Max9937, Detailed description, Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX9937 User Manual
Page 8: Pin description
MAX9937
Detailed Description
The MAX9937 unidirectional high-side, current-sense
amplifier features a 4V to 28V input common-mode volt-
age range that is independent of supply voltage (V
CC
=
2.7V to 5.5V). The MAX9937 monitors the current through
a current-sense resistor by converting the sense voltage
to a current output (OUT). Gain is set by the ratio of an
output resistor (R
OUT
) and an input resistor (R
RSP
). High-
side current monitoring with the MAX9937 does not inter-
fere with the ground path of the load, making it useful for
a variety of automotive battery/ECU monitoring.
Robust input ESD structure allows input common-mode
voltages to exceed the 28V maximum operating input
range for short durations, making the MAX9937 ideal
for applications that need to withstand short-duration
load-dump conditions. The MAX9937 is able to with-
stand reverse-battery conditions by a suitable choice of
input resistors (R
RSN
, R
RSP
). See the
Input Common-
Mode Voltages > 28V and < 0V
section
.
Current-Sense Amplifier Operation
The MAX9937 current-sense amplifier operation is best
understood as a specialized op-amp circuit with a
p-channel FET in the feedback path. The op amp
forces a current through an external gain resistor at
RSP (R
RSP
, see the
Typical Application Circuit
) so that
its voltage drop equals the voltage drop across the
external sense resistor, R
SENSE
, making the voltage at
RSP the same as RSN. An external resistor at RSN
(R
RSN
) has the same value as R
RSP
to minimize input
offset voltage due to input bias currents.
The current through R
RSP
is now sourced by the high-
voltage p-channel FET into an external resistor (R
OUT
)
at OUT. This produces an output voltage whose magni-
tude is given by the following equations:
The gain accuracy is primarily determined by the
matching of the two gain resistors, R
RSP
and R
OUT
. The
voltage gain error of the MAX9937 is less than 1.5%.
Total gain = 20V/V with R
OUT
= 10k
Ω
and R
RSP
= 500
Ω.
Low temperature drift of input bias currents and input
offset currents minimizes their impact on total input off-
set voltage of the current-sense amplifier.
Applications Information
Choosing R
SENSE
To measure lower currents more accurately, use a high
value for R
SENSE
. The high value develops a higher
sense voltage that reduces the effect of offset voltage
errors of the internal op amp. In applications monitoring
very high currents, however, R
SENSE
must be able to
dissipate the I
2
R losses. If the resistor’s rated power
dissipation is exceeded, its value may drift or it may fail
altogether, causing large differential voltages to devel-
op between RSP and RSN.
To minimize the effect of input offset voltage by produc-
tion calibration, see the
Skewed Input Offset Voltage for
Production Calibration
section. This can help reduce
the size of the sense resistor in high-current applica-
tions, as well as measure wide-dynamic-range currents
without sacrificing accuracy.
If I
SENSE
has a large high-frequency component, mini-
mize the inductance of R
SENSE
and use input differen-
tial filters (see the
Flexible EMI Filtering
section)
.
Low-inductance metal-film resistors are best suited for
these applications.
Calculation of Total Input Offset Voltage
Because of the use of op-amp style architecture, calcu-
lation of total input offset voltage involves the same
methodology as is used for any standard op-amp cir-
cuit. Interaction of the input bias currents and tolerance
of the external resistors, combined with the core input
offset voltage of the op amp, are important to consider.
Finally, RSS (root-sum-of-squares) calculation for all
these uncorrelated sources of error gives the final input
offset voltage.
