MTS Water Quality Guide User Manual
Page 7
Heat Exchanger Care and Water Quality Guide
Heat Exchanger Care
7
•
Shell–the shell is a seamless, nonferrous tube, usually made of brass. Both
ends are welded into the hubs. The shell encloses the baffles or fins very
closely to prevent any bypassing and ineffective flow areas.
•
Tubes–straight, seamless, nonferrous tubes are usually made from copper, a
copper-nickel alloy or stainless steel.
•
Tube sheets–brass tube sheets hold the cooling tubes in place. Tube sheets
are bonded to the inside of the hubs.
•
Baffles or fins–brass baffles or fins provide a contact area for dissipating
heat. The hot hydraulic fluid flows around the baffles (fins), while the
cooling water flows through the tubes.
•
Hubs–forged brass hubs are used to connect the shell with the end bonnets.
Vents and drains are located on the underside of the hubs.
•
Bonnets–cast iron bonnets provide an unrestricted connection for cooling
water flow. Renewable zinc anodes may be attached in the bonnet to prevent
electrolytic damage.
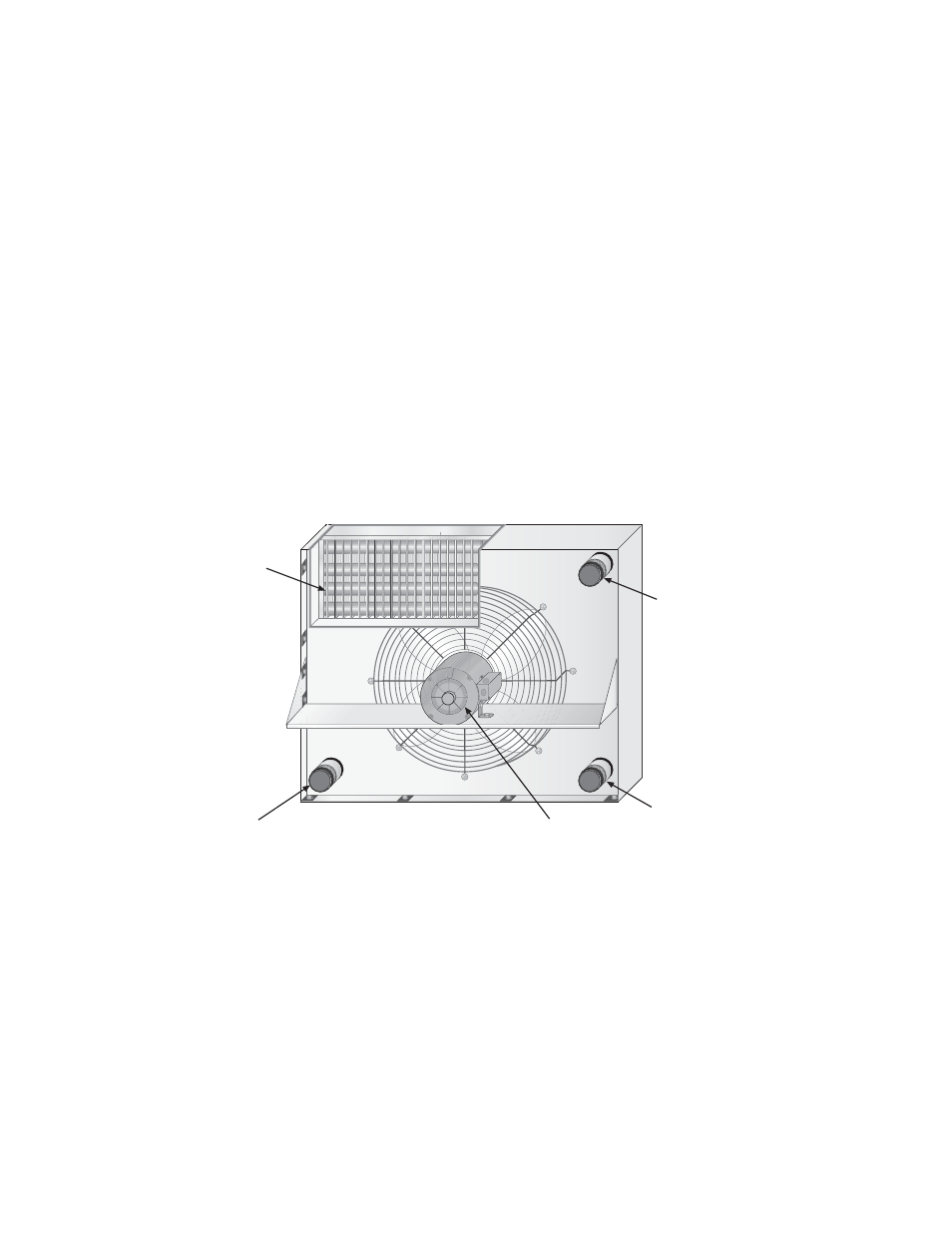
Hydraulic fluid-to-air
A hydraulic fluid-to-air heat exchanger is composed of a motor and fan, tubes,
fins and a cabinet.
Cutaway View of a Hydraulic Fluid-to-Air Heat Exchanger
Fluid In/Out Connection*
Fluid In/Out Connection*
Motor and Fan
Tubes and Fins
Fluid In/Out
Connection*
* Hot Fluid In/Cool Fluid Out connections vary between models
