Thermo Fisher Scientific Ion Selective Electrodes Ammonia User Manual
Page 10
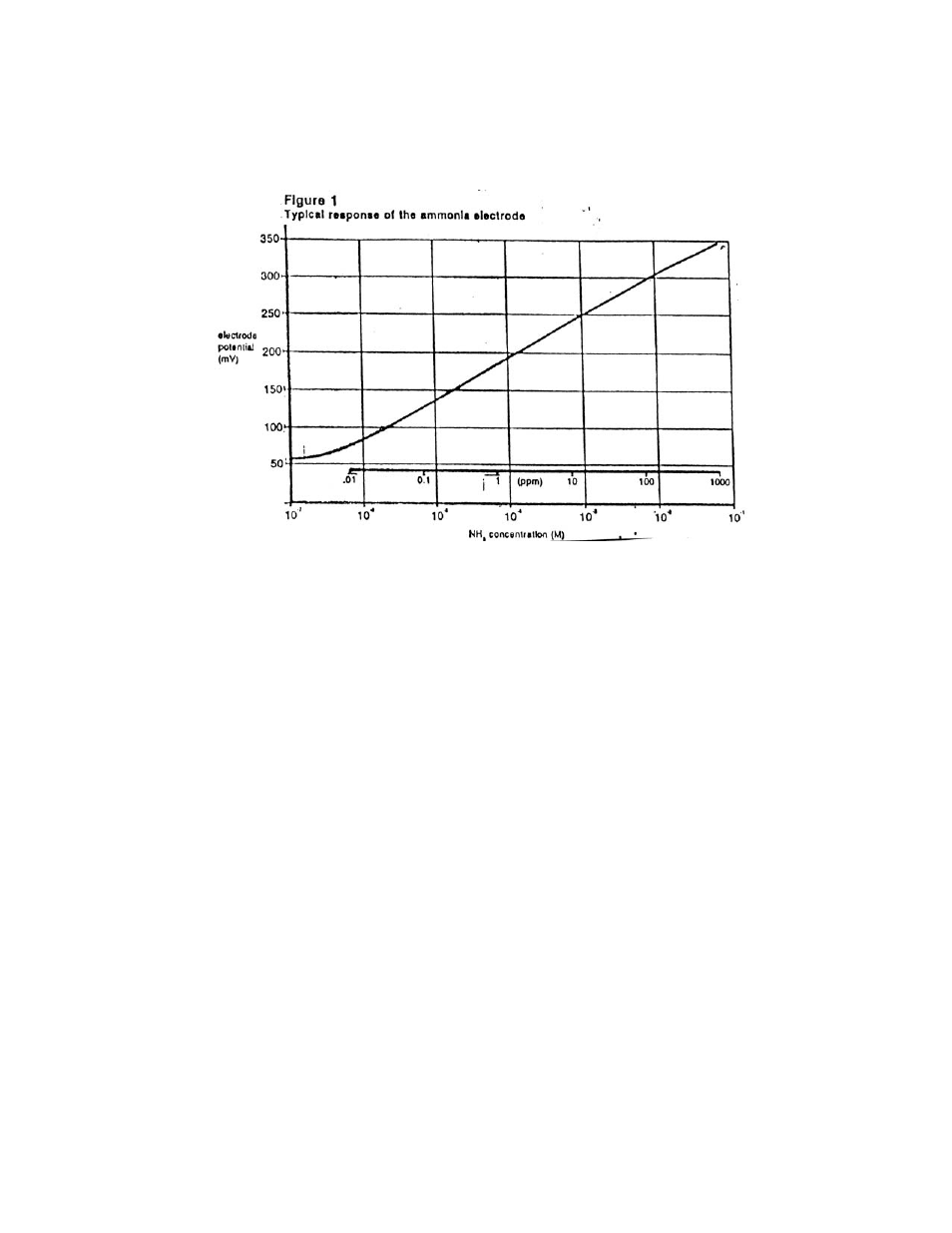
5.
Using the semi-logarithmic graph paper, plot the mV reading (linear axis) against the
concentration (log axis). Extrapolate the calibration curve down to about 1.0 x 10-
5
M. A
typical calibration curve can be found in Figure 1.
A calibration curve is constructed on semi-logarithmic paper when using the pH/mV
meter in the millivolt mode. The measured electrode potential in mV (linear axis) is
plotted against the standard concentration (log axis). In the linear region of the curve,
only three standards are necessary to determine a calibration curve. In the non-linear
region, additional points must be measured. The direct measurement procedures
given are for the linear portion of the curve. The non-linear portion of the curve
requires the use of low level procedures.
6.
To a clean, dry 150 ml beaker, add 100 ml of sample and 1 ml of ISA. Place the beaker on
the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a constant rate. Rinse the electrodes with distilled
water, blot dry, and lower the electrode tip into the solution. When the reading has
stabilized, record mV reading. Using the calibration curve, determine sample
concentration.
7.
The calibration should be checked every two hours. Assuming no change in ambient
temperature, place the electrode tips in the mid-range standard. After the reading has
stabilized, compare it to the original reading recorded in Step 3 above. A reading differing
by more than 0.5 mV or a change in the ambient temperature will necessitate the repetition
of steps 2-5 above. A new calibration curve should be prepared daily.
Direct Measurement of Ammonia (using an ion meter)
1.
By serial dilution of the 0.1M or 1,000 ppm ammonia standard, prepare two ammonia
standards whose concentration is near the expected sample concentration. Add 1 ml of ISA
to each 100 ml of standard.
