3B Scientific Laser Optics Supplemental Set User Manual
Page 9
24
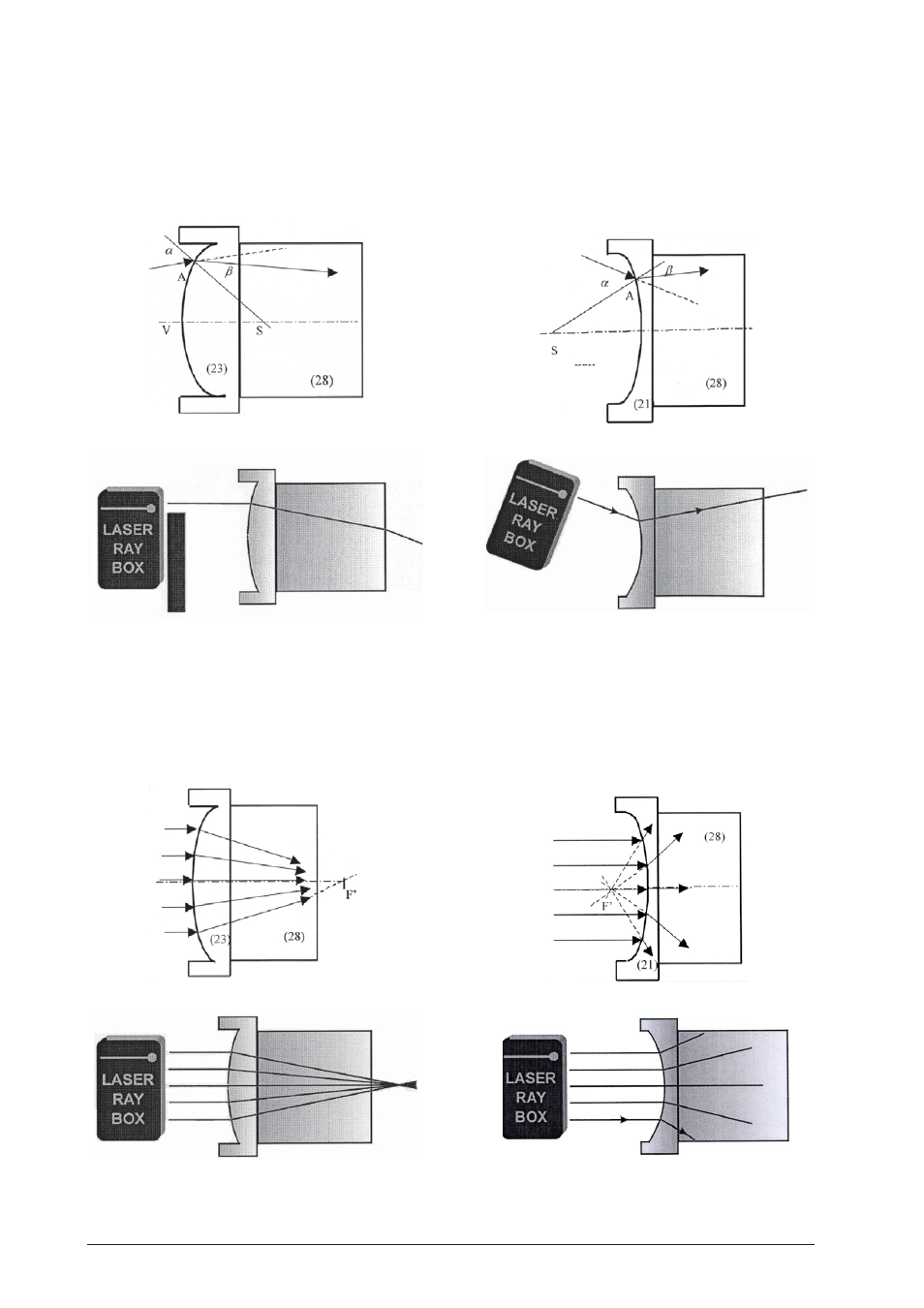
E13a Light ray passing a convex air-glass boundary
(U17301)
When a ray impinges the air-glass boundary at point
A, it is directed toward the normal. The normal is de-
fined as the line from point A to the centre of bound-
ary curvature S.
E13b Light beam passing through convex air-glass
boundary
(U17301)
Using a boundary of convenient curvature radius and
an auxiliary glass element, where the rays are refracted,
one can observe that the rays are met at the point F' in
the optical axis – figure focus.
E14a Light ray passing through concave air-glass
boundary
(U17301)
When a ray impinges the boundary at point A, refrac-
tion towards the normal is observed. The normal is
defined as the line from point A to the centre of bound-
ary curvature S.
E14b Light beam passing through concave air-glass
boundary
(U17301)
The beam after passing the boundary is divergent.
Elongating the refracted light to the other side one can
find a point on the optical axis where the line meets. It
is figure focus F'.
Acrylic
Air
Air
Acrylic
Acrylic
Acrylic
