Definitions – Rainbow Electronics MAX1092 User Manual
Page 17
High-frequency noise in the power supply (V
DD
) could
influence the proper operation of the ADC’s fast com-
parator. Bypass V
DD
to the star ground with a network
of two parallel capacitors, 0.1µF and 4.7µF, located as
close as possible to the MAX1090/MAX1092 power-
supply pin. Minimize capacitor lead length for best sup-
ply-noise rejection, and add an attenuation resistor (5
Ω)
if the power supply is extremely noisy.
__________________________Definitions
Integral Nonlinearity
Integral nonlinearity (INL) is the deviation of the values
on an actual transfer function from a straight line. This
straight line can be either a best-straight-line fit or a line
drawn between the end points of the transfer function,
once offset and gain errors have been nullified. The
MAX1090/MAX1092’s INL is measured using the end-
point method.
Differential Nonlinearity
Differential nonlinearity (DNL) is the difference between
an actual step width and the ideal value of 1LSB. A
DNL error specification of less than 1LSB guarantees
no missing codes and a monotonic transfer function.
Aperture Jitter
Aperture jitter (t
AJ
) is the sample-to-sample variation in
the time between the samples.
Aperture Delay
Aperture delay (t
AD
) is the time between the rising
edge of the sampling clock and the instant when an
actual sample is taken.
MAX1090/MAX1092
400ksps, +5V, 8-/4-Channel, 10-Bit ADCs
with +2.5V Reference and Parallel Interface
______________________________________________________________________________________
17
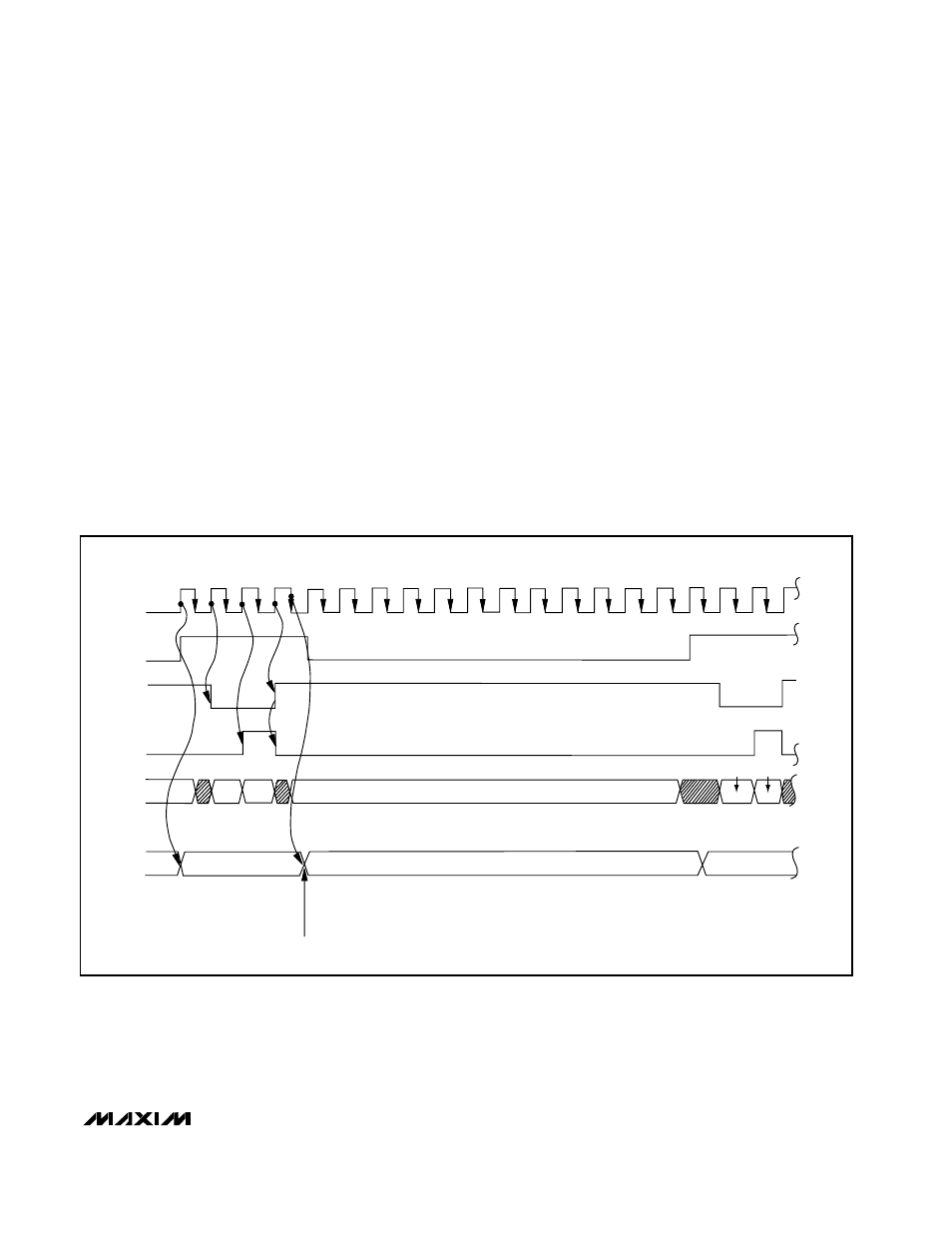
CLK
ACQUISITION
CONTROL BYTE
CONVERSION
LOW
BYTE
HIGH
BYTE
D7–D0 D9–D8
LOW
BYTE
HIGH
BYTE
D7–D0 D9–D8
ACQUISITION
SAMPLING INSTANT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
WR
RD
HBEN
D7–D0
STATE
CONTROL
BYTE
Figure 10. Timing Diagram for Fastest Conversion
