6 three-body wear resistance, Gc kalore technical manual, Kalore grandio† tetric evoceram† tph3 – GC EUROPE Kalore User Manual
Page 20
20
3 Body Wear (µm)
0
50
100
150
200
250
Filtek Supreme DL
†
Filtek Z250
†
Filtek Silorane
†
Prisma TPH3
†
EsthetX
†
Premise
†
4 Seasons
†
Grandio
†
Tetric Evoceram
†
Venus
†
CeramX Mono
†
KALORE
KALORE
Grandio†
Tetric Evoceram†
TPH3†
1mm
2mm
2mm
2mm
7mm
GC Kalore technical manual
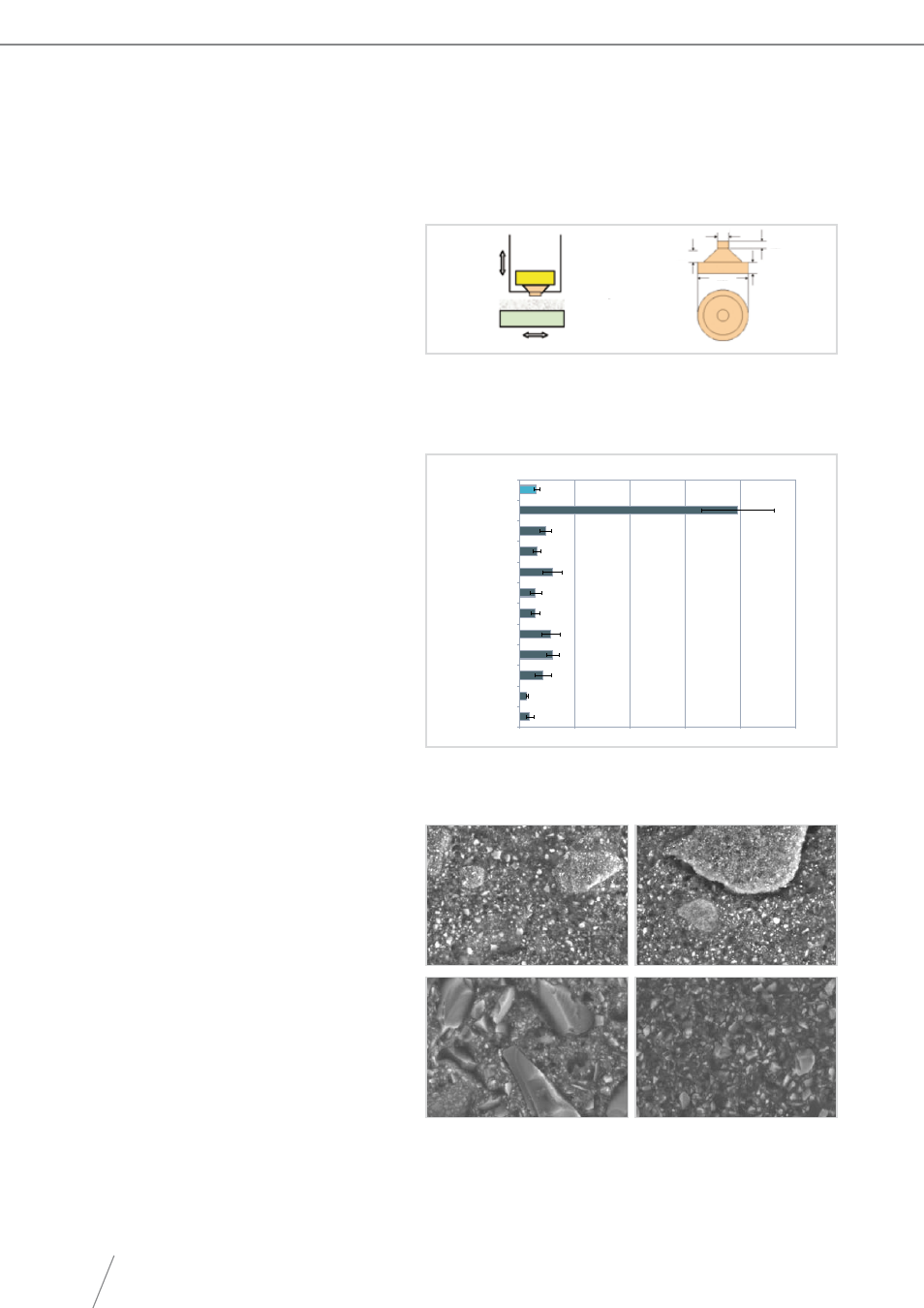
6.6 Three-Body Wear Resistance
to measure three-body wear resistance
in-house, composite specimens were
prepared and moved up and down
along a 5 cm path at a rate of 30 strokes
per minute. they were held in indirect
contact with an acrylic plate under a
load of 350 gf and, simultaneously, the
sample holder slid horizontally along a
2 cm path at a rate of 30 strokes per
minute. A mixture of PMMA and glycerol
(1:1 volume) was used as an intermediate
abrasive (Fig. 20). after 100,000 cycles
(with one complete lateral and vertical
movement being defined as one cycle),
material wear was evaluated by
measuring height loss. KALORE was
found to have high resistance to
three-body wear (Fig. 21).
Following this test, samples of
composites were processed for SEM
imaging. KALORE was found to have
durable and tight bonding between
the fillers and the resin matrix. In the
same
test,
other
products
demonstrated defects at the pre-
polymerized
filler
interface
(EvoCeram†) or at the interface with
the glass particle (Grandio† and
TPH3†). In addition, filler dropouts
were observed (Fig. 22).
Figure 21. three-body wear of various composite materials.
Source: GC Corporation.
Figure 20. three-body wear resistance test set-up.
Figure 22. SEM images of samples tested for three-body wear resistance (x5000).
Sample holder
Composite slurry
Acrylic plate
