Rhessi – Orbital RHESSI User Manual
Page 2
Specifications
Spacecraft
Launch Mass:
291 kg (641.5 lb.)
Solar Arrays:
Four deployable wings, triple-junction GaAs
cells, 505 W EOL
Orbit:
600 km circular @ 38
°
inclination
Stabilization:
Spin @ 15 RPM
Pointing Knowledge:
324 arcsec (3
s)
Data Storage:
32 Gbits
Data Downlink:
4 Mbps, S-band (CCSDS, STDN)
Propulsion:
None
Mission Life:
2 years
Current Status:
Operational
Launch
Launch Vehicle:
Pegasus
®
XL
Launch Site:
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida
Date:
February 5, 2002
Instrument
Imager/Spectrometer
The imager is a 1.7 meter long carbon fiber composite tube with grid tray
assemblies at each end. The grid trays are aluminum structures with nine sets
of collimating grids in each tray. The spectrometer is a cryostat containing the
nine germanium detectors. The nine sets of grids in the imager are required to be
aligned with the nine detectors in the spectrometer. Rotation of the spacecraft
causes the flux of high energy particles in the field of view of the instrument to
be modulated by the collimating grids. The instrument covers energies from soft
X-rays (3 keV) to high-energy gamma-rays (20 MeV).
Data Availability
Unlike most other scientific missions, there are no proprietary data rights.
All data, and the software needed to analyze them, are freely available online.
This allows many talented scientists around the world to analyze RHESSI data
along with the complementary observations of the same flares that are available
from other instruments in space and from ground-based observatories. For more
information, visit: http://hesperia.gsfc.nasa.gov/rhessidatacenter.
Mission Partners
University of California at Berkeley
Procuring agency. Program management and science
lead. System integrator, and operator of satellite on-orbit.
Developer of the instrument spectrometer.
Orbital Sciences Corporation
Contractor for spacecraft design and manufacture, with
support to payload integration and system test
NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center
Mission management, technical oversight, and data
archiving. Developer of the instrument grids and
cryocooler.
Paul Scherrer Institut (Switzerland)
Developer of the imaging telescope and optical aspect
system for the payload instrument
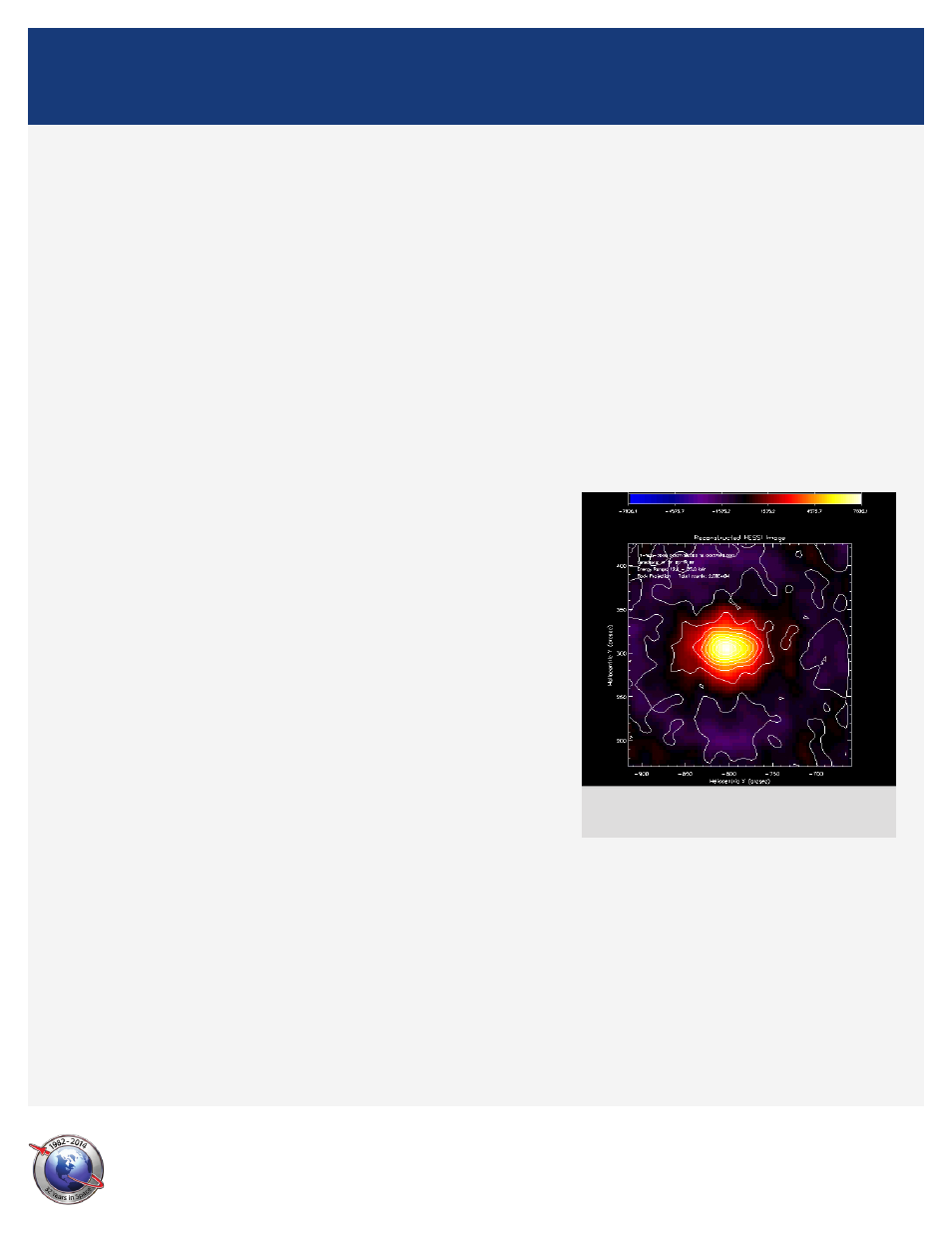
A solar flare reconstructed by the RHESSI "Image Widget."
(Graphic courtesy NASA)
Orbital Sciences Corporation
45101 Warp Drive
•
Dulles, Virginia 20166
•
www.orbital.com
©2014 Orbital Sciences Corporation
FS004_11_2998
RHESSI
