0 mounting, 0 capacitive loads, Lm62 – Rainbow Electronics LM62 User Manual
Page 5
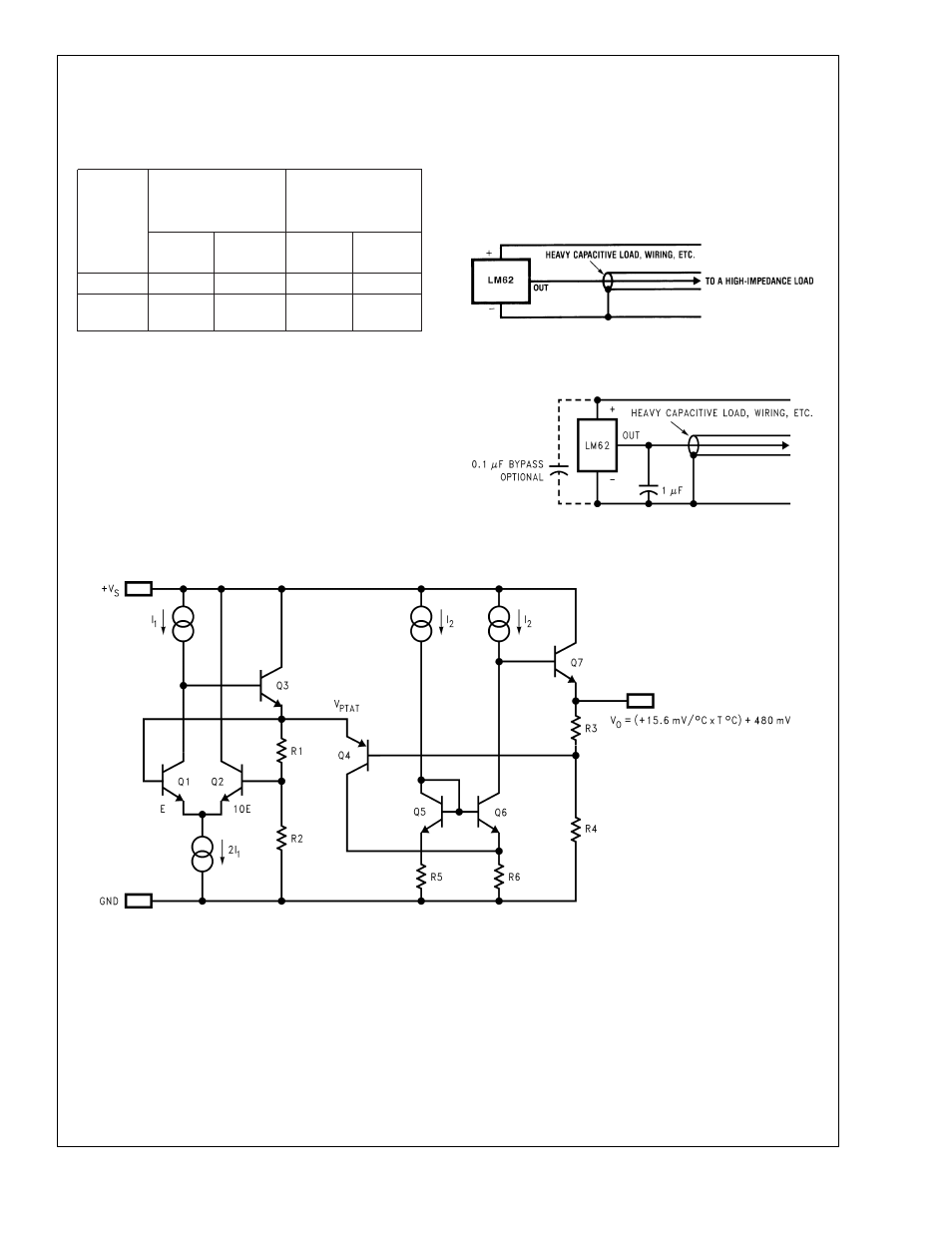
1.0 Mounting
(Continued)
The table shown in
Figure 3 summarizes the rise in die
temperature of the LM62 without any loading, and the ther-
mal resistance for different conditions.
2.0 Capacitive Loads
The LM62 handles capacitive loading well. Without any spe-
cial precautions, the LM62 can drive any capacitive load as
shown in
Figure 4. Over the specified temperature range the
LM62 has a maximum output impedance of 4.7 k
Ω
. In an
extremely noisy environment it may be necessary to add
some filtering to minimize noise pickup. It is recommended
that 0.1 µF be added from +V
S
to GND to bypass the power
supply voltage, as shown in
Figure 5. In a noisy environment
it may be necessary to add a capacitor from the output to
ground. A 1 µF output capacitor with the 4.7 k
Ω
maximum
output impedance will form a 34 Hz lowpass filter. Since the
thermal time constant of the LM62 is much slower than the
30 ms time constant formed by the RC, the overall response
time of the LM62 will not be significantly affected. For much
larger capacitors this additional time lag will increase the
overall response time of the LM62.
SOT-23
SOT-23
no heat sink
small heat fin
(Note 13)
(Note 12)
θ
JA
T
J
− T
A
θ
JA
T
J
− T
A
(˚C/W)
(˚C)
(˚C/W)
(˚C)
Still air
450
0.17
260
0.1
Moving
air
180
0.07
Note 12: Heat sink used is
1
⁄
2
" square printed circuit board with 2 oz. foil with
part attached as shown in
Figure 2 .
Note 13: Part soldered to 30 gauge wire.
FIGURE 3. Temperature Rise of LM62 Due to
Self-Heating and Thermal Resistance (
θ
JA
)
DS100893-15
FIGURE 4. LM62 No Decoupling Required for
Capacitive Load
DS100893-16
FIGURE 5. LM62 with Filter for Noisy Environment
DS100893-17
FIGURE 6. Simplified Schematic
LM62
www.national.com
5
