Security—how to configure kerberos authentication – Symbol Technologies WS 2000 User Manual
Page 59
Security—How to Configure Kerberos Authentication
Security—How to Configure Kerberos Authentication
Kerberos provides strong authentication method for client/server applications by using
secret-key cryptography. Using this protocol, a client can prove its identity to a server (and
vice versa) across an insecure network connection. After a client and server use Kerberos to
prove their identity, they can encrypt all communications to assure privacy and data
integrity.
1. Select
the
Kerberos radio button to enable Kerberos authentication.
2. Click
the
Kerberos Configuration button to display a sub-screen for authentication
settings.
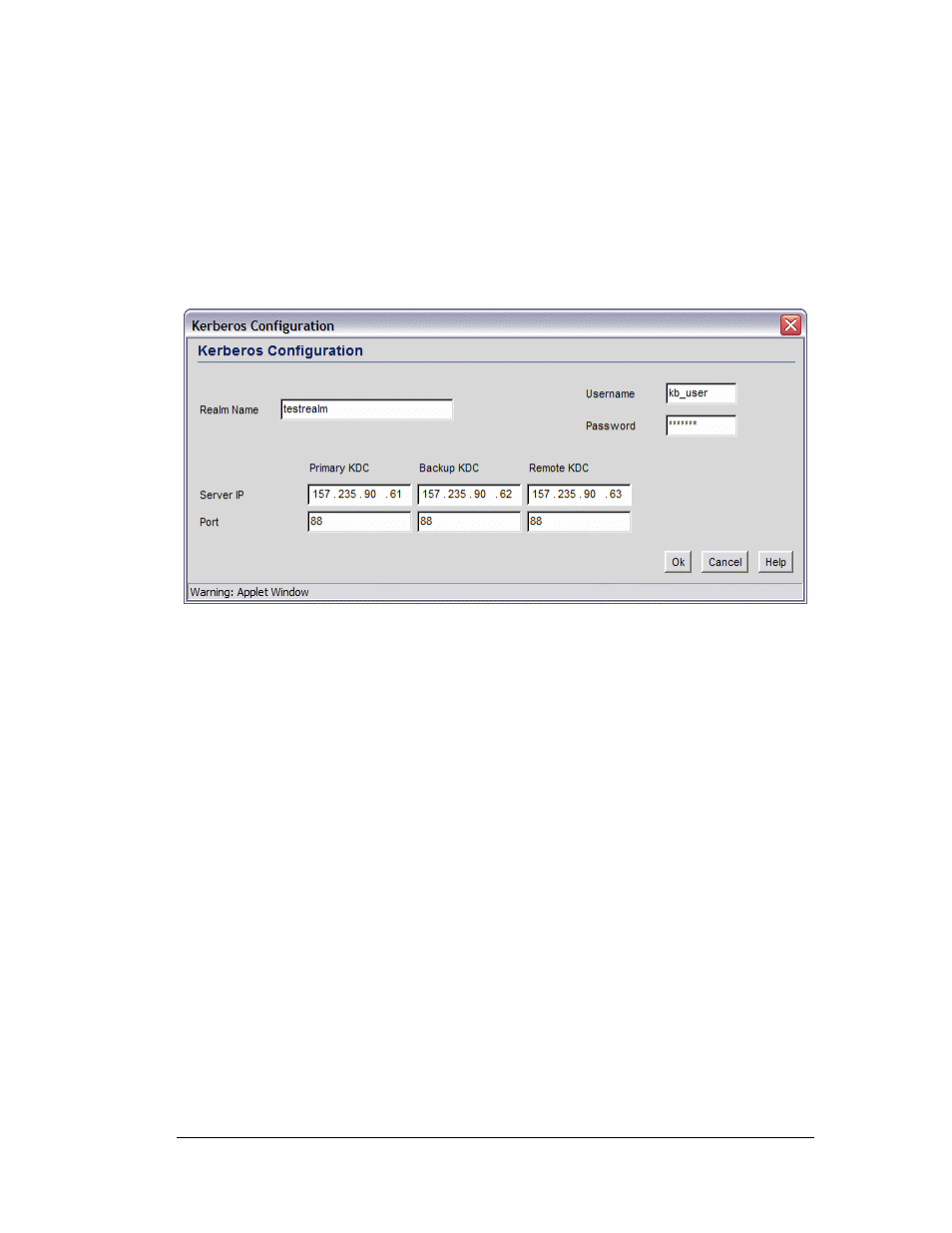
3. A realm name functions similarly to a DNS domain name. In theory, the realm name is
arbitrary; however, in practice a Kerberos realm is typically named using an uppercase
version of the DNS domain name that is associated with hosts in the realm. Specify a
realm name that is case-sensitive, for example, MYCOMPANY.COM.
4. Specify
a
Username for the Kerberos configuration.
5. Specify
a
Password for the Kerberos configuration.
The KDC (Key Distribution Center) implements an Authentication Service and a ticket
granting service, whereby an authorized user is granted a ticket that is encrypted with
the user’s password. The KDC has a copy of every user password.
6. Specify a server IP address and a port to be used as the Primary KDC.
7. Optionally, specify a Backup KDC server by providing the IP address and port.
8. Optionally, specify a Remote KDC server by providing the IP address and port.
9. Click
OK when done.
Copyright © 2004 Symbol Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved
59
WS 2000 Wireless Switch: 1.0 Date of last Revision: March 2004
