Block numbers and freqeuncy ranges, Astronomy – Lectrosonics UH400a User Manual
Page 9
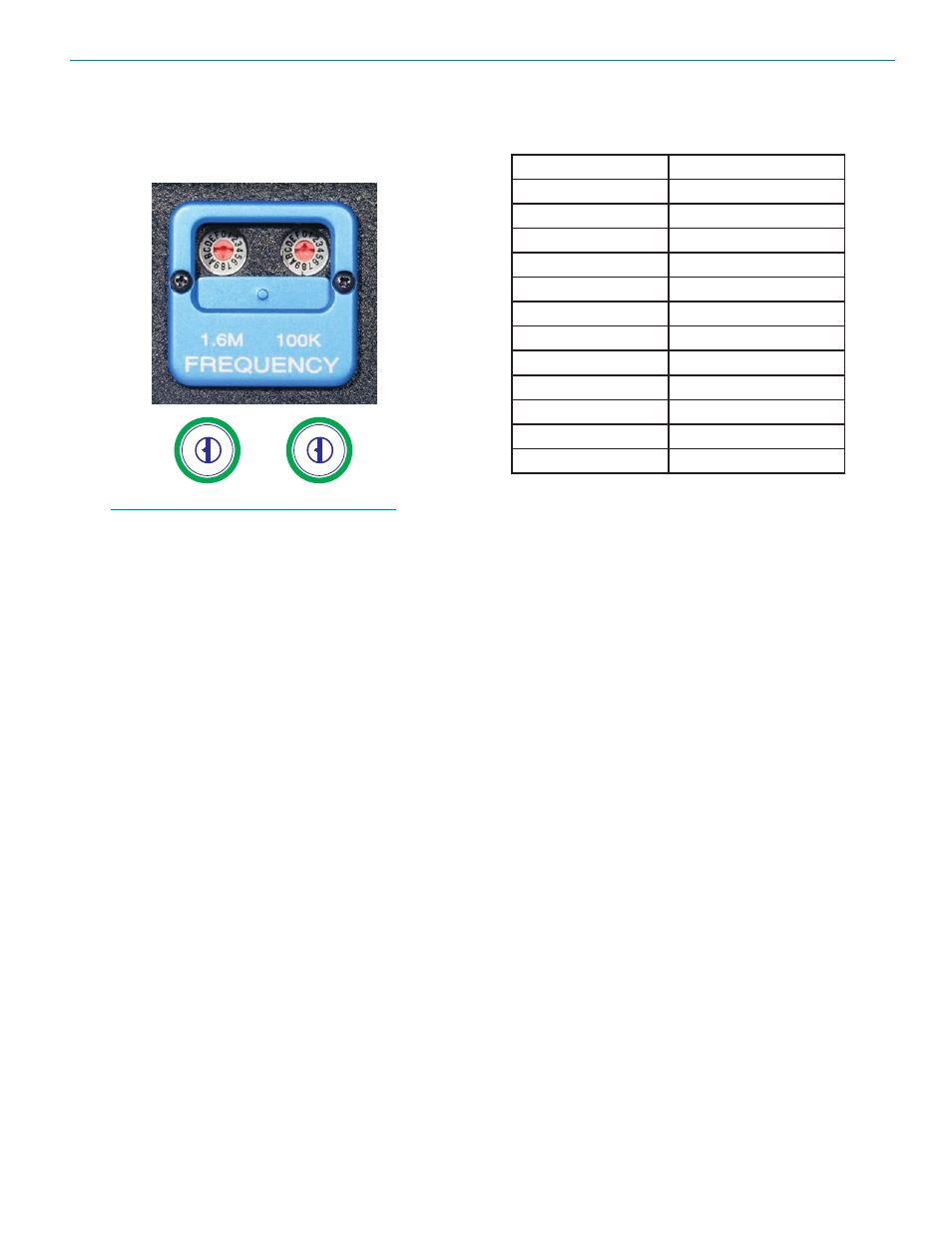
Frequency Agile Plug-On UHF Transmitter
Block Numbers and Freqeuncy Ranges
The transmitter will tune to any of 256 different frequen-
Block Numbers and Frequency Ranges (MHz):
cies within a factory assigned block.
0 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
0 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Block 470
470.100 - 495.600
Block 19
486.400 - 511.900
Block 20
512.000 - 537.500
Block 21
537.600 - 563.100
Block 22
563.200 - 588.700
Block 23 (lower)
588.8 00- 607.900
Block 23 (upper)
614.100 - 614.300
Block 24
614.400 - 639.900
Block 25
640.000 - 665.500
Block 26
665.600 - 691.100
Block 27
691.200 - 716.700
Block 28
716.800 - 742.300
Block 29
742.400 - 767.900
Part of block 23 (TV channel 37) is not available since it
Two 16- position switches adjust the operating
covers a 608 to 614 MHz band that is allocated for radio
frequency in 100 kHz steps yielding the 256 in a
astronomy.
block (16 x 16 = 256).
To determine a frequency from a block number:
25.6 × Block Number = Lowest freq. (MHz) in the block
Example: 25.6 x 24 = 614.400
To determine a block number from a frequency:
Freq. (MHz) divided by 25.6 = Block number
(first two digits are the block number)
Example: 685.500 divided by 25.6 = 26.77734375
The first two digits left of the decimal are the block num
ber. In this case, 685.500 MHz falls within block 26.
It is handy to remember these formulas, in case you do
not have a copy of the table.
Rio Rancho, NM
9
