3zener barriers - operating instructions, Multi-channel barriers, Hazardous area safe area – VEGA Z728 Zener barriers User Manual
Page 3: 2 multi-channel barriers, 3 grounding of zener barriers
3
Zener barriers - operating instructions
Multi-channel barriers
Subject to reasonable modifications due to technical advances.
Copyright Pepperl+Fuchs, Printed in Germany
Pepperl+Fuchs Group • Tel.: Germany +49 621 776-0 • USA +1 330 4253555 • Singapore +65 67799091 • Internet http://www.pepperl-fuchs.com
Da
te of issu
e
05/2
3
/03
1.2
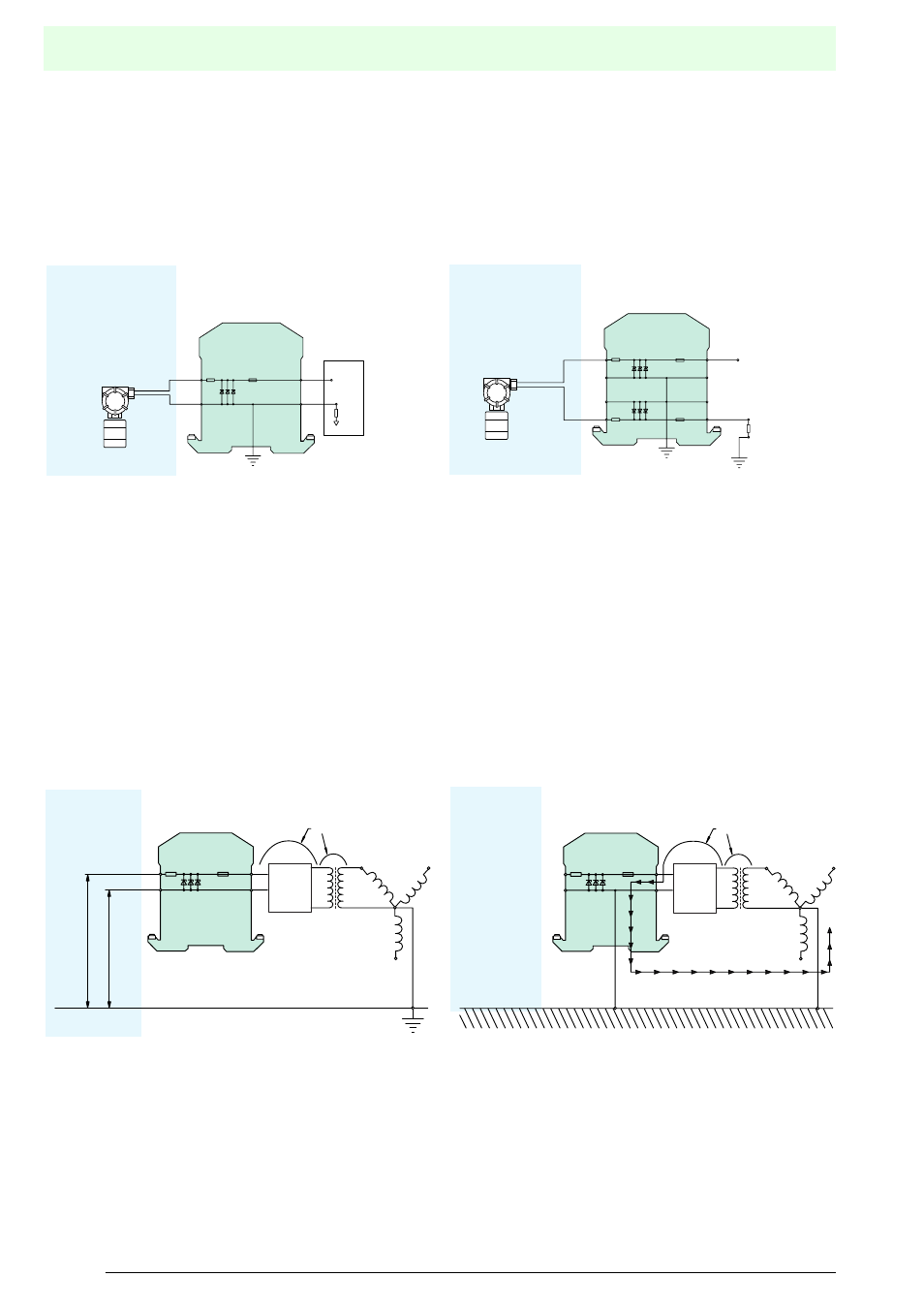
Multi-channel barriers
Analogue circuits are often connected to two-channel barriers
(see Figure 1.5). Since there is no grounding on this type of
circuit, the system is a quasi floating one. It is termed "quasi
floating", because it is "one Zener voltage" above the ground
potential. Although it does not actually float, the signal-to-noise
ratio is improved.
A further advantage of multi-channel Zener barriers is that a
higher packing density can be achieved.
.
Figure 1.4
Single-channel Zener barrier
Figure 1.5
Two-channel Zener barrier
1.3
Grounding of Zener barriers
Intrinsically safe circuits with Zener barriers without galvanic
isolation must be grounded. The cross-section of the ground
connection, using a copper conductor, must be at least 4 mm
2
(for further details see EN 60079-14, section 12.2.4). The
maintenance of these requirements prevents the occurrence of
a dangerous potential with respect to ground.
A fault of the type illustrated in figure 8.6 can cause a
dangerous spark if the Zener barrier is not grounded, but
grounding is provided via the field device in the intrinsically
safe circuit (Figure 1.5). If a potential occurs in the fault case,
which is higher than permitted (see Figure 1.6) the Zener
diodes become conducting and the current is conducted away
via the ground. The fuse "blows".
.
Figure 1.6
Non-grounded Zener barrier
Figure 1.7
Grounded Zener barriers
The system must have its own independent ground
conductor, through which no supply system current
flows.
Power supply can
not be grounded.
Hazardous area
4 mA ... 20mA
transmitter
Safe area
24 V
R
M
(+)
Hazardous area
4 mA ... 20mA
transmitter
Safe area
24 V
R
M
(+)
Fault
Transformer
Hazardous potential
Hazardous potential
Power supply
AC/DC
supply
voltage
Hazardous
area
Safe area
Fault
Transformer
Power supply
Hazardous
area
Safe area
Fault current
Intrinsically
safe ground