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
V
V
I
R
I
R
OS FINAL
OS
B
RS
B
RS
−
=
+
Ч
+
Ч
2
2
2
2
Δ
Δ
V
I
R
V
V
R
R
SENSE
LOAD
SENSE
OUT
SENSE
OUT
RSP
=
Ч
=
Ч
Automotive Current-Sense Amplifier
with Reverse-Battery Protection
8
_______________________________________________________________________________________
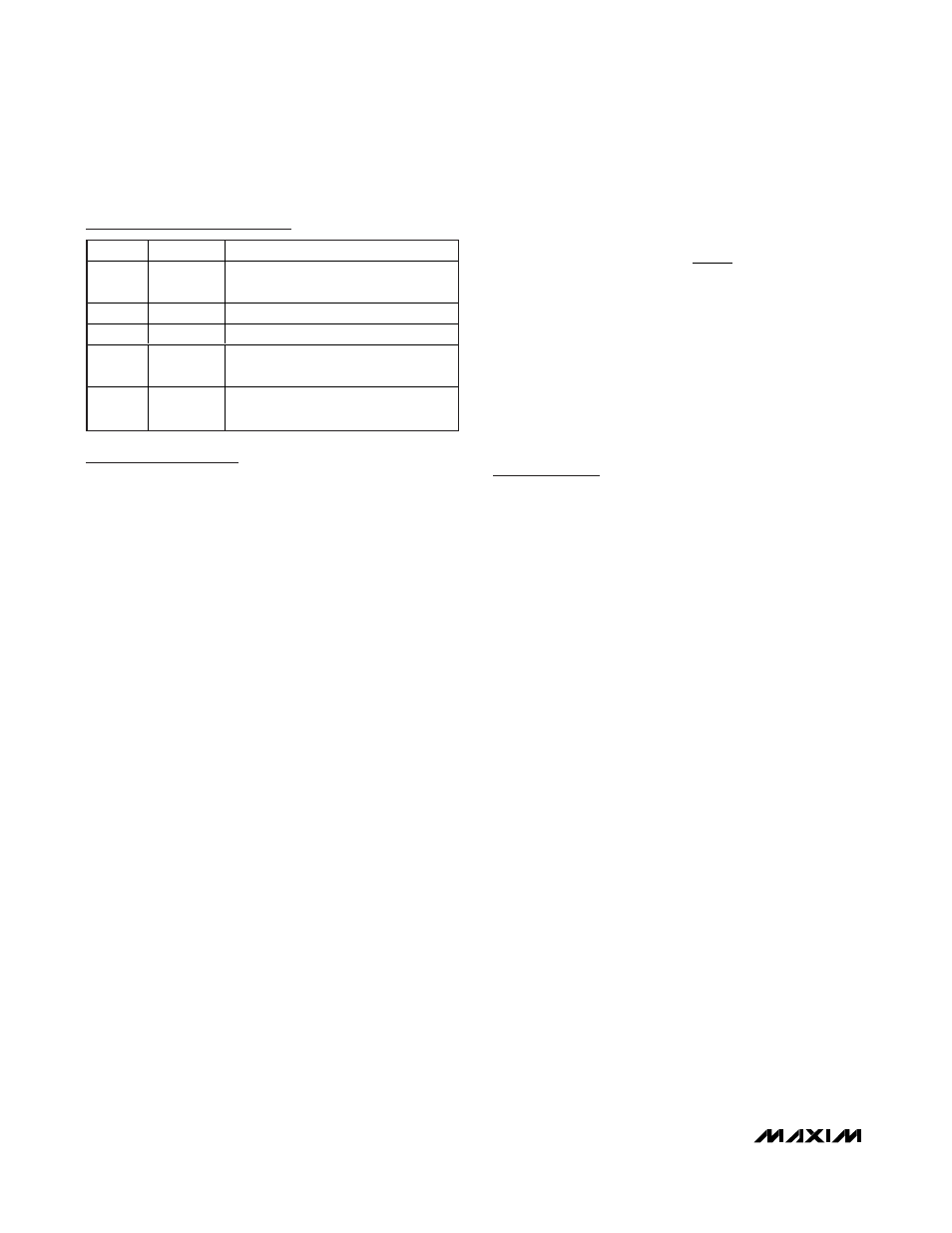
Pin Description
PIN
NAME
FUNCTION
1
V
CC
Power Supply. Bypass to GND with a
0.1µF capacitor.
2
GND
Ground
3
OUT
Current Output
4
RSN
Load-Side Connection Through
External R
RSN
Resistor
5
RSP
Supply-Side Connection Through
External R
RSP
Resistor
