General description, Pin description – Rainbow Electronics MAX1623 User Manual
Page 6
MAX1623
3A, Low-Voltage, Step-Down Regulator with
Synchronous Rectification and Internal Switches
6
_______________________________________________________________________________________
General Description
The MAX1623 current-mode, PWM, DC-DC regulator is
designed for 5V-input step-down applications. It fea-
tures a 55m
Ω (typ) PMOS switch and a 60mΩ (typ)
NMOS synchronous-rectifier switch. Simple constant-off-
time control allows switching frequencies up to 350kHz.
Adjust the off-time with an external resistor R
TOFF
to
optimize performance trade-offs among efficiency, com-
ponent size, output switching noise, and cost. Idle Mode
operation enhances light-load efficiency by switching to
a pulse-skipping mode that reduces transition and gate-
charge losses. The power-switching circuit consists of
the IC and an LC output filter. The output voltage is the
average of the AC voltage at the switching node (LX).
The MAX1623 regulates the output voltage by changing
the PMOS switch on-time relative to the constant off-
time, thereby adjusting the duty cycle.
The MAX1623 contains six major circuit blocks (Figure 1):
a PWM comparator, a current-sense circuit, a PWM
logic block, an internal feedback mux, an off-time con-
trol block, and a 1.1V precision reference. The input
supply directly powers the internal blocks.
Modes of Operation
The load current determines the mode of operation:
Idle Mode (load currents less than 0.625A) or PWM
mode for inductor currents of 1.25A (which corre-
sponds to load currents greater than 0.625A). The
PWM current limit is continuously adjusted by the PWM
comparator and can vary from 0A to the maximum cur-
rent limit (4A). If the inductor current falls below the Idle
Mode threshold (1.25A), skip mode takes over.
Whenever the P-channel switch turns on, it stays on
until the sensed current reaches the active current limit.
The PWM current limit automatically adjusts with the
PMOS switch duty cycle required to generate the
desired output voltage. When the active current limit is
met, the PMOS switch turns off for the programmed
minimum off-time, and the N-channel synchronous rec-
tifier turns on. The synchronous rectifier stays on until
the P-channel switch turns back on or until the inductor
current reaches zero. At the end of the off-time, the P-
channel switch turns on again if the output voltage indi-
cates that energy is required at the output.
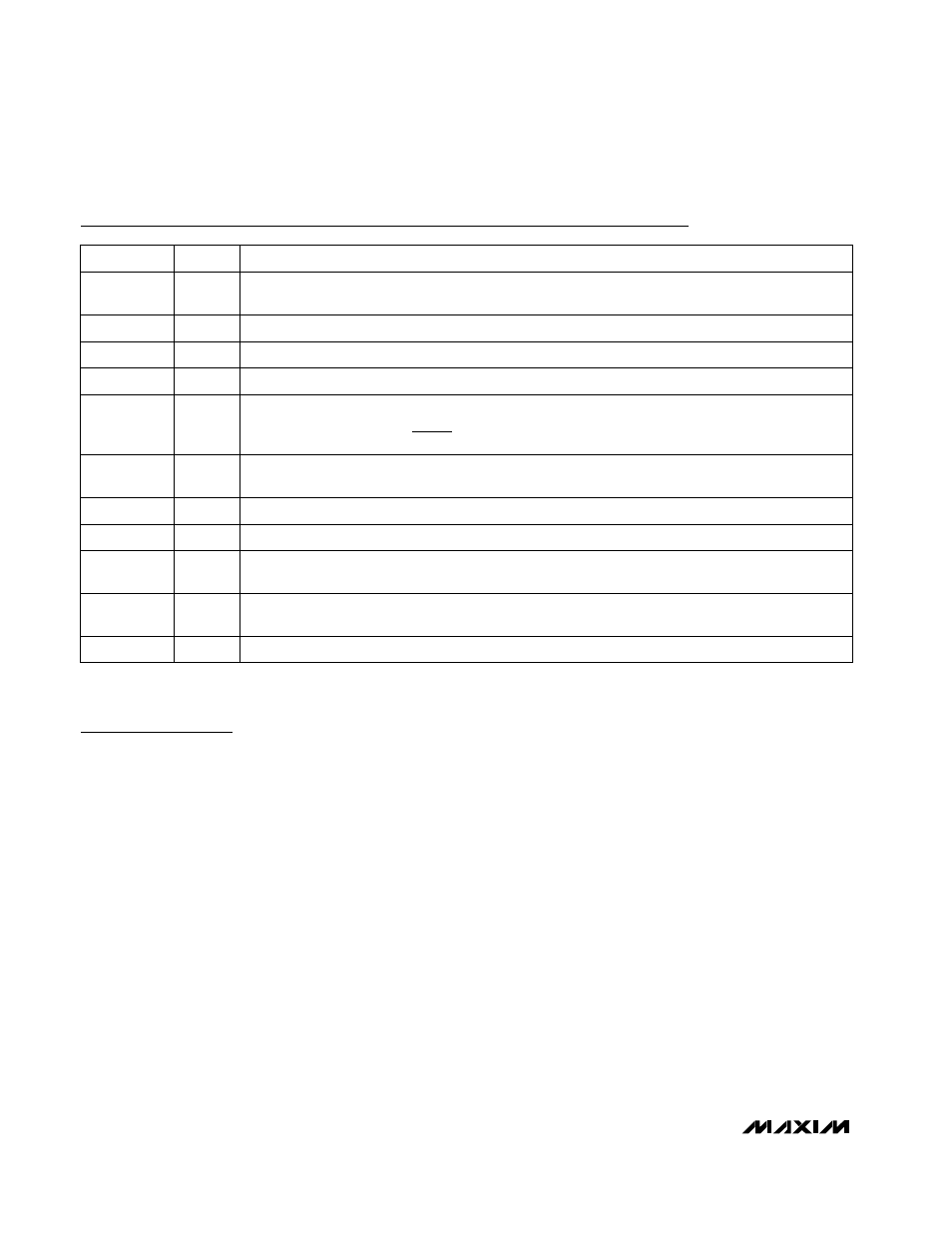
Pin Description
NAME
FUNCTION
1, 3, 5,
16,18, 20
LX
Connection to the internal power switches.
2, 4, 6
IN
Power Input. Internally connected to the PMOS switch source. Connect to 5V.
PIN
7
SHDN
Active-Low Shutdown Input. Connect to V
CC
for normal operation.
8
FBSEL
Feedback Select Input. See Table 1.
12
REF
Reference Output. Bypass with a minimum 0.1µF capacitor to GND. See the Internal Reference section.
11
GND
Analog Ground
10
FB
Feedback input for both fixed-output and adjustable operating modes. Connect to the output directly
for fixed-voltage operation or to a resistor-divider for adjustable operating modes.
9
TOFF
Off-Time Select Input. Connect a resistor from TOFF to GND to adjust the switch off-time, and there-
fore the frequency: t
OFF
= . See the Typical Operating Characteristics.
15, 17, 19
PGND
Power Ground. Internally connected to the NMOS synchronous rectifier source.
14
V
CC
Analog Supply-Voltage Input. Supplies internal analog circuitry. Connect to 5V. Bypass V
CC
with 10
Ω
and 4.7µF (Figure 2).
13
COMP
Integrator Capacitor Connection. Connect a 470pF (470pF to 2000pF range) capacitor to GND to set
the typical integration time-constant. See the Integrator Amplifier section.
R
110k
s)
TOFF
Ω
(
µ
