3B Scientific Laser Optics Supplemental Set User Manual
Page 7
22
E10a Air prism deviation of light
(U17301)
Light passes through the glass-air border at point A.
Then it is directed away from the normal axis and af-
ter light passes through point B, it is then directed to-
ward the normal. The sum of the refraction angles is
referred as the deviation angle
δ
. It is the angle be-
tween the incidence and the outgoing ray.
E10b Air prism minimal deviation
(U17301)
In the case of minimal deviation
δ
min,
the incidence
angle
α
is equal to the angle of the outgoing ray ß. The
direction of the refracted light in the prism is parallel
to the edge the ray does not pass through. The refrac-
tive index of the prism obey formula (see E9b). The
deviation has an opposite direction as in the case of a
glass prism.
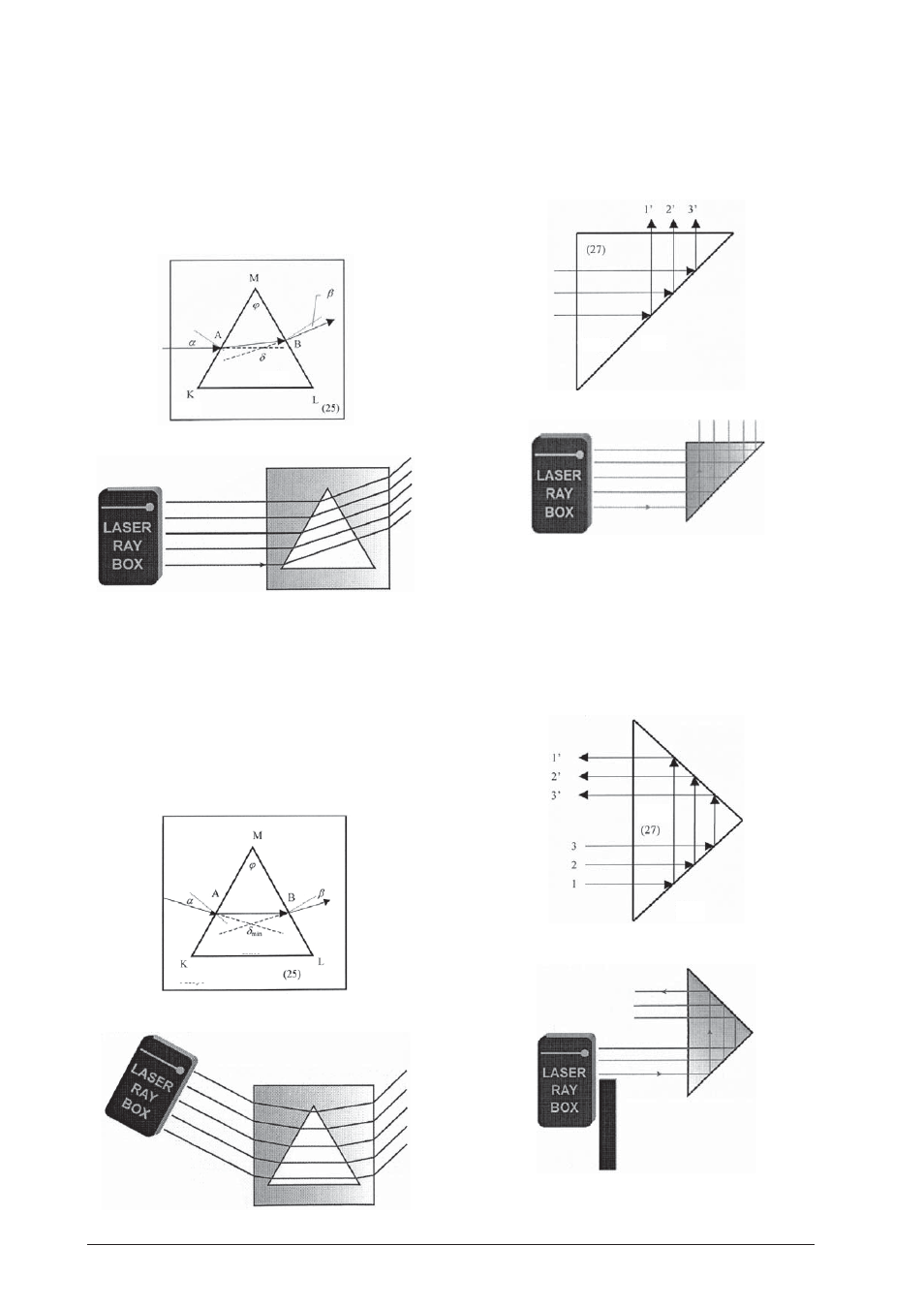
E11a Reflection of light on one edge of glass prism
(U17301)
When the rays impinge the edge, they are totally re-
flected. If the prism is slightly adjusted reflection and
refraction can be observed.
E11b Reflection of light on two edges of glass
prism
(U17301)
The conditions for total reflections are fulfilled on both
edges of the prism. If the top ray of the incidence
light is eliminated, the bottom ray of the outgoing light
disappears. The picture is 180° rotated.
Acrylic
Air
Air
Air
Air
Acrylic
Acrylic
Acrylic
