Zip 30 - mul, Material classification and choice of tool – Dake Model Zip 30 User Manual
Page 13
13
ZIP 30 - MUL
ZIP 30 - MUL
ZIP 30 - MUL
ZIP 30 - MUL
ZIP 30 - MULTI MODE
TI MODE
TI MODE
TI MODE
TI MODE
TYPES OF STEEL
CHARACTERISTICS
USE
I
UNI
D
DIN
F
AF NOR
GB
SB
USA
AISI-SAE
Hardness
BRINELL
HB
Hardness
ROCKWELL
HRB
R=N/mm²
Construction
steels
Fe360
Fe430
Fe510
St37
St44
St52
E24
E28
E36
----
43
50
----
----
----
116
148
180
67
80
88
360ч480
430ч560
510ч660
Carbon
steels
C20
C40
C50
C60
CK20
CK40
CK50
CK60
XC20
XC42H1
----
XC55
060 A 20
060 A 40
----
060 A 62
1020
1040
1050
1060
198
198
202
202
93
93
94
94
540ч690
700ч840
760ч900
830ч980
Spring
steels
50CrV4
60SiCr8
50CrV4
60SiCr7
50CV4
----
735 A 50
----
6150
9262
207
224
95
98
1140ч1330
1220ч1400
Alloyed steels for
hardening and
tempering and for
nitriding
35CrMo4
39NiCrMo4
41CrAlMo7
34CrMo4
36CrNiMo4
41CrAlMo7
35CD4
39NCD4
40CADG12
708 A 37
----
905 M 39
4135
9840
----
220
228
232
98
99
100
780ч930
880ч1080
930ч1130
Alloyed
casehardening
steels
18NiCrMo7
20NiCrMo2
----
21NiCrMo2
20NCD7
20NCD2
En 325
805 H 20
4320
4315
232
224
100
98
760ч1030
690ч980
Alloyed for
bearings
100Cr6
100Cr6
100C6
534 A 99
52100
207
95
690÷980
Tool steel
52NiCrMoKU
C100KU
X210Cr13KU
58SiMo8KU
56NiCrMoV7C100K
C100W1
X210Cr12
----
----
----
Z200C12
Y60SC7
----
BS 1
BD2-BD3
----
----
S-1
D6-D3
S5
244
212
252
244
102
96
103
102
800ч1030
710ч980
820ч1060
800ч1030
Stainless
steels
X12Cr13
X5CrNi1810
X8CrNi1910
X8CrNiMo1713
4001
4301
----
4401
----
Z5CN18.09
----
Z6CDN17.12
----
304 C 12
----
316 S 16
410
304
----
316
202
202
202
202
94
94
94
94
670ч885
590ч685
540ч685
490ч685
Copper alloys
Special brass
Bronze
Aluminium copper alloy G-CuAl11Fe4Ni4 UNI 5275
Special manganese/silicon brass G-CuZn36Si1Pb1 UNI5038
Manganese bronze SAE43 - SAE430
Phosphor bronze G-CuSn12 UNI 7013/2a
220
140
120
100
98
77
69
56,5
620ч685
375ч440
320ч410
265ч314
Cast iron
Gray pig iron G25
Spheroidal graphite cast iron GS600
Malleable cast iron W40-05
212
232
222
96
100
98
245
600
420
MATERIAL
CLASSIFICATION AND
CHOICE OF TOOL
9
Since the aim is to obtain excellent cutting quality, the vari-
ous parameters such as hardness of the material, shape
and thickness, transverse cutting section of the part to
be cut, selection of the type of cutting blade, cutting
speed and control of saw frame lowering.These specifi-
cations must therefore be harmoniously combined in a sin-
gle operating condition according to practical considerations
and common sense, so as to achieve an optimum condition
that does not require countless operations to prepare the
machine when there are many variations in the job to be
performed.The various problems that crop up from time to
time will be solved more easily if the operator has a good
knoledge of these specifications.
WE THEREFORE RECOMMEND YOU TO ALWAYS USE
GENUINE SPARE BLADES THAT GUARANTEE SUPERIOR
QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE.
9.1 - Definition of materials
The table at the foot of the page lists the characteristics of the
materials to be cut, so as to choose the right tool to use.
