Rainbow Electronics MAX5043 User Manual
Page 16
MAX5042/MAX5043
where R
He
is the external high-side resistor, R
Le
is the
external low-side resistor, R
Hi
is the internal high-side
resistor (1.2MΩ, typ), R
Le
is the internal low-side resistor
(50kΩ, typ), V
REF
is 1.27V (typ), and V
IN
is the desired
threshold.
Use an external 100kΩ pullup resistor to POSINPWM to
override UVLO functionality for either lockout.
Internal Regulators
An internal high-voltage linear regulator provides a 15V
output at REG15. This serves as the input to the 9V reg-
ulator that provides bias for the internal MOSFET dri-
vers. The 15V regulator also provides the bias for REG5,
a 5V supply used both by internal as well as external cir-
cuitry. Bypass the REG15, REG9, and REG5 regulators
with 1µF ceramic capacitors. A voltage greater than 18V
and less than 40V on REG15 disables the internal high-
voltage startup regulator. The REG9 regulator steps
down the voltage on REG15 to an output of 9V with a
current limit of 100mA. The REG5 regulator steps down
the voltage on REG15 to an output of 5V with a current
limit of 40mA. Disabling the REG15 regulator by power-
ing REG15 with an external power supply considerably
reduces the internal power dissipation in the
MAX5042/MAX5043. The voltage and power necessary
to override the REG15 internal regulator can be generat-
ed with a rectifier and an extra winding from the main
transformer.
Soft-Start
Program the MAX5042/MAX5043 soft-start with an
external capacitor between CSS and PWMNEG. When
the device turns on, the soft-start capacitor (C
CSS
)
charges with a constant current of 33µA, ramping up to
7.3V. During this time, OPTO is clamped to CSS + 0.6V.
This initially holds the duty cycle lower than the value
the regulator tries to impose, limiting the current inrush
and the voltage overshoot at the secondary. When the
MAX5042/MAX5043 turn off, the soft-start capacitor
internally discharges to PWMNEG.
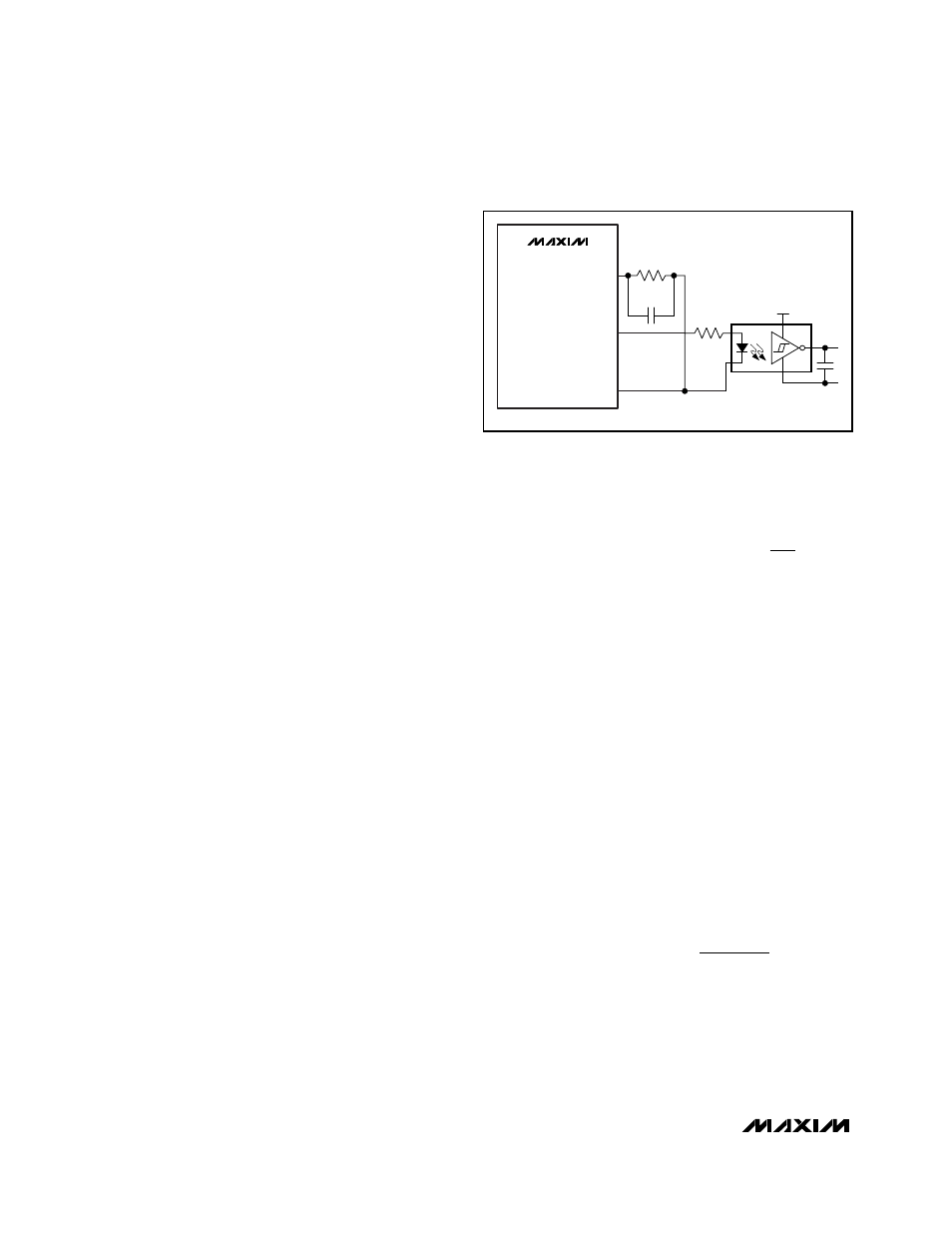
Secondary-Side Synchronization
The MAX5042/MAX5043 provide convenient synchro-
