Apple Aperture Digital Photography Fundamentals User Manual
Page 18
18
Chapter 1
How Digital Cameras Capture Images
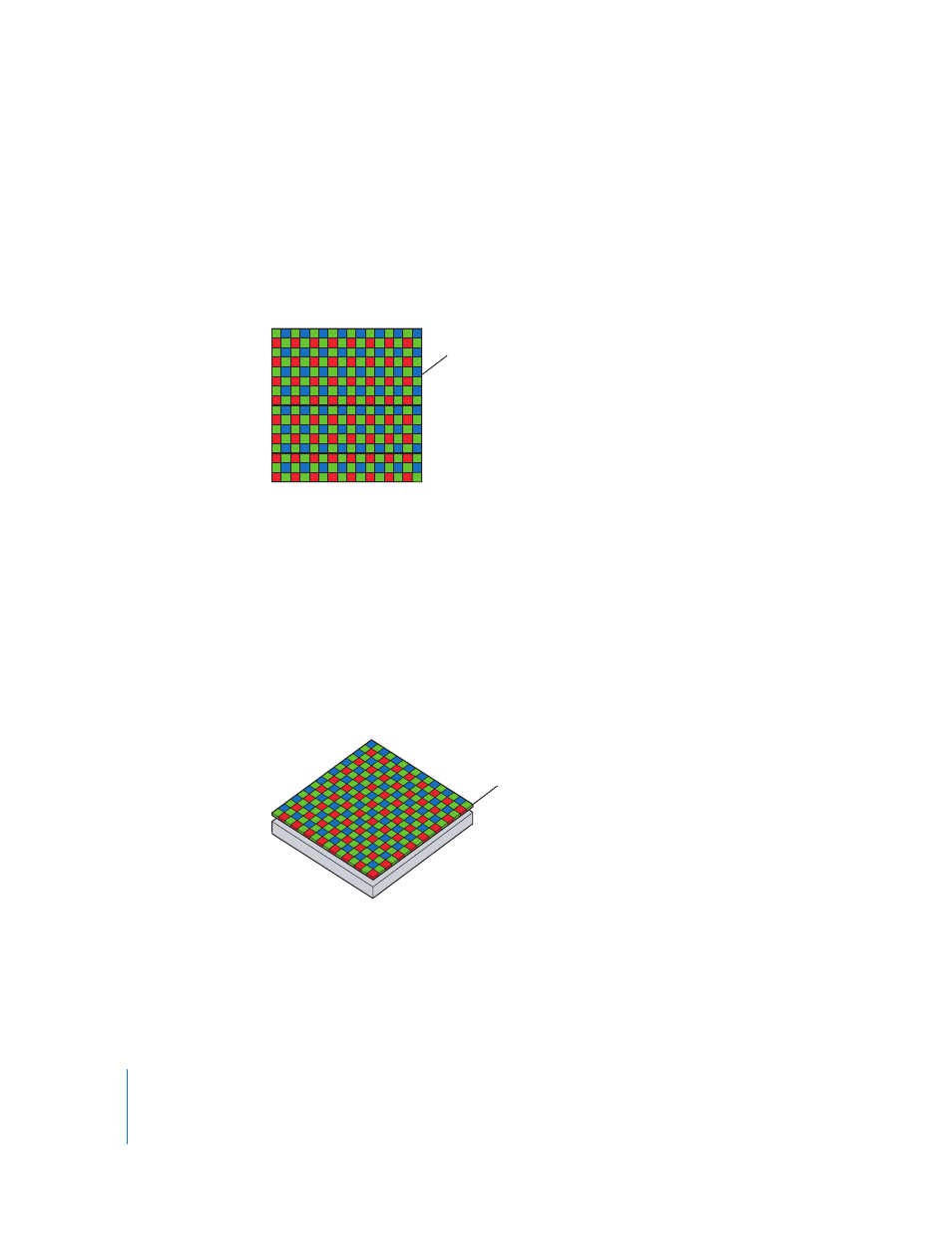
Each light-sensitive element on a digital image sensor is fitted with either a red, green,
or blue filter, corresponding to a color channel in a pixel in the image that is captured.
There are roughly twice as many green filters as blue and red to accommodate how the
eye perceives color. This color arrangement is also known as the Bayer pattern color filter
array. (For more information on how the eye perceives color, see “
” on page 29.) A process known as color interpolation is
employed to ascertain the additional color values for each element.
Common Types of Digital Image Sensors
There are two types of digital image sensors typically used: a charge-coupled device
(CCD) and a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS).
CCD
CCD sensors were originally developed for video cameras. CCD sensors record the
image pixel by pixel and row by row. The voltage information from each element in the
row is passed on prior to descending to the next row. Only one row is active at a time.
The CCD does not convert the voltage information into digital data itself. Additional
circuitry is added to the camera to digitize the voltage information prior to transferring
the data to the storage device.
Bayer pattern
color filter array
Bayer RGB pattern on CCD sensor
Voltage values are collected row by row.
Each element records only one color.
