Schreiber Chillers MC75WC User Manual
Page 7
MC75 - WC
2.3.2. Place unit in position on wedges located at four
points (two below approximate center of driver and
two below approximate center of pump). Adjust
wedges to level unit. Level or plumb suction and
discharge flanges.
2.3.3. Make sure bedplate is not distorted and final
coupling alignment can be made within the limits of
movement of motor and by shimming, if necessary.
2.3.4. Tighten foundation bolts finger tight and build
dam around foundation. Pour grout under bedplate
making sure th e areas under pump and motor feet
are solid. Allow grout to harden 48 hours before fully
tightening foundation bolts.
2.3.5. Tighten pump and motor hold-down bolts
before connecting the piping to pump.
3.1. Low static suction lift and short, direct, suction piping is
desired. For suction lift over 10 feet and liquid temperatures
over 120 F, consult pump performance curve for Net Positive
Suction Head Required.
3.2. Suction pipe must be as large as the suction connection
of the pump. Smaller size will d egrade performance.
3.3. If larger pipe is required, and eccentric pipe reducer (with
straight side up) must be installed at the pump.
3.4. Installation with pump below source of supply:
3.4.1. Install full flow isolation valve in piping for
inspection and maintenance.
1
CAUTION
Do not use suction isolation valve to throttle pump.
3.5. Installation with pump above source of supply:
3.5.1. Avoid air pockets. No part of piping should
be higher than pump suction connection. Slope
piping upward from liquid source.
3.5.2. All joints must be airtight.
3.5.3. Foot valve to be used only if necessary for
priming, or to hold prime on intermittent service.
3.5.4. Suction strainer open area must be at least
triple the pipe area.
3.6. Size of the inlet from liquid source and minimum
submergence over inlet, must be sufficient to prevent air
from entering pump through vortexing. See figs. 2 -5.
4.1. Arrangement must include a check valve located
between a gate valve and the pump. The gate valve is
for regulation of capacity, or for inspection of the
pump or check valve.
4.2. If an increaser is required, place between check
valve and pump.
4.3. Use 3 -4 wraps of Teflon tape to seal threaded
connections.
5.1. Close-coupled Units:
5.1.1. No field alignment necessary.
5.2. Frame-Mounted Units:
5.2.1. Even though the pump-motor unit may
have a factory alignment, this could be
disturbed in transit and must be checked
prior to running.
5.2.2 Tighten all hold-down bolts before
checking the alignment.
5.2.3. If re-alignment is necessary, always
move the motor. Shim is required.
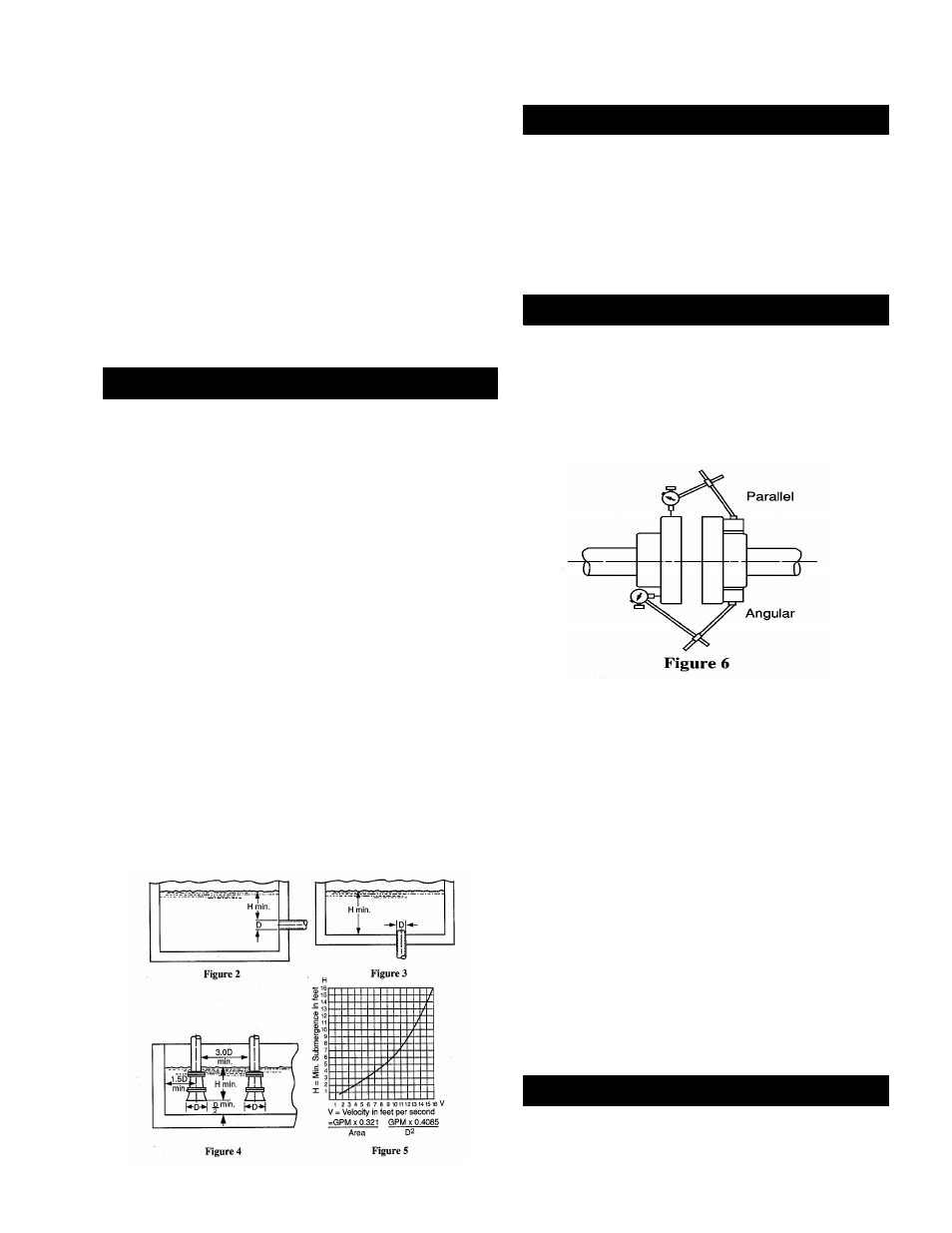
5.2.4. Parallel misalignment – shafts with
axis parallel but not concentric. Place a dial
indicator on one hub and rotate this hub
360° while taking readings on the outside
diameter of the other hub. Parallel alignment
occurs when Total indicator reading is .005”,
or less.
5.2.5. Angular misalignment – shafts with
axiz parallel but not concentric. Place dial
indicator on one hub and rotate this hub
360° while taking readings on the face of the
other hub. Angular alignment is achieved
when Total Indicator Reading is .005”, or
less.
5.2.6. Final alignment is achieved when
parallel and angular requirements are
satisfied with motor hold-down bolts tight.
CAUTION
Always recheck both alignments after making any
adjustment.
3. Suction Piping:
4. Discharge Piping:
5. Motor-To-Pump Shaft Alignment:
6. Rotation:
8
