Definitions, Integral nonlinearity, Differential nonlinearity – Rainbow Electronics MAX1289 User Manual
Page 13
Definitions
Integral Nonlinearity
Integral nonlinearity (INL) is the deviation of the values
on an actual transfer function from a straight line. This
straight line can be either a best-straight-line fit or a line
drawn between the end points of the transfer function,
once offset and gain errors have been nullified. The sta-
tic linearity parameters for the MAX1286–MAX1289 are
measured using the end-point method.
Differential Nonlinearity
Differential nonlinearity (DNL) is the difference between
an actual step width and the ideal value of 1LSB. A
DNL error specification of less than 1LSB guarantees
no missing codes and a monotonic transfer function.
MAX1286–MAX1289
150ksps, 12-Bit, 2-Channel Single-Ended, and
1-Channel True-Differential ADCs in SOT23
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
CNVST
SCLK
DOUT
SAMPLING INSTANT
4
1
8
12
B11
MSB
B10
B9
B8
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
LSB
HIGH-Z
16
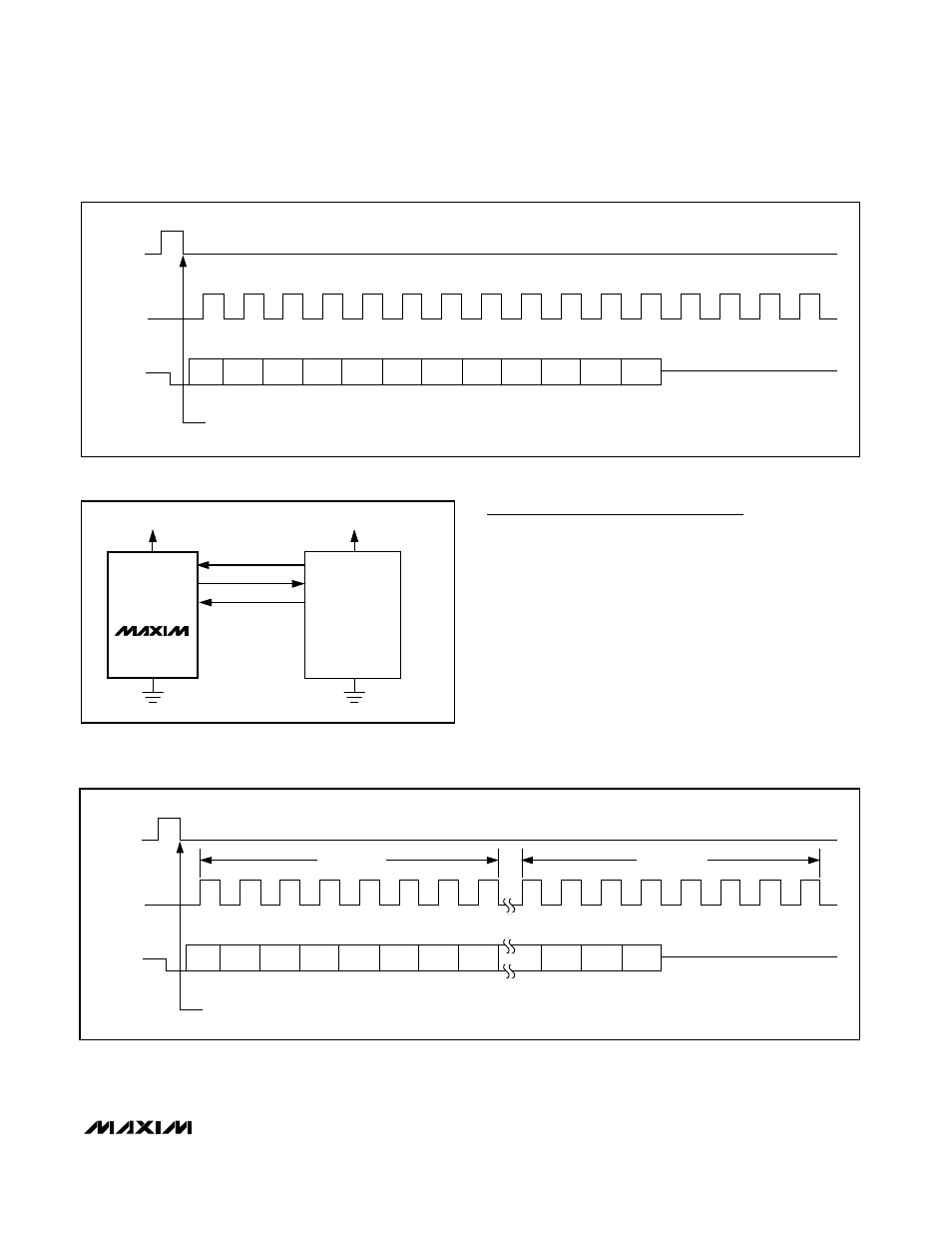
Figure 9b. QSPI Interface Timing Sequence (CPOL = CPHA = 0)
SCK
SDI
GND
GND
I/O
SCLK
DOUT
CNVST
V
DD
V
DD
MAX1286–
MAX1289
PIC16/PIC17
Figure 10a. SPI Interface Connection for a PIC16/PIC17 Controller
CNVST
1ST BYTE READ
SCLK
DOUT
2ND BYTE READ
SAMPLING INSTANT
4
1
8
12
B11
MSB
B10
B9
B8
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
LSB
HIGH-Z
16
Figure 10b. SPI Interface Timing with PIC16/PIC17 in Master Mode (CKE = 1, CKP = 0, SMP = 0, SSPM3 - SSPM0 = 0001)
