Rainbow Electronics MAX1092 User Manual
Page 10
Analog Input Protection
Internal protection diodes, which clamp the analog
input to V
DD
and GND, allow each input channel to
swing within (GND - 300mV) to (V
DD
+ 300mV) without
damage. However, for accurate conversions near full
scale, neither input should exceed (V
DD
+ 50mV) or be
less than (GND - 50mV).
If an off-channel analog input voltage exceeds the
supplies by more than 50mV, limit the forward-bias
input current to 4mA.
Track/Hold
The MAX1090/MAX1092 T/H stage enters its tracking
mode on the rising edge of WR. In external acquisition
mode, the part enters its hold mode on the next rising
edge of WR. In internal acquisition mode, the part enters
its hold mode on the fourth falling edge of the clock after
writing the control byte. Note that in internal clock mode,
this is approximately 1µs after writing the control byte.
In single-ended operation, IN- is connected to COM
and the converter samples the positive (+) input. In
pseudo-differential operation, IN- connects to the nega-
tive input (-) and the difference of
|
(IN+) - (IN-)
|
is sam-
pled. At the beginning of the next conversion, the
positive input connects back to IN+ and C
HOLD
charges to the input signal.
The time required for the T/H stage to acquire an input
signal depends on how quickly its input capacitance is
charged. If the input signal’s source impedance is high,
the acquisition time lengthens and more time must be
allowed between conversions. The acquisition time,
t
ACQ
, is the maximum time the device takes to acquire
the signal and is also the minimum time required for the
signal to be acquired. Calculate this with the following
equation:
t
ACQ
= 7 (R
S
+ R
IN
) C
IN
where R
S
is the source impedance of the input signal,
R
IN
(800
Ω) is the input resistance, and C
IN
(12pF) is
the input capacitance of the ADC. Source impedances
below 3k
Ω have no significant impact on the MAX1090/
