3B Scientific Basic Experiment Board (115 V, 50__60 Hz) User Manual
Page 7
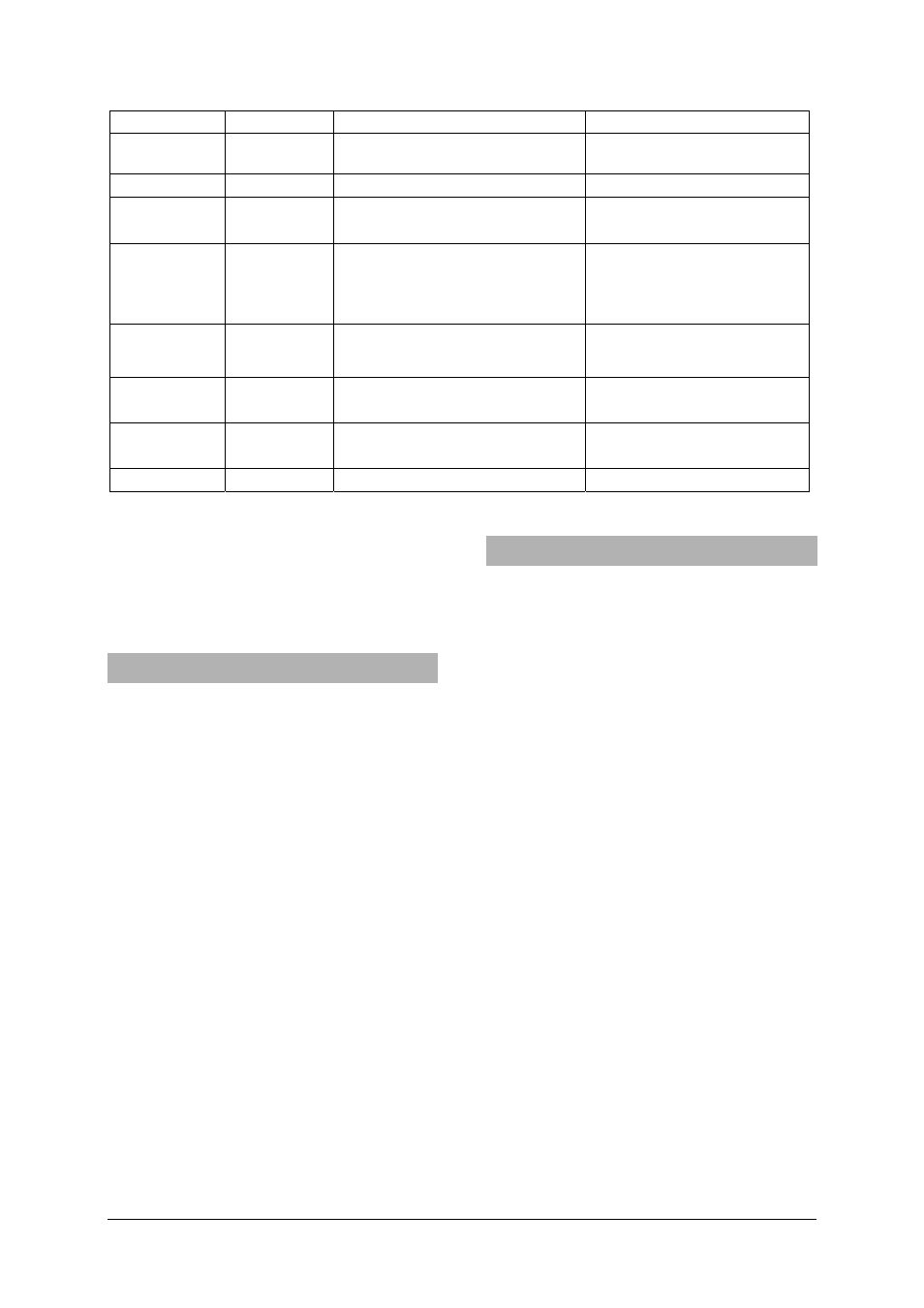
3
C2,C3 39-42
Capacitors
2.2
µF
C4 43-44
Capacitor
100 µF (2x 220 µF electrolytic, in
series +pole to -pole)
KEY 55,
56
Push-buttons
NEON LAMP
57, 58
Fluorescent lamp (neon)
Trigger voltage:
≤ 90 V
Current: 1.7 mA
L1, L2
59-62
Transformer
Primary: L1 (50, 51) / 12 V
Secondary: L2 (52, 53) / 12 V at
29 mA / 20.3 V no load
Max. power: 350 mW
V5 64,
65
Diode
Max. reverse voltage: 1000 V
Max. forward current: 1 A
Forward bias: 56 ---> 57
V6
67, 68
Zener diodes
Zener voltage: 6.2 V at 35 mA
Reverse bias: 67
--->
68
V7
70, 71
Light-emitting diode
2.25 V / 20 mA
Forward direction: 58
--->
59
X2-X7
72-77
4-mm adapter to 2-mm banana plug
1% tolerance and max. 1 W power dissipation applies to all resistors.
For connecting the components, experiment cables
or jumpers with 2-mm banana plugs are used.
6 adapters are available for connecting cables with
4-mm banana plugs.
4. Operation
Basic experiments on electricity can be conducted
by using the basic experiment board (see section 5).
At terminals 1 to 5, different types of voltage can
be read off:
1.
Direct current voltage between 4(+) and 5(–)
(S3 in up position)
2.
Alternating voltage between 1 and 2
3.
Half-wave rectifier, AC voltage, between 3
and 2
4.
Full-wave rectifier, AC voltage, between 3
and 5 (S3 in down position)
For most experiments, at least 2 multimeters are
required (voltage/current, AC/DC, recommended:
U17450/U17452/U11805/U11808). With a stor-
age/digital oscilloscope and/or function generator,
further experiments can also be conducted. The 3B
NETlog™ computer interface combines the func-
tions of these measuring instruments in one and is
therefore ideally suited for operations on the ex-
periment board.
5. Experiment examples
5.1
Resistance and Ohm’s law
By measuring current and voltage, the value of
unknown resistor R2 can be determined. Alterna-
tively, a Wheatstone bridge circuit can also be used.
(Required equipment: 3B NETlog™ or 2 multime-
ters)
5.2 Rectifiers
The output voltage of the half-wave and full-wave
rectifiers can be observed on an oscilloscope.
Smoothing capacitor C1 can also be connected and
the behaviour of the resulting DC voltage source
under load can be investigated. (Required equip-
ment: 3B NETlog™ or oscilloscope)
5.3 Charging and discharging of capacitors
Depending on the choice of the time constant RC,
the charging and discharging characteristics of the
capacitors can be recorded with a multimeter or an
oscilloscope. (Required equipment: multime-
ter/storage or digital oscilloscope or 3B NETlog™)
5.4 Resonant circuits
Damped electrical oscillation can be displayed with
the help of an oscilloscope. Depending on the cycle
period, the inductance of the circuit can be calcu-
lated if the capacitance and resistance are known.
(Required equipment: oscilloscope or 3B NETlog™)
5.5 Potentiometer
The effects of a load on voltage regulation by a
potentiometer circuit can be qualitatively investi-
gated. (Required equipment: 3B NETlog™ or 2 mul-
timeter)
