Max3738 – Rainbow Electronics MAX3738 User Manual
Page 10
MAX3738
Safety Circuitry
The safety circuitry contains a disable input
(TX_DISABLE), a latched fault output (TX_FAULT), and
fault detectors (Figure 5). This circuitry monitors the
operation of the laser driver and forces a shutdown if a
fault is detected (Table 1). The TX_FAULT pin should
be pulled high with a 4.7kΩ to 10kΩ resistor to V
CC
as
required by the SFP MSA. A single-point fault can be a
short to V
CC
or GND. See Table 2 to view the circuit
response to various single-point failure. The transmit
fault condition is latched until reset by a toggle or
TX_DISABLE or V
CC
. The laser driver offers redundant
laser diode shutdown through the optional shutdown
circuitry as shown in the Typical Applications Circuit.
This shutdown transistor prevents a single-point fault at
the laser from creating an unsafe condition.
Safety Circuitry Current Monitors
The MAX3738 features monitors (BC_MON, PC_MON)
for bias current (I
BIAS
) and photocurrent (I
MD
). The
monitors are realized by mirroring a fraction of the cur-
rents and developing voltages across external resistors
connected to ground. Voltages greater than V
REF
at
PC_MON or BC_MON result in a fault state. For exam-
ple, connecting a 100Ω resistor to ground at each mon-
itor output gives the following relationships:
V
BC_MON
= (I
BIAS
/ 82) x 100Ω
V
PC_MON
= I
MD
x 100Ω
External sense resistors can be used for high-accuracy
measurement of bias and photodiode currents. On-chip
isolation resistors are included to reduce the number of
components needed to implement this function.
1Gbps to 2.7Gbps SFF/SFP Laser Driver with
Extinction Ratio Control
10
______________________________________________________________________________________
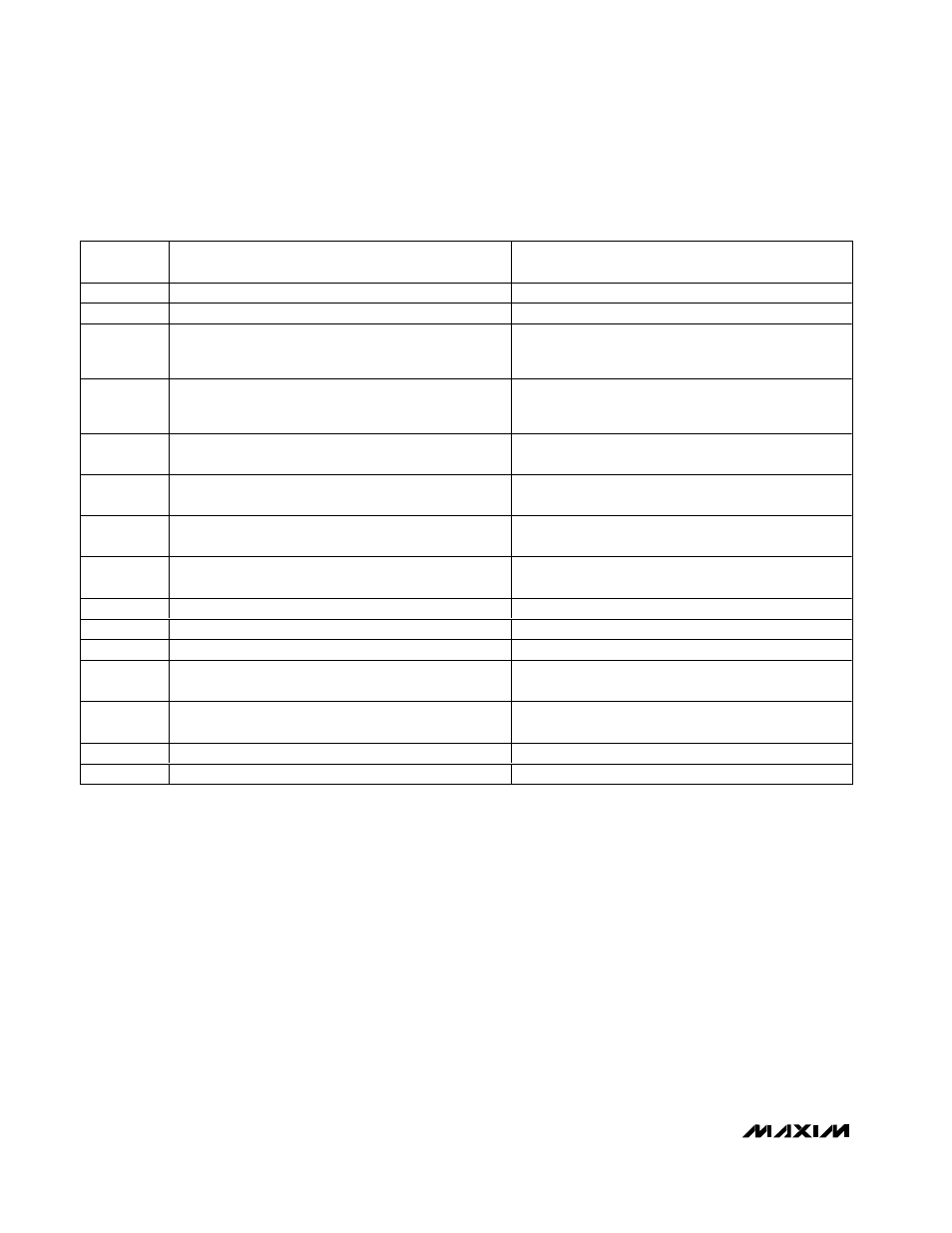
PIN
CIRCUIT RESPONSE TO OVERVOLTATGE OR
SHORT TO V
CC
CIRCUIT RESPONSE TO UNDERVOLTAGE OR
SHORT TO GROUND
TX_FAULT
Does not affect laser power.
Does not affect laser power.
TX_DISABLE
Modulation and bias currents are disabled.
