3B Scientific Laser Optics Supplemental Set User Manual
Page 6
21
E8
Light ray shift by air planparallel plate
(U17301)
In this case, a shift between the incoming and the out-
going ray can be observed. This shift has an opposite
direction than in the case of the glass plate.
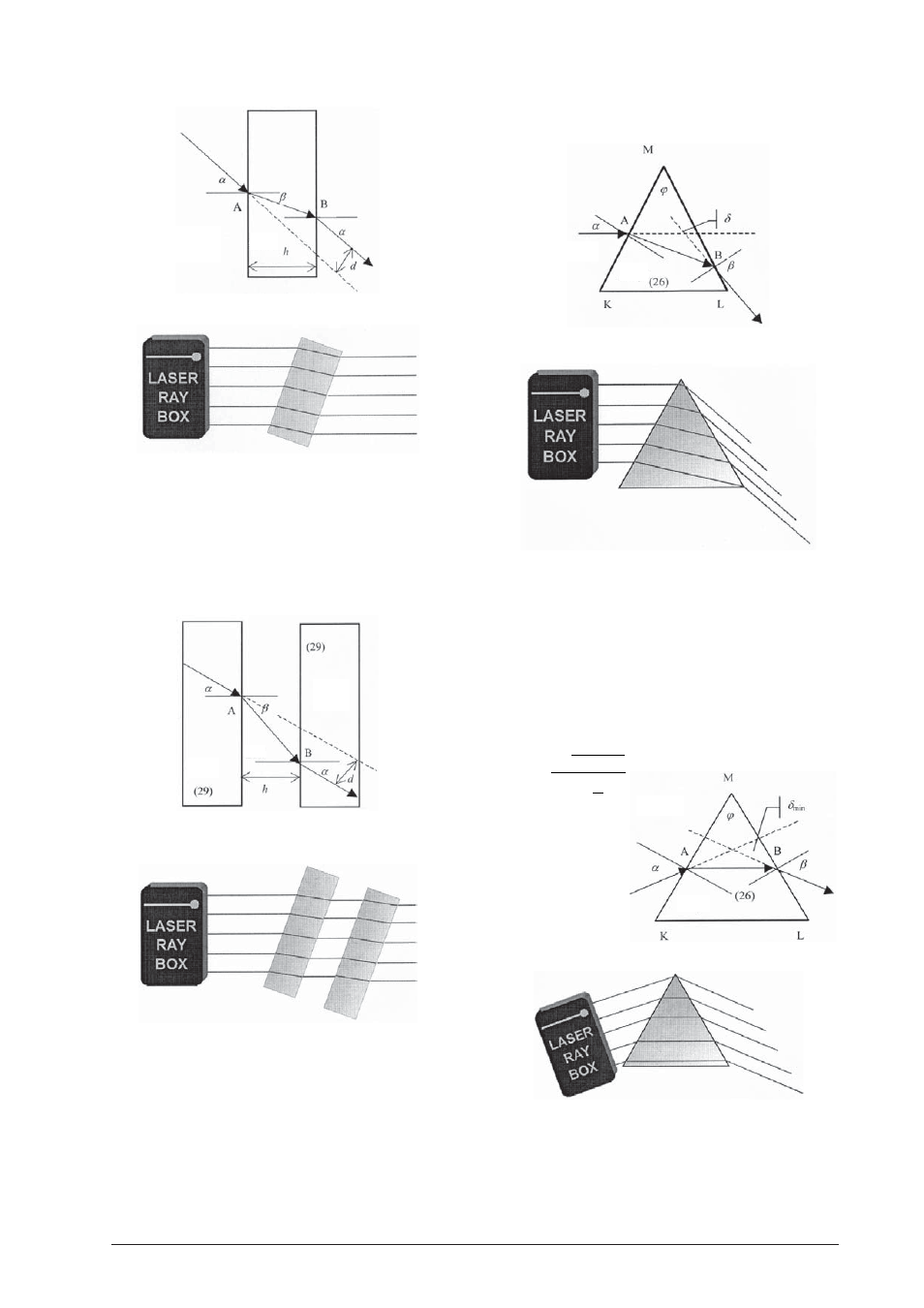
E9a Glass prism deviation of light ray
(U17300/U17301)
If the prism is glass, after the light impinges the point
A, it is bent toward the normal and refracts to point B.
At this point it is bent into the air away from the nor-
mal. The sum of all refraction angles is the deviation
angle
δ
. It is the angle between the incidence and the
outgoing ray.
E9b Glass prism minimal deviation
(U17300/U17301)
It can be seen that in the case of minimal deviation
δ
min
the incidence angle
α
is equal to the angle of the
outgoing ray ß. The direction of the refraction of light
in the prism is parallel to the edge the ray does not
pass through. The refractive index of the prism obeys
the formula:
Air
Acrylic
Acrylic
Acrylic
Air
Acrylic
Acrylic
Air
Air
n
=
+
sin
sin
2
min
δ
ϕ
ϕ
2
