GC EUROPE G-aenial Bond User Manual
Page 22
22
Hy
Hy
Ar
Ar
Ar
Ud
500nm
100nm
100nm
500nm
Ud
Ud
Ud
NIZ
NIZ
NIZ
NIZ
G-ænial Bond Technical Manual
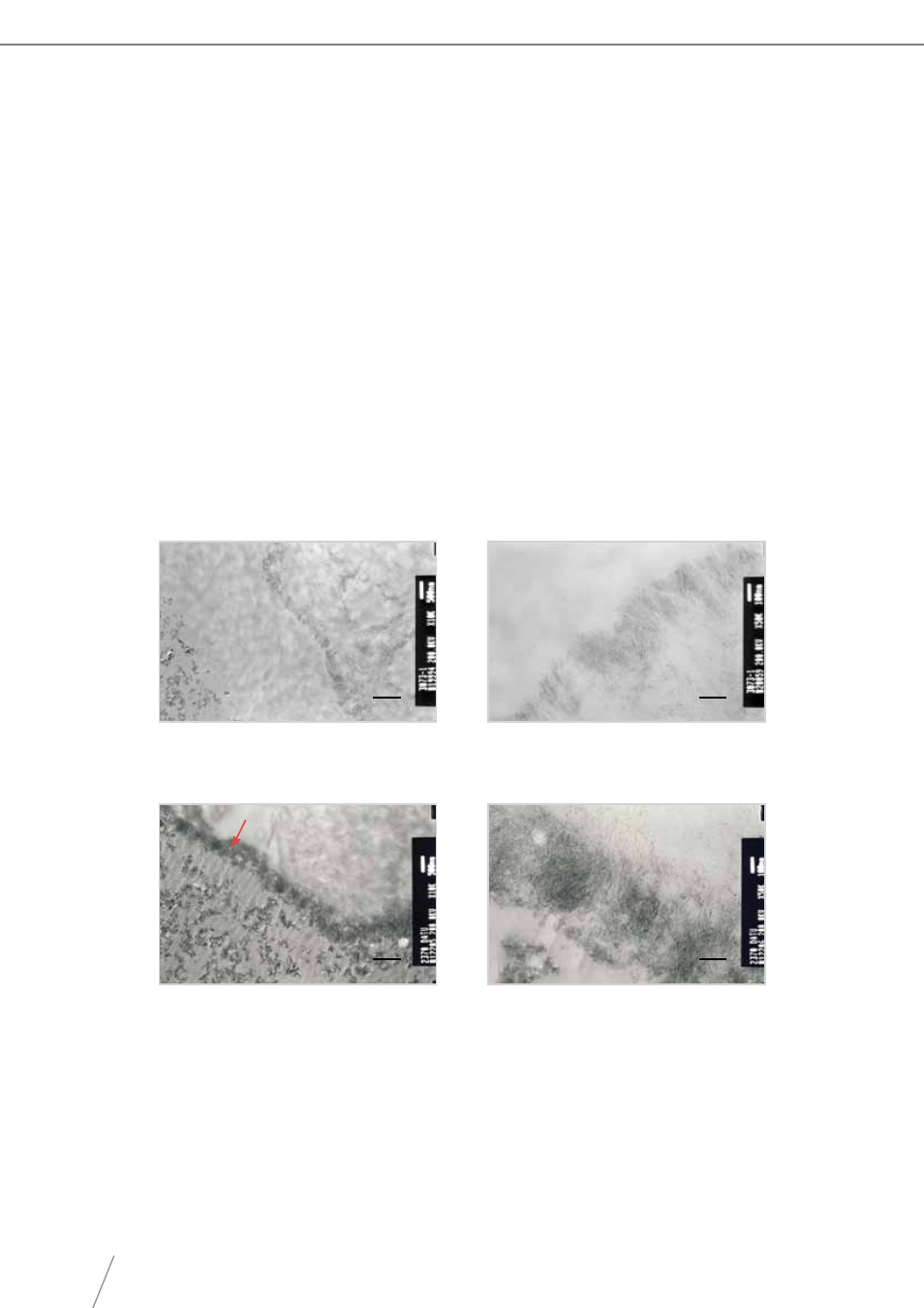
TEM observations on dentine
Test performed by GC R&D, Japan
in order to better understand the influence of etching on the adhesion mechanism to dentine,
interfaces of G-ænial Bond with dentine prepared with and without prior acid etching were
examined using tem by Gc R&D.
Test set-up: Bovine dentine specimens were polished with 320-grit Sic paper. For the etch(+) group etching was conducted
for 10 seconds with a 37% phosphoric acid etching gel (LINK MASTER ETCHANT, GC). No etching agent was apply to the
etch(-) surfaces. G-ænial Bond was then applied to the surfaces of the etch (+) and etch (-) samples according to the
manufacturer’s instructions. Clearfil AP-X (Kuraray) was placed on the surface using an Ultradent mould (D=2.38mm) and light-
cured. the tem specimen used to assess the interface between the etched dentine and G-ænial Bond was demineralised with
eDta and embedded in epoxy resin. the specimen was then cut with a microtome in 80-90 nm thickness. then, the surface
was carbon-spattered and observed by tem.
Figure 17: TEM images of etched dentine/adhesive interface of G-ænial Bond. (left X10K, right X50K)
hy: hybrid layer; ar: adhesive resin; ud: unaffected dentine; niZ: nano-interaction zone; Source: Gc corporation, Japan, 2009
Figure 18: TEM images of dentine/adhesive interface of G-ænial Bond without etching of the dentine. (left X10K, right X50K)
hy: hybrid layer; ar: adhesive resin; ud: unaffected dentine; niZ: nano-interaction zone; Source: Gc corporation, Japan, 2009
tem observations on the etched specimen (Figure 17) revealed the presence of a nano-interaction
zone (niZ) at the interface between the hybrid layer and the unaffected dentine, which means that
adhesive monomers certainly penetrated into the base of the demineralized dentine, even when
the dentine was etched. a comparison with the adhesive/ dentine interface in the self-etch
technique can be made when looking at Figure 18. inadvertent etching will still allow the formation
of a nano-interaction zone at the base of the hybrid layer, however the amount of residual
hydroxyapatite will decrease. Residual hydroxyapatitie crystals are important to ensure the quality
of the chemical adhesion and the durability of the bond. Therefore, the quality and longevity of
the chemical adhesion will be improved when no etching is used prior to the application of
G-ænial Bond on dentine.