nization of the secondary-side synchronous rectifiers.
Figure 5 shows the connection diagram with a high-
speed optocoupler. Choose an optocoupler with a
propagation delay of less than 50ns.
For optimum results, adjust the resistor connected to
DRVDEL to provide the required amount of delay
between the leading edge of the PPWM signal and the
turn-on of the power MOSFETs. Use the following formu-
la to calculate the approximate resistance (R
DRVDEL
)
required to set the delay between the PPWM and the
power pulse applied to the transformer:
where t
DRVDEL
is the required delay from the rising edge
of PPWM to the switching of the internal power MOSFETs.
PWM Regulation
The MAX5042/MAX5043 are multimode PWM power
ICs supporting both voltage and current-mode control.
Voltage-Mode Control and the PWM Ramp
For voltage-mode control, the feed-forward PWM ramp
is generated at RCFF. From RCFF connect a capacitor
to PWMNEG and a resistor to POSINPWM. The ramp
generated is applied to the noninverting input of the
PWM comparator at RAMP and has a minimum voltage
of 1.5V to 2.5V. The slope of the ramp is determined by
the voltage at POSINPWM and affects the overall loop
gain. The ramp peak must remain below the dynamic
range of RCFF (0 to 5.5V). Assuming the maximum duty
cycle approaches 50% at a minimum input voltage
(PWM UVLO turn-on threshold), use the following for-
mula to calculate the minimum value of either the ramp
capacitor or resistor:
where:
V
INUVLO
= the minimum input supply voltage (typically
the PWM UVLO turn-on voltage),
f
s
= the switching frequency,
V
rP-P
= the peak-to-peak ramp voltage (2V, typ).
R
C
V
f
V
RCFF
RCFF
INUVLO
S
rP P
Ч
≥
Ч
2
-
R
t
ns
k
ns
DRVDEL
DRVDEL
=
−
(
)
(
)
100
2
Ω
Two-Switch Power ICs with Integrated
Power MOSFETs and Hot-Swap Controller
16
______________________________________________________________________________________
DRVDEL
PWMNEG
PPWM
MAX5042/MAX5043
R1
C1
0.22µF
R2
C2
5V
PS9715
OR EQUIVALENT
HIGH-SPEED
OPTOCOUPLER
Figure 5. Secondary-Side Synchronous Rectifier Driver Using a
High-Speed Optocoupler
