Rainbow Electronics MAX6649 User Manual
Page 7
MAX6646/MAX6647/MAX6649
+145°C Precision SMBus-Compatible Remote/
Local Sensors with Overtemperature Alarms
_______________________________________________________________________________________
7
To ensure valid extended data, read extended resolu-
tion temperature data using one of the following
approaches:
1) Put the MAX6646/MAX6647/MAX6649 into standby
mode by setting bit 6 of the configuration register to 1.
Initiate a one-shot conversion using command byte
0Fh. When this conversion is complete, read the con-
tents of the temperature data registers.
2) If the MAX6646/MAX6647/MAX6649 is in run mode,
read the status byte. If the BUSY bit indicates that a
conversion is in progress, wait until the conversion is
complete (BUSY bit set to zero) before reading the
temperature data. Following a conversion comple-
tion, immediately read the contents of the tempera-
ture data registers. If no conversion is in progress,
the data can be read within a few microseconds,
which is a sufficiently short period of time to ensure
that a new conversion cannot be completed until
after the data has been read.
SMBCLK
A = START CONDITION
B = MSB OF ADDRESS CLOCKED INTO SLAVE
C = LSB OF ADDRESS CLOCKED INTO SLAVE
D = R/W BIT CLOCKED INTO SLAVE
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
SMBDATA
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STA
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
SU:DAT
t
SU:STO
t
BUF
L
M
K
E = SLAVE PULLS SMBDATA LINE LOW
F = ACKNOWLEDGE BIT CLOCKED INTO MASTER
G = MSB OF DATA CLOCKED INTO SLAVE
H = LSB OF DATA CLOCKED INTO SLAVE
I = MASTER PULLS DATA LINE LOW
J = ACKNOWLEDGE CLOCKED INTO SLAVE
K = ACKNOWLEDGE CLOCK PULSE
L = STOP CONDITION
M = NEW START CONDITION
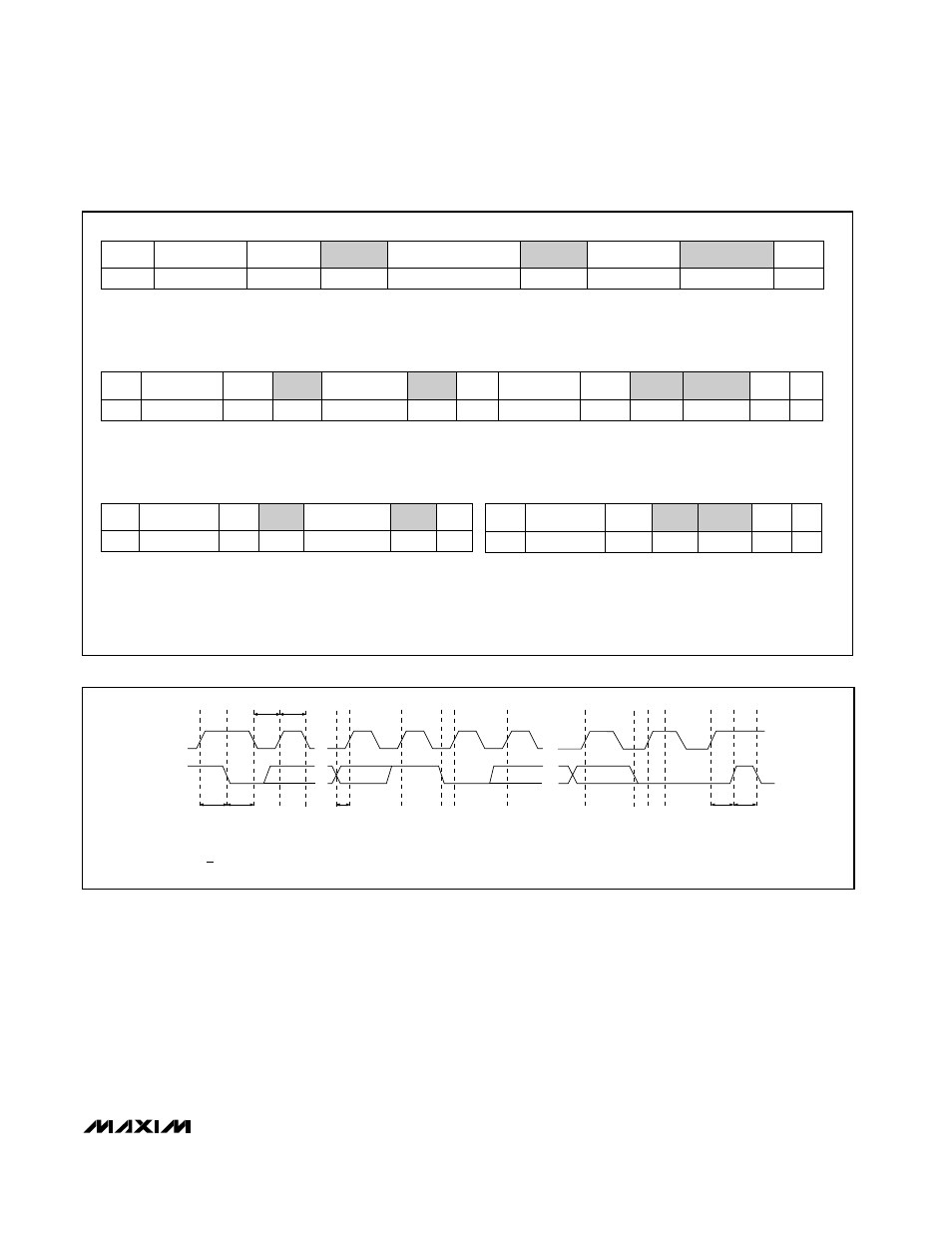
Figure 2. SMBus Write Timing Diagram
Write Byte Format
Read Byte Format
Send Byte Format
Receive Byte Format
Slave Address: equiva-
lent to chip-select line of
a 3-wire interface
Command Byte: selects which
register you are writing to
Data Byte: data goes into the register
set by the command byte (to set
thresholds, configuration masks, and
sampling rate)
Slave Address: equiva-
lent to chip-select line
Command Byte: selects
which register you are
reading from
Slave Address: repeated
due to change in data-
flow direction
Data Byte: reads from
the register set by the
command byte
Command Byte: sends com-
mand with no data, usually
used for one-shot command
Data Byte: reads data from
the register commanded
by the last Read Byte or
Write Byte transmission;
also used for SMBus Alert
Response return address
S = Start condition
Shaded = Slave transmission
P = Stop condition
/// = Not acknowledged
Figure 1. SMBus Protocols
S
ADDRESS
WR
ACK
COMMAND
7 bits
8 bits
ACK
DATA
8 bits
ACK
P
1
S
ADDRESS
WR
ACK
COMMAND
ACK
S
ADDRESS
RD
ACK
DATA
///
P
8 bits
7 bits
8 bits
7 bits
S
ADDRESS
WR
ACK
COMMAND
ACK
P
7 bits
8 bits
S
ADDRESS
RD
ACK
DATA
///
P
8 bits
7 bits
