Max1623 – Rainbow Electronics MAX1623 User Manual
Page 9
A high capacitor value maintains a constant average
output voltage but slows the loop response to changes
in output voltage. A low capacitor value speeds up the
loop response to changes in output voltage. Choose
the capacitor value that results in optimal performance.
Current Limiting
The current-sense circuit enables when the PMOS
power switch is on. This circuit’s corresponding output
voltage feeds three separate comparators: the skip cur-
rent comparator (1.25A), the maximum current com-
parator (4.15A), and the PWM current comparator (see
the Modes of Operation section).
Oscillator Frequency and
Programming the Off-Time
The MAX1623 features a programmable off-time that is
set by R
TOFF
connected from TOFF to GND. Connecting
a 110k
Ω resistor from TOFF to GND achieves a 1µs
(nominal) off-time. The off-time is inversely proportional
to R
TOFF
according to the formula:
t
OFF
= R
TOFF
/ 110k (µs)
t
OFF
is adjustable between 0.5µs to 4µs (see the
Typical Operating Characteristics). To set the switching
frequency when the inductor operates in continuous-
conduction mode, the off-time has to be set to:
where:
t
OFF
= the programmed off-time
V
I
= input voltage
V
O
= output voltage
f = desired switching frequency during continuous
inductor current
V
PCH
= the voltage drop across the internal P-channel
switch
V
NCH
= the voltage drop across the internal N-channel
synchronous rectifier
Switching frequency decreases as load current is
decreased below the 625mA Idle Mode trip point.
Internal Reference
The 1.10V internal reference (available at REF) is accu-
rate to ±1.5% over the -40°C to +85°C operating range,
making it useful as a precision system reference. Bypass
the reference to ground with a minimum 0.1µF ceramic
capacitor. For low noise and jitter performance, use a
0.47µF ceramic capacitor. The reference can supply up
to 10µA for external loads. However, if tight accuracy
specifications for either reference or the main output are
essential, avoid reference loads in excess of 5µA.
Loading the reference reduces the main output voltage
slightly, according to the reference-voltage load-regula-
tion error.
Start-Up
To prevent the MAX1623 from false output regulation,
the internal PMOS and NMOS switches will not switch
on until all of the following conditions are true: the sup-
ply voltage is above the undervoltage lockout thresh-
old, SHDN is pulled high, the internal reference voltage
is at 75% of its nominal (1.1V) value, and the die tem-
perature is below +145°C. When the above conditions
are satisfied, the MAX1623 will regulate the output volt-
age to the selected level. The MAX1623 typically starts
up in 1ms for full output load.
Thermal Shutdown and
Overload Conditions
Thermal overload protection limits the MAX1623’s total
power dissipation. When the junction temperature
reaches T
j
= +145°C, the device turns off, allowing it to
cool down. Switching resumes after the IC’s junction
temperature decreases by 20°C. If the thermal overload
condition persists, the output pulses on and off.
Thermal overload protection is designed to protect the
MAX1623 during fault conditions, such as an output
short circuit.
Thermal Resistance
Junction to ambient thermal resistance (
θ
JA
) strongly
depends on the amount of copper area immediately
surrounding the IC’s leads. The MAX1623 evaluation kit
has 0.8in
2
of copper area.
θ
JA
on this board was mea-
sured to have 45°C/W of thermal resistance with no air
t
V
V
V
f V
V
V
OFF
I
O
PCH
I
PCH
NCH
(
)
=
+
−
−
−
MAX1623
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
3A, Low-Voltage, Step-Down Regulator with
Synchronous Rectification and Internal Switches
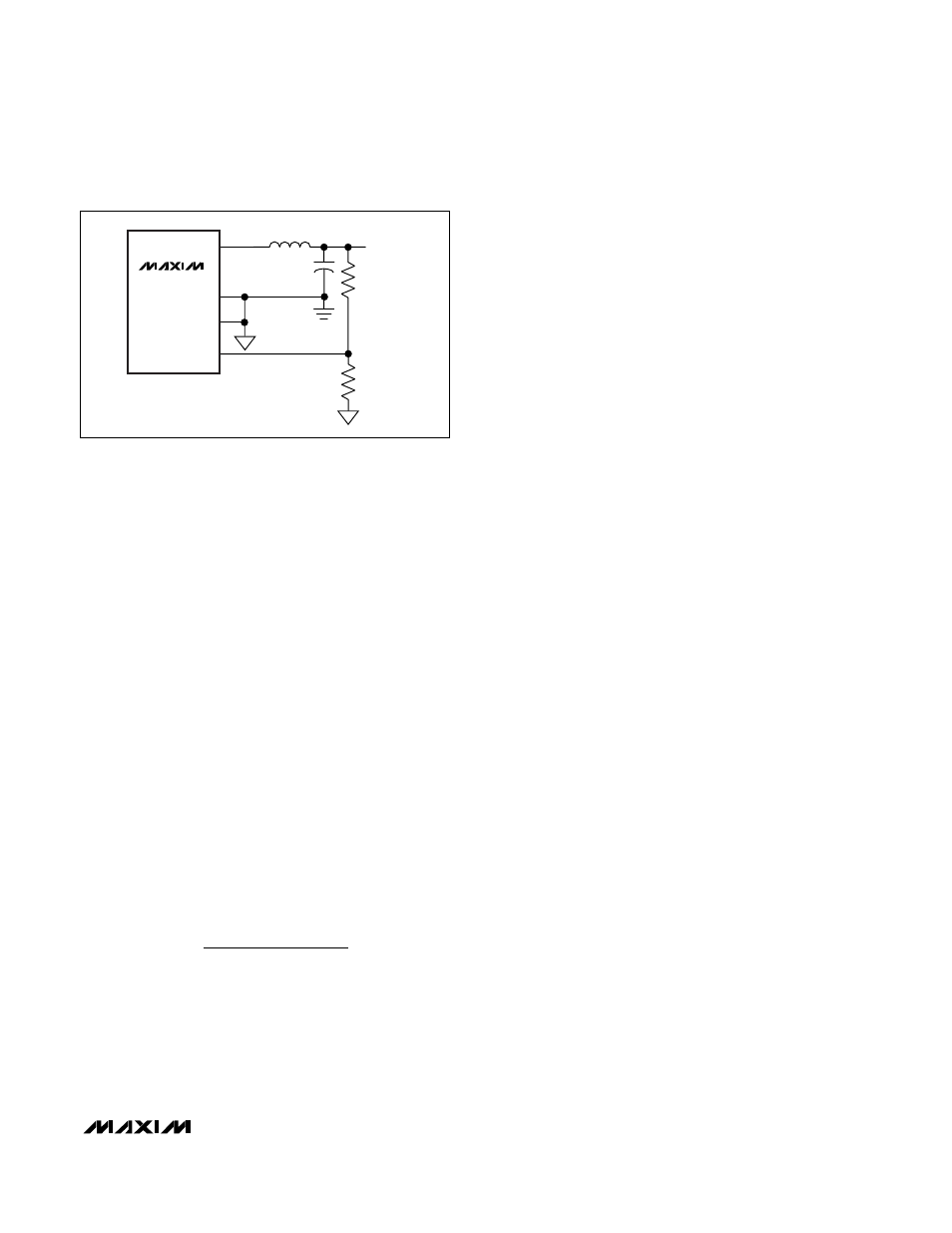
MAX1623
V
OUT
LX
R2
R1
R1 = 10k
Ω to 500kΩ
R2 = R1(V
OUT
/ V
REF
- 1)
V
REF
= 1.1V
PGND
GND
FB
Figure 3. Adjustable Output Voltage