9.2 - Selecting blade
First of all the pitch of the teeth must be chosen, in the other
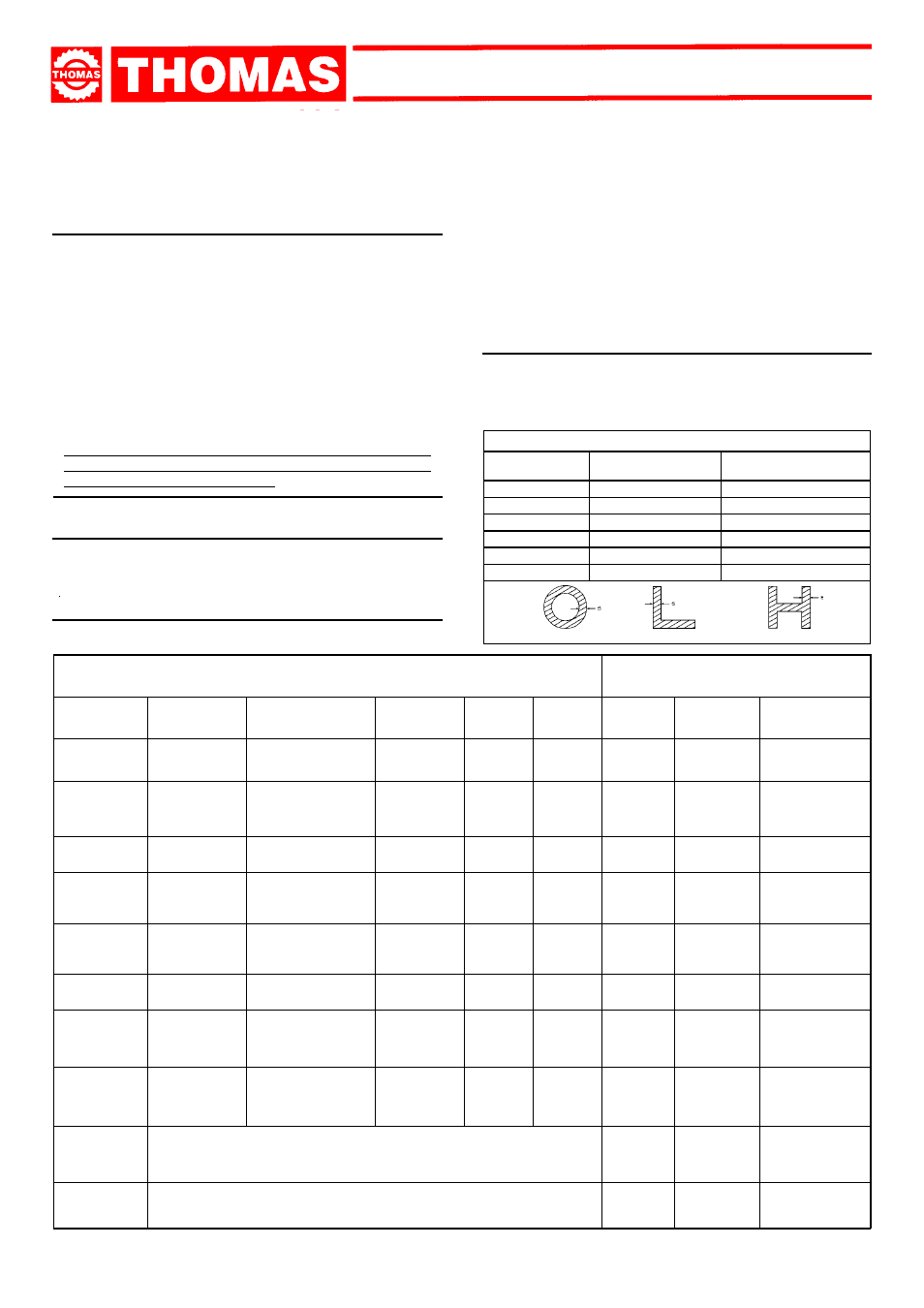
BLADE TEETH SELECTION TABLE
THICKNESS MM
Z CONTINUOUS
TOOTH DESIGN
Z COMBO
TOOTH DESIGN
TILL 1.5
14
10/14
FROM 1 TO 2
8
8/12
FROM 2 TO 3
6
6/10
FROM 3 TO 5
6
5/8
FROM 4 TO 6
6
4/6
MORE THAN 6
4
4/6
S = THICKNESS
words, the number of teeth per inch (25,4 mm) suitable for
thematerial to be cut, according to these criteria:
- parts with a thin and/or variable section such as profiles, pipes
and plate, need close toothing, so that the number of teeth
used simultaneously in cutting is from 3 to 6;
- parts with large transverse sections and solid sections need
widely spaced toothing to allow for the greater volume of the
shavings and better tooth penetration;
- parts made of soft material or plastic (light alloys, mild bronze,
teflon, wood, etc.) also require widely spaced toothing;
- pieces cut in bundles require combo tooth design.
9.3 - Teeth pitch
As already stated, this depends on the following factors:
- hardness of the material
- dimensions of the section
- thickness of the wall.