MAX1092’s AC performance.
Higher source impedances can be used if a 0.01µF
capacitor is connected to the individual analog inputs.
Along with the input impedance, this capacitor forms
an RC filter, limiting the ADC’s signal bandwidth.
Input Bandwidth
The MAX1090/MAX1092 T/H stage offers a 350kHz full-
linear and a 6MHz full-power bandwidth. These fea-
tures make it possible to digitize high-speed transients
and measure periodic signals with bandwidths exceed-
ing the ADC’s sampling rate by using undersampling
techniques. To avoid aliasing high-frequency signals
into the frequency band of interest, anti-alias filtering is
recommended.
Starting a Conversion
Initiate a conversion by writing a control byte that
selects the multiplexer channel and configures the
MAX1090/MAX1092 for either unipolar or bipolar opera-
tion. A write pulse (WR + CS) can either start an acqui-
MAX1090/MAX1092
400ksps, +5V, 8-/4-Channel, 10-Bit ADCs
with +2.5V Reference and Parallel Interface
10
______________________________________________________________________________________
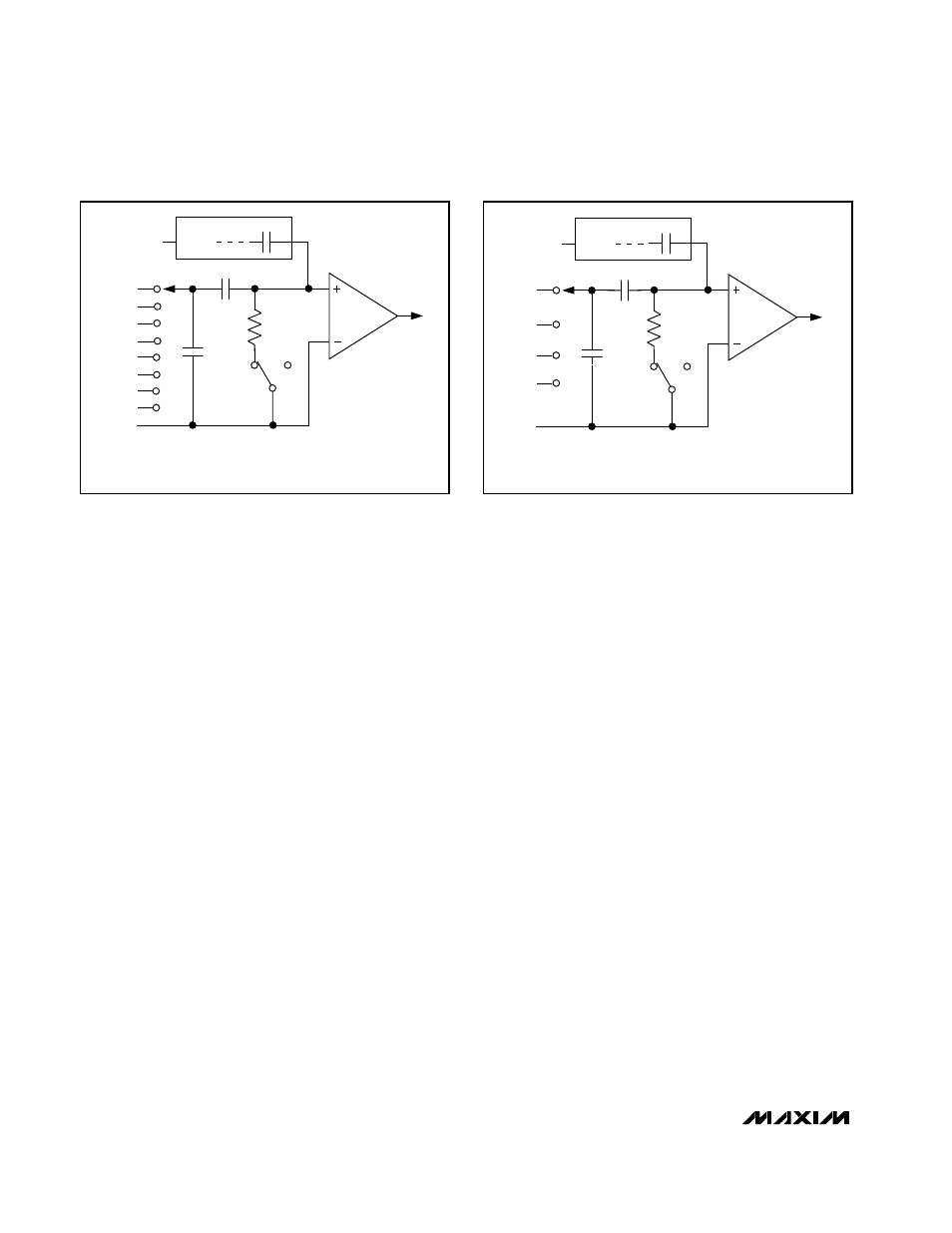
CH0
CH2
CH1
CH3
CH4
CH6
CH7
CH5
COM
C
SWITCH
TRACK
T/H
SWITCH
R
IN
800
Ω
C
HOLD
HOLD
10-BIT CAPACITIVE DAC
REF
ZERO
COMPARATOR
–
+
12pF
SINGLE-ENDED MODE: IN+ = CH0–CH7, IN- = COM
PSEUDO-DIFFERENTIAL MODE: IN+ AND IN- SELECTED FROM PAIRS OF
CH0/CH1, CH2/CH3, CH4/CH5, AND CH6/CH7
AT THE SAMPLING INSTANT,
THE MUX INPUT SWITCHES
FROM THE SELECTED IN+
CHANNEL TO THE SELECTED
IN- CHANNEL.
INPUT
MUX
Figure 3a. MAX1090 Simplified Input Structure
CH0
CH1
CH2
CH3
COM
C
SWITCH
TRACK
T/H
SWITCH
R
IN
800
Ω
C
HOLD
HOLD
10-BIT CAPACITIVE DAC
REF
ZERO
COMPARATOR
–
+
12pF
SINGLE-ENDED MODE: IN+ = CH0–CH3, IN- = COM
PSEUDO-DIFFERENTIAL MODE: IN+ AND IN- SELECTED FROM PAIRS OF
CH0/CH1 AND CH2/CH3
AT THE SAMPLING INSTANT,
THE MUX INPUT SWITCHES
FROM THE SELECTED IN+
CHANNEL TO THE SELECTED
IN- CHANNEL.
INPUT
MUX
Figure 3b. MAX1092 Simplified Input Structure
