A1 f3 f4 c5, 1 procedure with 3b net log, At the output v – 3B Scientific Teltron Critical Potentials Tube S with He-Filling User Manual
Page 3: Connect the 3b net log ™ unit to the computer, Enter the formula i = -667 * “input_b“ (unit pa), Start the graph-plotting of the experimental data, S peak at 19.8 ev and determine its position t, On the time axis, With the unit ev; in this expression enter the
3
HERTZ TUBE CONSOLE
60
V
A
+
1
RING
2
SLOW
RUN
MIN
MAX
V
A
SET
3
4
1 SLOW 2
1
2
FAST
0...±1 VOLT OUT
0...±1 VOLT OUT
OUT
3
4
200 mV
!
A1
F3
F4
C5
-
+
Battery Unit
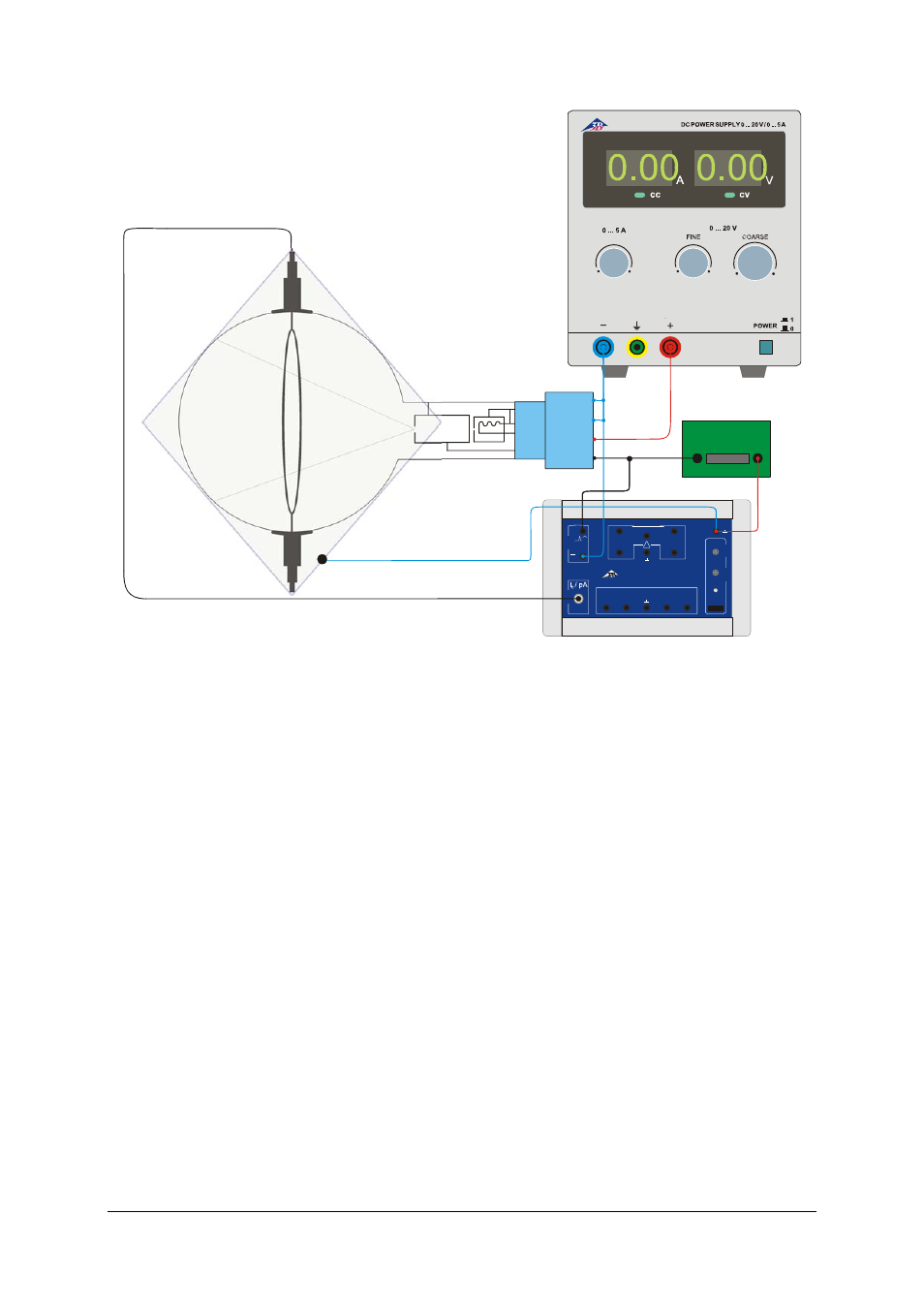
Fig. 1 Experiment set-up with the control unit for critical potential tubes
7.2.1
Procedure with 3B NETlog
TM
•
At the output V
A
of the control unit, set the
minimum voltage to about 10 V and the
maximum voltage to about 35 V, by using
the 3B NETlog™ unit to measure the
voltages (smaller by a factor of 1000)
between socket 3 and earth and that
between socket 4 and earth. Alternatively,
the voltages can be set up with the help of a
multimeter.
•
Connect the 3B
NETlog™ unit to the
computer.
•
Connect the output “Fast 1” from the control
unit to input A of the 3B NETlog™ unit and
the output “Fast 2” to input B. (See Fig. 2)
•
Switch on the 3B NETlog™ unit and start the
3B NETlab™ program on the computer.
•
Select the “Measurement lab” function and
open a new data record.
•
Select analogue inputs A and B and DC
voltage mode (VDC), setting the
measurement ranges to 200 mV for A and
2 V for B.
•
Enter the formula I = -667 * “Input_B“ (unit
pA).
•
Set the following parameters: Measurement
interval = 50 µs, Measurement duration =
0.05 s, Mode = Recorder.
•
Set triggering on the input A with rising edge
(20%).
•
On the DC power supply, set the heater
voltage to 3.5 V.
•
Start the graph-plotting of the experimental
data.
•
Set up the graph with “relative time t in s” on
the x-axis and the quantity I on the y-axis.
•
Repeat the measurements with slightly
higher heater voltages and vary the
minimum and maximum accelerating
voltages U
A
to find the optimum graph.
•
In the spectrum, identify the 2
3
S peak at
19.8 eV and determine its position t
1
on the
time axis.
•
Identify the ionisation threshold at 24.6 eV
and determine its position t
2
on the time
axis.
•
Enter a new formula for the quantity E
defined as 19.8 + 4.8 * (t - t
1
)/( t
2
- t
1
) with
the unit eV; in this expression enter the