Normal condition for circuit operation.
IN+
The optical average power increases, and a fault occurs
if V
PC_MON
exceeds the threshold. The APC loop
responds by decreasing the bias current.
The optical average power decreases, and the APC loop
responds by increasing the bias current. A fault state
occurs if V
BC_MON
exceeds the threshold voltage.
IN-
The optical average power decreases and the APC loop
responds by increasing the bias current. A fault state
occurs if V
BC_MON
exceeds the threshold voltage.
The optical average power increases and a fault occurs
if V
PC_MON
exceeds the threshold. The APC loop
responds by decreasing the bias current.
MD
This disables bias current. A fault state occurs.
The APC circuit responds by increasing the bias current
until a fault is detected; then a fault* state occurs.
SHUTDOWN
Does not affect laser power. If the shutdown circuitry is
used, the laser current is disabled.
Does not affect laser power.
BIAS
In this condition, the laser forward voltage is 0V and no
light is emitted.
Fault state* occurs. If the shutdown circuitry is used, the
laser current is disabled.
OUT+
The APC circuit responds by increasing the bias current
until a fault is detected; then a fault state* occurs.
Fault state* occurs. If the shutdown circuitry is used, the
laser current is disabled.
OUT-
Does not affect laser power.
Does not affect laser power.
PC_MON
Fault state* occurs.
Does not affect laser power.
BC_MON
Fault state* occurs.
Does not affect laser power.
APCFILT1
I
BIAS
increases until V
BC_MON
exceeds the threshold
voltage.
I
BIAS
increases until V
BC_MON
exceeds the threshold
voltage.
APCFILT2
I
BIAS
increases until V
BC_MON
exceeds the threshold
voltage.
I
BIAS
increases until V
BC_MON
exceeds the threshold
voltage.
MODSET
Does not affect laser power.
Fault state* occurs.
APCSET
Does not affect laser power.
Fault state* occurs.
Table 2. Circuit Responses to Various Single-Point Faults
*A fault state asserts the TX_FAULT pin, disables the modulation and bias currents, and asserts the SHUTDOWN pin.
