Detailed description, Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX993 User Manual
Page 7
MAX985/MAX986/MAX989/MAX990/MAX993/MAX994
Micropower, Low-Voltage, UCSP/SC70,
Rail-to-Rail I/O Comparators
_______________________________________________________________________________________
7
_______________Detailed Description
The MAX985/MAX986/MAX989/MAX990/MAX993/
MAX994 are single/dual/quad low-power, low-voltage
comparators. They have an operating supply voltage
range between 2.5V and 5.5V and consume only 11µA.
Their common-mode input voltage range extends 0.25V
beyond each rail. Internal hysteresis ensures clean out-
put switching, even with slow-moving input signals.
Large internal output drivers allow rail-to-rail output
swing with up to 8mA loads.
The output stage employs a unique design that mini-
mizes supply-current surges while switching, virtually
eliminating the supply glitches typical of many other
comparators. The MAX985/MAX989/MAX993 have a
push-pull output structure that sinks as well as sources
current. The MAX986/MAX990/MAX994 have an open-
drain output stage that can be pulled beyond V
CC
to an
absolute maximum of 6V above V
EE
.
Input Stage Circuitry
The devices’ input common-mode range extends from
-0.25V to (V
CC
+ 0.25V). These comparators may oper-
ate at any differential input voltage within these limits.
Input bias current is typically 1.0pA if the input voltage
is between the supply rails. Comparator inputs are pro-
tected from overvoltage by internal body diodes con-
nected to the supply rails. As the input voltage exceeds
the supply rails, these body diodes become forward
biased and begin to conduct. Consequently, bias cur-
rents increase exponentially as the input voltage
exceeds the supply rails.
Output Stage Circuitry
These comparators contain a unique output stage
capable of rail-to-rail operation with up to 8mA loads.
Many comparators consume orders of magnitude more
current during switching than during steady-state oper-
ation. However, with this family of comparators, the
