Introduction, Target inflation pressure – GE Healthcare GE DINAMAP SuperSTAT Algorithm User Manual
Page 3
3
Introduction
The GE DINAMAP
®
SuperSTAT
™
Non-Invasive Blood Pressure
(NIBP) algorithm in the CARESCAPE
™
Patient Data Module,
Dash
®
and CARESCAPE V100 monitors incorporates
patented curve fitting [1] and cuff pressure managment [2,3]
technologies which enable the use of lower target inflation
pressures. Setting a lower target inflation pressure improves
patient comfort and safety, can reduce determination times
and improves overall NIBP performance.
An additional feature of the CARESCAPE Patient Data Module
with the GE DINAMAP SuperSTAT NIBP algorithm is the ability
to work at lower signal levels while still maintaining accuracy.
This is accomplished through the use of various measures of
signal quality, which are used to reduce the impact of noise
[4,5,6].
Target inflation pressure
The factory default target inflation pressures currently
programmed into the Solar
®
8000m/i monitor with V5.0D
software are for use with the CARESCAPE Patient Data
Module containing the GE DINAMAP SuperSTAT algorithm:
Adult cuff pressure
135 mmHg
Pediatric cuff pressure
125 mmHg
Neonatal cuff pressure
100 mmHg
These factory default target pressures are also in
the CARESCAPE V100 and Dash monitors with the GE
DINAMAP SuperSTAT algorithm.
As described in this whitepaper, there are advantages to
lowering the target pressure from the current defaults.
One feature of the GE DINAMAP SuperSTAT algorithm
is the ability to obtain an NIBP determination when the
target pressure (P
t
) is equal to, or even slightly below, the
patient’s systolic pressure (P
SYS
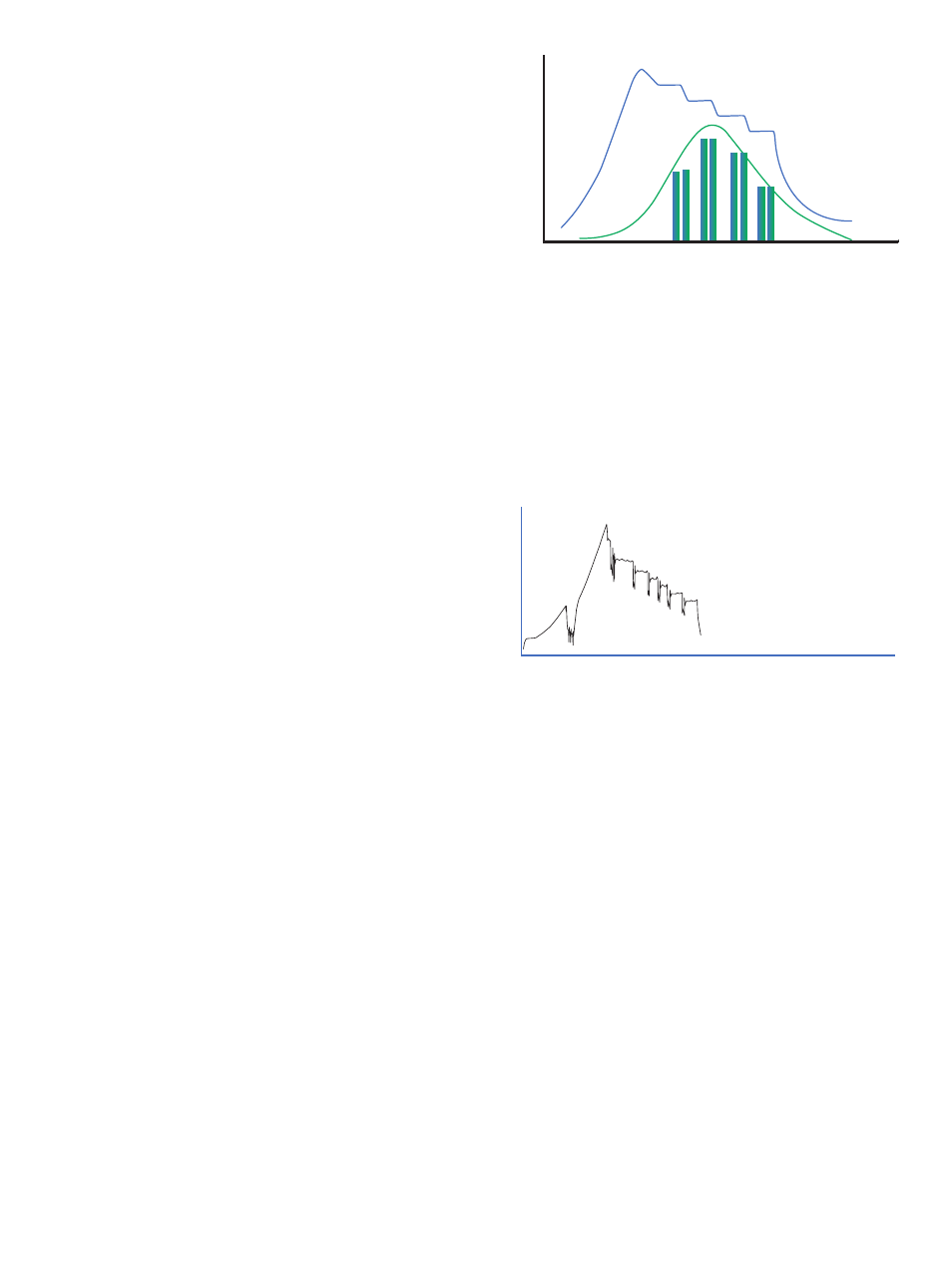
). As shown in Figure 1a, this
is accomplished through the use of the curve fit algorithm in
the GE DINAMAP SuperSTAT that enables the extrapolation of
systolic pressure of up to approximately 10 mmHg beyond
the target pressure.
Figure 1a – Extrapolation of Systolic Pressure with GE
DINAMAP SuperSTAT Algorithm
Figure 1b shows a recording of an NIBP determination
made with a computerized data collection system. The
target pressure was set to 135 mmHg and the GE DINAMAP
SuperSTAT algorithm correctly obtained the patient’s blood
pressure (145/89).
Figure 1b – Extrapolation of Systolic Pressure (BP = 145/89)
In cases where the target pressure is more than 10 mmHg
below the patient’s systolic pressure, the ability of the GE
DINAMAP SuperSTAT algorithm to manage cuff pressure
allows it to search at higher cuff pressures to obtain the
patient’s blood pressure without significantly increasing
determination time.
Cuff Pressure
(mmHg)
Cuff
Oscillations
Time (seconds)
P
t
= 135 mmHg
0
60
20
40
180
120
60
Cuff Pr
essur
e (mmHg)
Time (seconds)
