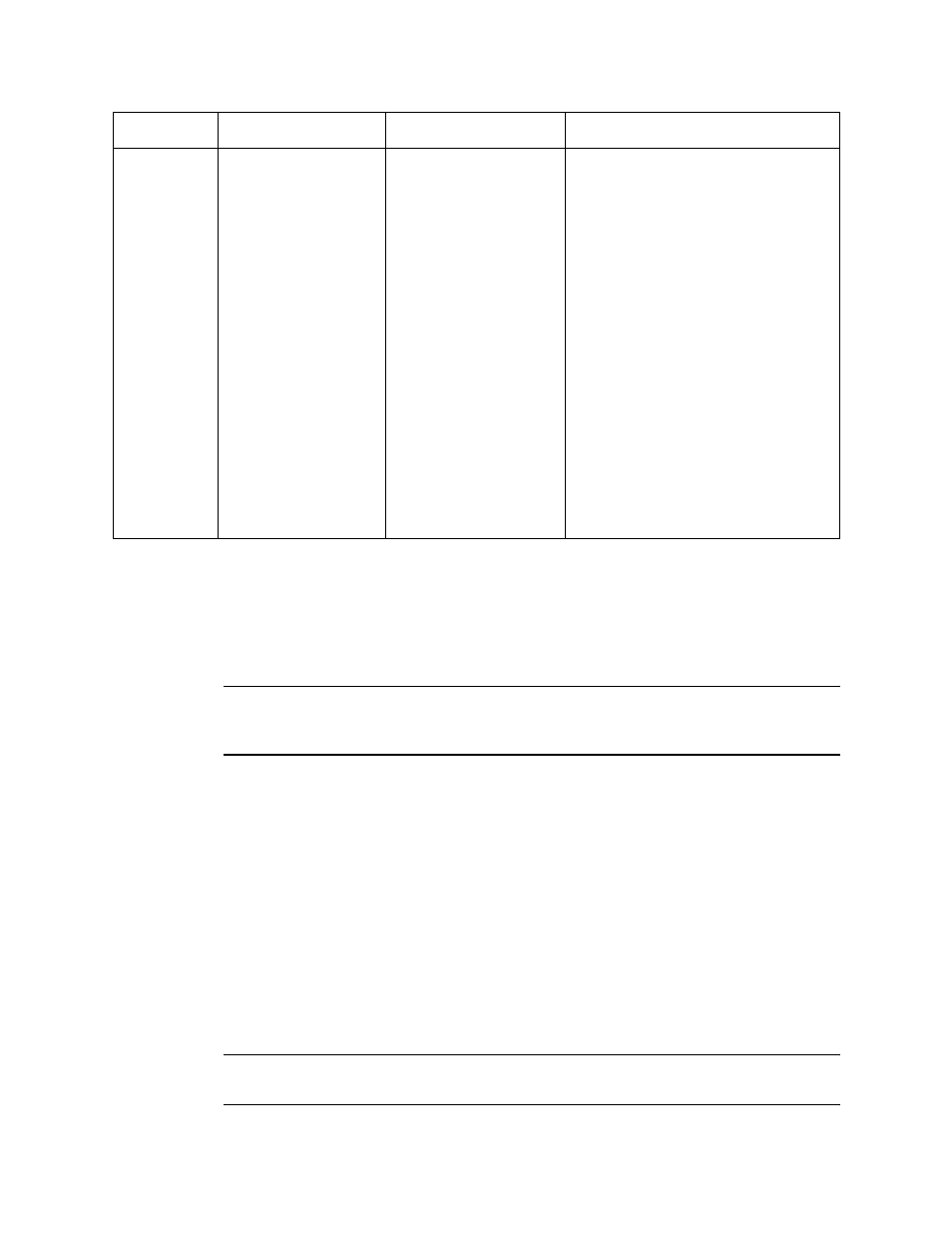
Slow or No
Response/
Difficult or
Unable to
Calibrate
• Transmitter responds
slowly or does not
respond to response
test.
• Unable to accurately
set the zero or
response reading
during calibration.
• Transmitter requires
frequent calibration.
Note: Under “normal”
circumstances, the
transmitter requires
calibration once every 3
months.
Some applications
may require a more
frequent calibration
schedule.
• The calibration cylinder
is low, out-dated, or
defective.
• The hydrophobic
membrane in the
detector housing cap is
wet or clogged with dirt
or other particulates.
• The calibration gas is
not an appropriate
concentration.
• The transmitter is
malfunctioning.
1. Verify that the calibration cylinder
contains an adequate supply of a
fresh test sample.
2. Check the face of the detector
housing cap and remove any
particulate contamination from the
hydrophobic membrane if necessary.
If the membrane appears saturated
with contamination or damaged,
replace the membrane as described
in the next section.
3. Verify that the calibration gas
concentration is appropriate for the
transmitter. Zero emission air (20.9%
oxygen) is normally used for a zero
adjustment if the environment is
suspect and 25 PPM H
2
S in nitrogen
is normally used for a response test.
4. If the calibration/response difficulties
continue, replace the plug-in sensor
as described later in this section.
5. If the calibration/response difficulties
continue, contact RKI for further
instruction.
Condition
Symptom(s)
Probable Causes
Recommended Action