supply-current change during an output transition is
extremely small. The Typical Operating Characteristics
graph Supply Current vs. Output Transition Frequency
shows the minimal supply-current increase as the out-
put switching frequency approaches 1MHz. This char-
acteristic eliminates the need for power-supply filter
capacitors to reduce glitches created by comparator
switching currents. Another advantage realized in high-
speed, battery-powered applications is a substantial
increase in battery life.
__________Applications Information
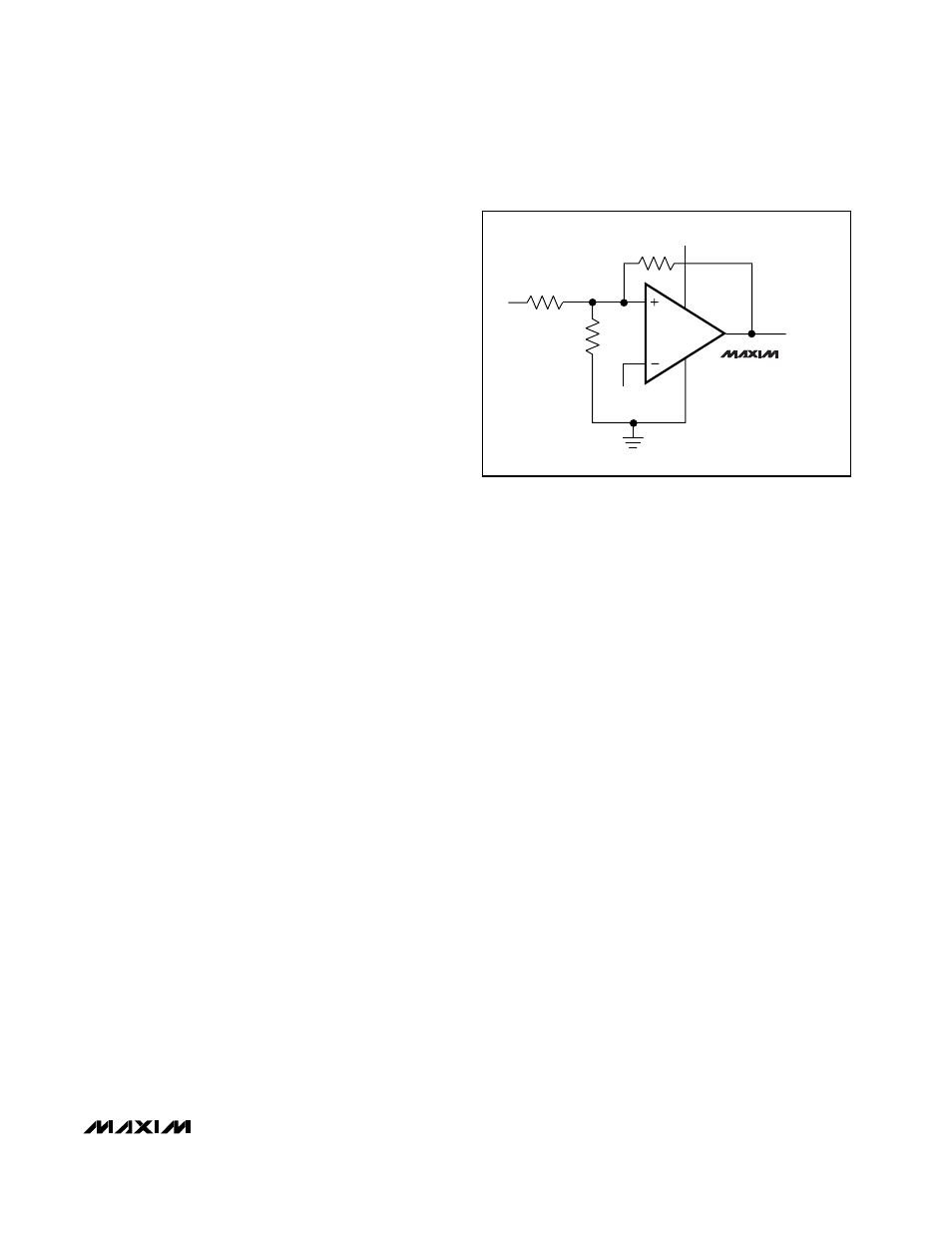
Additional Hysteresis
MAX985/MAX989/MAX993
The MAX985/MAX989/MAX993 have ±3mV internal
hysteresis. Additional hysteresis can be generated with
three resistors using positive feedback (Figure 1).
Unfortunately, this method also slows hysteresis
response time. Use the following procedure to calcu-
late resistor values for the MAX985/MAX989/MAX993.
1) Select R3. Leakage current at IN is under 10nA, so
the current through R3 should be at least 1µA to
minimize errors caused by leakage current. The cur-
rent through R3 at the trip point is (V
REF
- V
OUT
) /
R3. Considering the two possible output states in
solving for R3 yields two formulas: R3 = V
REF
/ 1µA
or R3 = (V
REF
- V
CC
) / 1µA. Use the smaller of the
two resulting resistor values. For example, if V
REF
=
1.2V and V
CC
= 5V, then the two R3 resistor values
are 1.2M
Ω and 3.8MΩ. Choose a 1.2MΩ standard
value for R3.
2) Choose the hysteresis band required (V
HB
). For this
example, choose 50mV.
3) Calculate R1 according to the following equation:
R1 = R3 x (V
HB
/ V
CC
)
For this example, insert the values R1 = 1.2M
Ω x
(50mV / 5V) = 12k
Ω.
4) Choose the trip point for V
IN
rising (V
THR
; V
THF
is
the trip point for V
IN
falling). This is the threshold
voltage at which the comparator switches its output
from low to high as V
IN
rises above the trip point. For
this example, choose 3V.
V
CC
MAX985
MAX989
MAX993
OUT
R3
R1
R2
V
REF
V
EE
V
IN
V
CC
Figure 1. Additional Hysteresis (MAX985/MAX989/MAX993)
