Detailed description— theory of operation – Rainbow Electronics MAX1213 User Manual
Page 11
MAX1213
1.8V, 12-Bit, 170Msps ADC for
Broadband Applications
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
Detailed Description—
Theory of Operation
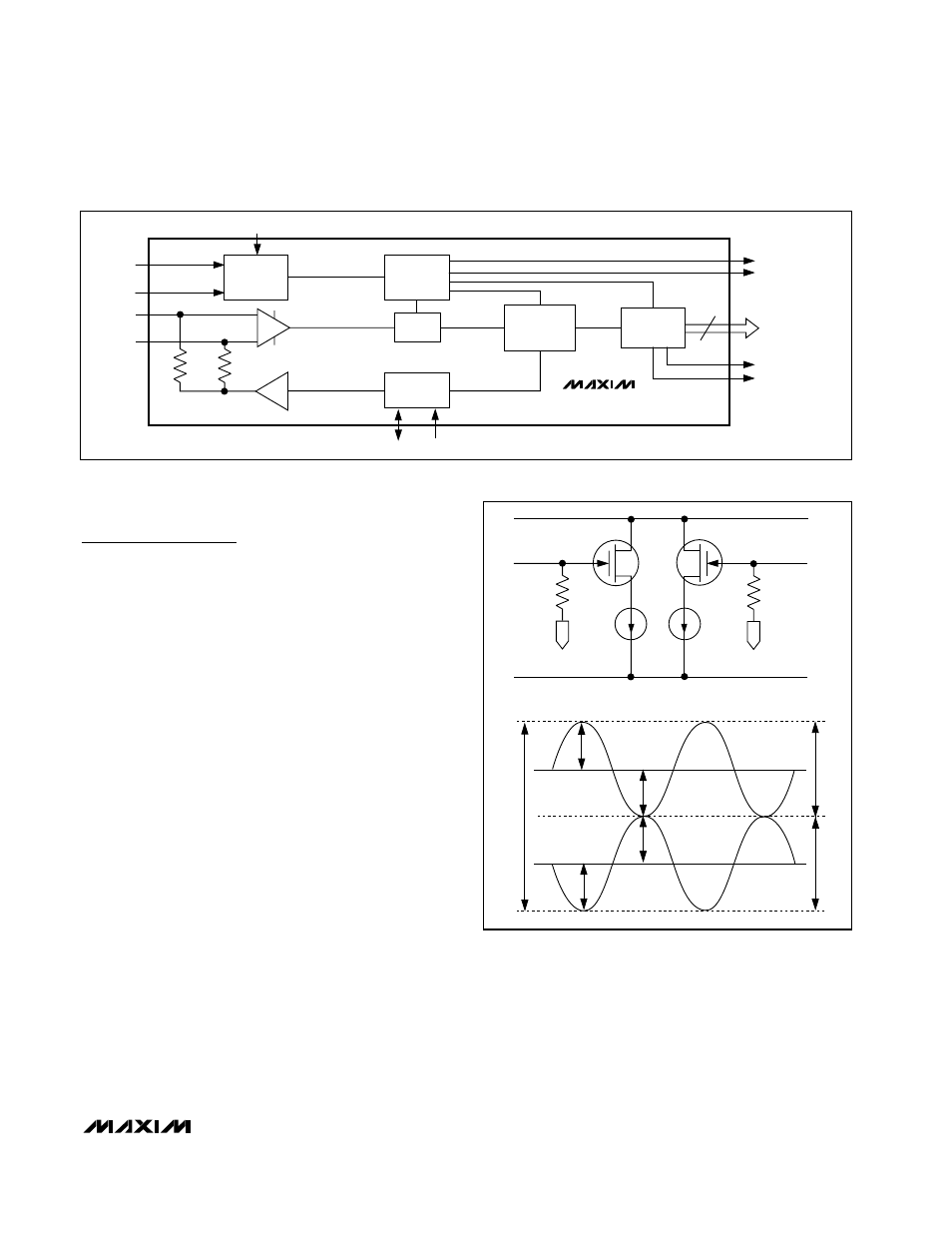
The MAX1213 uses a fully differential pipelined archi-
tecture that allows for high-speed conversion, opti-
mized accuracy, and linearity while minimizing power
consumption and die size.
Both positive (INP) and negative/complementary ana-
log input terminals (INN) are centered around a com-
mon-mode voltage of 1.365V, and accept a differential
analog input voltage swing of ±0.371V each, resulting in
a typical differential full-scale signal swing of 1.485V
P-P
.
Inputs INP and INN are buffered prior to entering each
T/H stage and are sampled when the differential sam-
pling clock signal transitions high.
Each pipeline converter stage converts its input voltage
to a digital output code. At every stage, except the last,
the error between the input voltage and the digital out-
put code is multiplied and passed along to the next
pipeline stage. Digital error correction compensates for
ADC comparator offsets in each pipeline stage and
ensures no missing codes. The result is a 12-bit parallel
digital output word in user-selectable two’s complement
or offset binary output formats with LVDS-compatible
output levels. See
Figure
1 for a more detailed view of
the MAX1213 architecture.
Analog Inputs (INP, INN)
INP and INN are the fully differential inputs of the
MAX1213. Differential inputs usually feature good
rejection of even-order harmonics, which allows for
enhanced AC performance as the signals are pro-
gressing through the analog stages. The MAX1213
analog inputs are self-biased at a common-mode volt-
age of 1.365V and allow a differential input voltage
swing of 1.485V
P-P
(
Figure
2). Both inputs are self-
biased through 2kΩ resistors, resulting in a typical dif-
ferential input resistance of 4kΩ. It is recommended to
drive the analog inputs of the MAX1213 in AC-coupled
configuration to achieve best dynamic performance.
See the Single-Ended, AC-Coupled Analog Input sec-
tion for a detailed discussion of this configuration.
MAX1213
CLOCK-
DIVIDER
CONTROL
CLKDIV
CLOCK
MANAGEMENT
INPUT
BUFFER
DCLKP
D0P/N–D11P/N
DCLKN
12
ORP
ORN
2.2kΩ
2.2kΩ
CLKP
CLKN
INP
INN
COMMON-MODE
BUFFER
REFIO
REFADJ
LVDS
DATA PORT
REFERENCE
T/H
12-BIT PIPELINE
QUANTIZER
CORE
2.2kΩ
INP
2.2kΩ
AGND
COMMON-MODE
VOLTAGE (1.365V)
COMMON-MODE
VOLTAGE (1.365V)
INN
TO COMMON MODE
TO COMMON MODE
1.485V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL FSR
INP
-371mV
-371mV
+371mV
742mV
P-P
742mV
P-P
+371mV
INN
AV
CC
Figure
1. Simplified MAX1213 Block Diagram
Figure
2. Simplified Analog Input Architecture and Allowable
Input Voltage Range
