3B Scientific Laser Optics Supplemental Set User Manual
Page 10
25
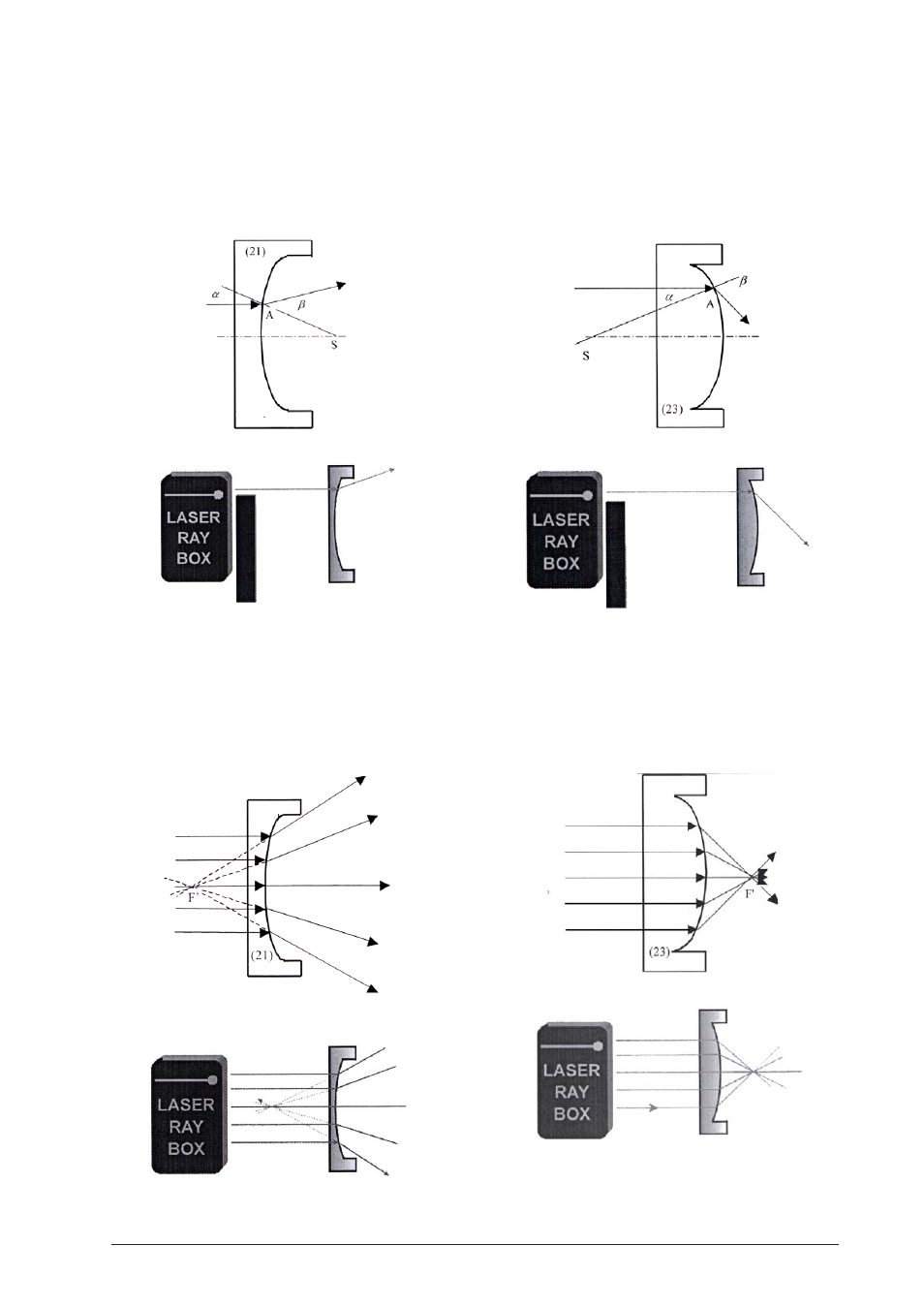
E15a Light ray passing through convex glass-air
boundary
(U17301)
When a ray impinges the boundary at point A, refrac-
tion away from the normal is observed. The normal
can be defined as the line from point A to the centre of
boundary curvature S.
E15b Light beam passing through convex glass-air
boundary
(U17301)
The beam after passing the boundary is divergent. Elon-
gating the refracted light to the other side one can find
a point on the optical axis where the line meets. It is
figure focus F'.
E16a Light ray passing through concave glass-air
boundary
(U17301)
When a ray impinges the boundary at point A, refrac-
tion away from the normal is observed. The normal is
defined as the line from point A to the centre of bound-
ary curvature S.
E16b Light beam passing through concave glass-air
boundary
(U17301)
The beam is convergent after passing the boundary.
Parallel rays meet in one point of the optical axis –
figure focus F'.
Air
Air
Acrylic
Acrylic
Acrylic
Acrylic
