A.7.1 benchmark platform, A-10, Deep shelf ddr ib test configuration – HP StorageWorks Scalable File Share User Manual
Page 70
For workloads that require a lot of disk head movement relative to the amount of data moved,
SAS disk drives provide a significant performance benefit.
Random writes present additional complications beyond those involved in random reads. These
additional complications are related to Lustre locking, and the type of RAID used. Small random
writes to a RAID6 volume requires a read-modify-write sequence to update a portion of a RAID
stripe and compute a new parity block. RAID1, which does not require a read-modify-write
sequence, even for small writes, can improve performance. This is why RAID1 is recommended
for the MDS.
A.7 DDR InfiniBand Performance Using MSA2312 with Three Attached
JBODs
This section provides results of tests performed with two MSA2312 controllers, each with three
attached expansion shelf JBODs, also known as deep shelf configuration. Tests were run with
HP SFS G3.1-0 and MVAPICH2. The OSTs were populated with 450 GB SATA drives. Stripe
placement was controlled by default operation of the HP SFS file system software. Specific control
of striping can affect performance. Due to variability in configuration, hardware, and software
versions, it is not valid to directly compare the results indicated in this section with those indicated
in other sections.
A.7.1 Benchmark Platform
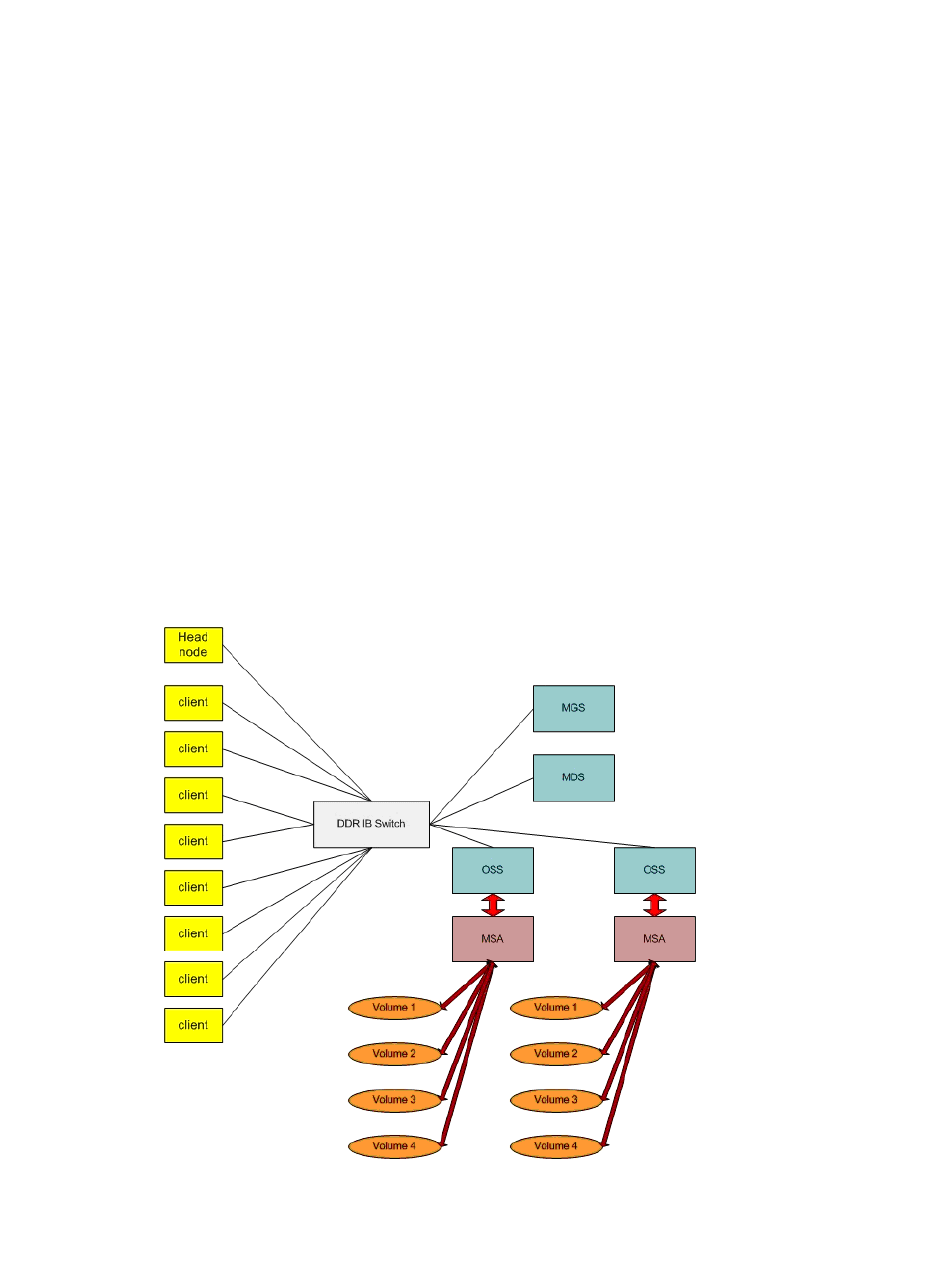
The client configuration for deep shelf testing is shown in
. Solid grey lines indicate
DDR IB connections. The head node launched the tests but did not access the HP SFS file system
while tests were in progress.
Figure A-10 Deep Shelf DDR IB Test Configuration
70
HP SFS G3 Performance
