9 stp (spanning tree protocol) – Planet Technology MGSW-2402 User Manual
Page 13
- 13 -
You can add, edit and remove port members of each trunk and then press "Apply" button after
you have finished configuring the trunks you need.
( Note: Make sure trunking ports are in the same VLAN group. )
3.9 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
Spanning tree is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing
undesirable loops in the network. For Layer 2 Ethernet network to function properly, only one
active path must exist between two stations.
The spanning-tree algorithm calculates the best loop-free path throughout a switched network.
STP forces redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If a network segment in the
spanning tree fails and a redundant path exists, the spanning-tree algorithm recalculates the
spanning tree topology and activates the standby path.
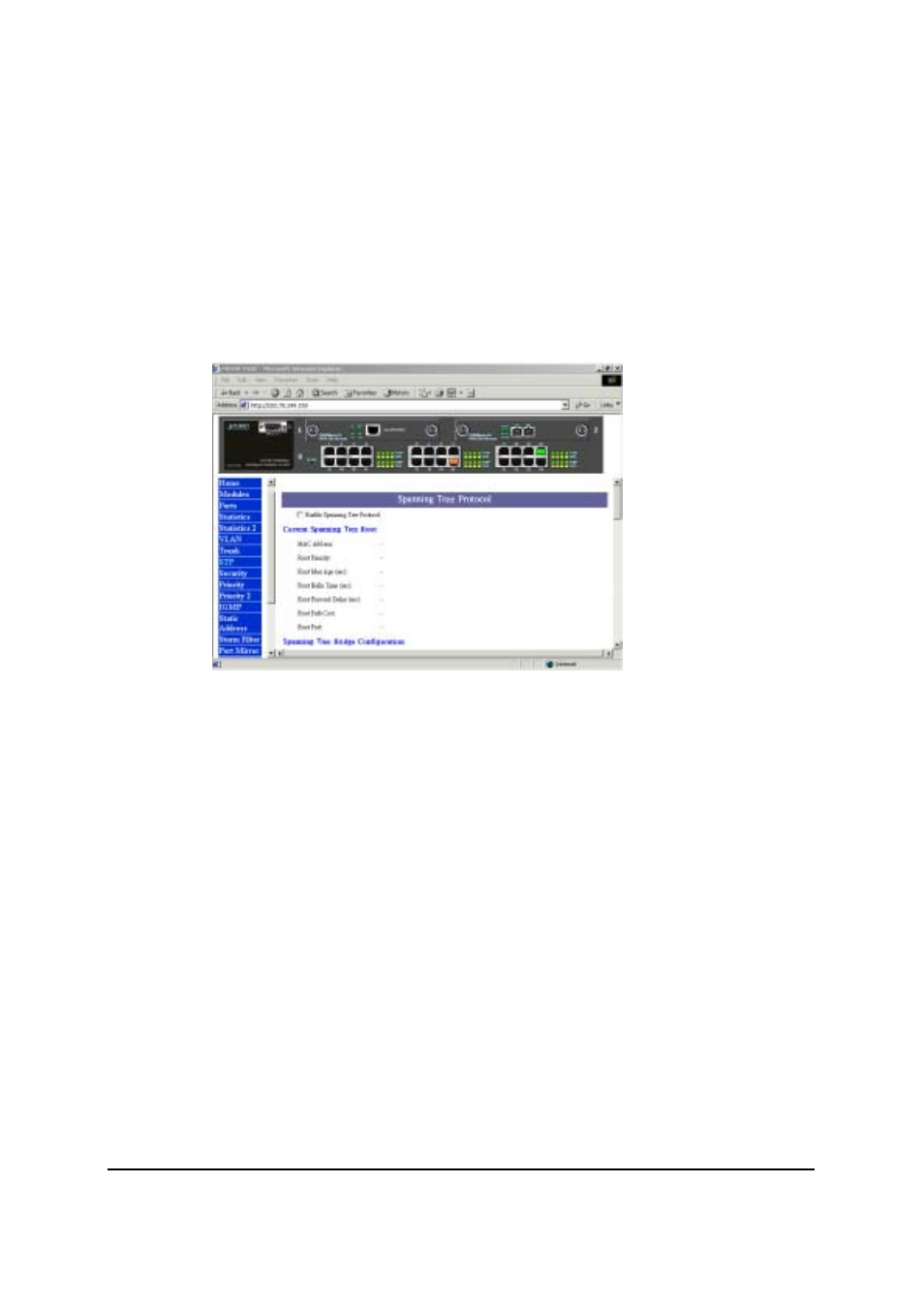
Figure 3-8 The STP page
If you want to participate in spanning tree, have the "Enable Spanning Tree Protocol"
checkbox selected.
The Current Spanning Tree Root describes the unique root switch information for the instance
of spanning tree.
MAC Address: the MAC address of the root switch
Root Max Age: the amount of time (in seconds) protocol information received on a port is
stored by the root switch
Root Hello Time: how often the root switch broadcasts Hello message to other switches
Root Forward Delay: the amount of time a port will remain in the listening and learning states
before entering the forwarding state
Root Path Cost: the path cost to the root switch from this switch
Root Port: the port providing the best path from the switch to the root switch
The Spanning Tree Bridge Configuration describes this switch information in the spanning
tree.
