State SBL100 76 NE User Manual
Page 15
15
If the water heater is being installed as a replacement for an
existing heater in pre-existing venting, a thorough inspection of
existing venting system must be performed prior to any installation
work.
VENT DAMPERS - Any vent damper, whether it is operated
thermally or otherwise must be removed if its use inhibits proper
drafting of the water heater.
Thermally Operated Vent Dampers: this gas-fired water heater
has a thermal efficiency at or above 80% which may produce
a relatively low flue gas temperature. Such temperatures may
not be high enough to properly open thermally operated vent
dampers. This would cause spillage of the flue gases and may
cause carbon monoxide poisoning. Vent dampers must bear
evidence of certification as complying with the current edition of
the American National Standard ANSI Z21.66 CGA 6.14 (covering
electrically and mechanically actuated vent dampers). Before
installation of any vent damper, consult the local gas utility for
further information.
To insure proper venting of this gas-fired water heater, the correct
vent pipe diameter must be utilized. Any additions or deletions
of other gas appliances on a common vent with this water heater
may adversely affect the operation of the water heater. Consult
your gas supplier if any such changes are planned.
For proper venting in certain installations, a larger diameter vent
pipe may be necessary. Consult your gas supplier to aid you in
determining the proper venting for your water heater from the vent
tables in the current edition of the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54 or the Natural Gas and Propane Installation
code cAN\cSA B 149.1.
Periodically check the venting system for signs of obstruction or
deterioration and replace if needed.
The combustion and ventilation air flow must not be obstructed.
The water heater with draft hood installed must be connected
to a chimney or listed vent pipe system, which terminates to the
outdoors. Never operate the water heater unless it is vented to the
outdoors and has adequate air supply to avoid risks of improper
operation, explosion or asphyxiation.
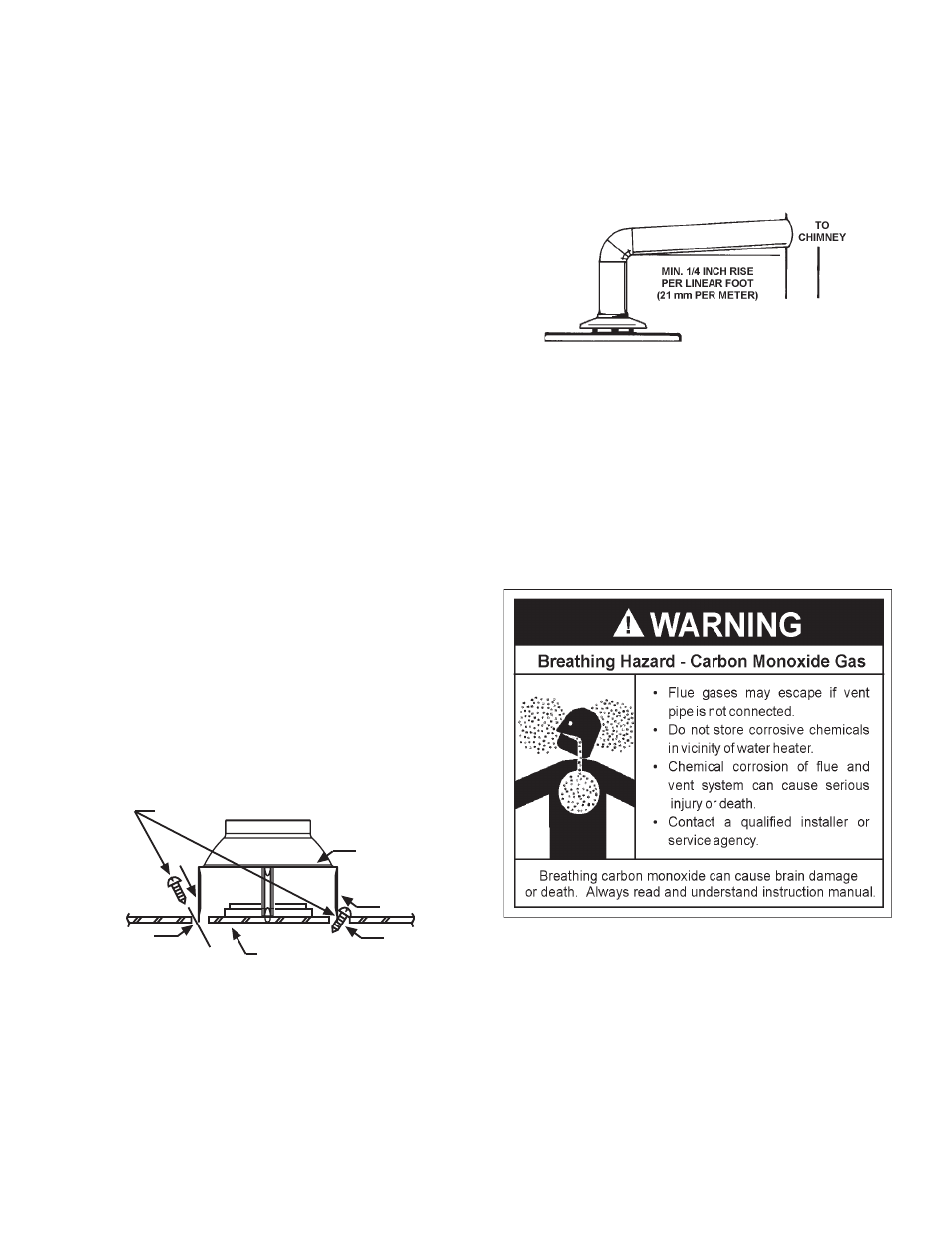
Align the legs of the draft hood with the slots provided. Insert
the legs and secure the draft hood to the water heater’s top
with the four screws provided as shown in Figure 13. Do not
alter the draft hood in any way. If you are replacing an existing
water heater, be sure to use the new draft hood supplied with
the water heater.
Obstructed or deteriorated vent systems may present serious
health risk or asphyxiation.
DRAFT HOOD
SHEET METAL SCREWS (FOUR PROVIDED)
LEGS
SLOT
INSTALL THE DRAFT HOOD WITH
THE FOUR SCREWS PROVIDED.
JACKET TOP
SLOT
LEGS
fIGure 13.
The vent pipe from the water heater must be no less than the
diameter of the draft hood outlet on the water heater and must
slope upward at least 1/4 inch per linear foot (21 mm per meter).
See Figure 14.
All vent gases must be completely vented to the outdoors of the
structure (dwelling). Install only the draft hood provided with the
new water heater and no other draft hood.
Vent pipes must be secured at each joint with sheet metal screws.
fIGure 14.
There must be a minimum of 6” (153 mm) clearance between single
wall vent pipe and any combustible material. Fill and seal any
clearance between single wall vent pipe and combustible material
with mortar mix, cement, or other noncombustible substance. For
other than single wall, follow vent pipe manufacturer’s clearance
specifications. To insure a tight fit of the vent pipe in a brick chimney,
seal around the vent pipe with mortar mix cement.
Failure to have required clearances between vent piping and
combustible material will result in a fire hazard.
Be sure vent pipe is properly connected to prevent escape of
dangerous flue gases which could cause deadly asphyxiation.
Chemical vapor corrosion of the flue and vent system may occur
if air for combustion contains certain chemical vapors. Spray can
propellants, cleaning solvents, refrigerator and air conditioner
refrigerants, swimming pool chemicals, calcium and sodium
chloride, waxes, bleach and process chemicals are typical
compounds which are potentially corrosive.
