Structure of the multiplexer protocol, Introduction of the multiplexer protocol, Data link layer – Siemens Mux_guide_v06 User Manual
Page 17: Figure 3: data link layer, 4 structure of the multiplexer protocol, 1 introduction of the multiplexer protocol, 2 data link layer, Multiplexer user's guide confidential / released
Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
m
o
b
i
l
e
Mux_guide_v06
Page 17 of 36
30.06.2004
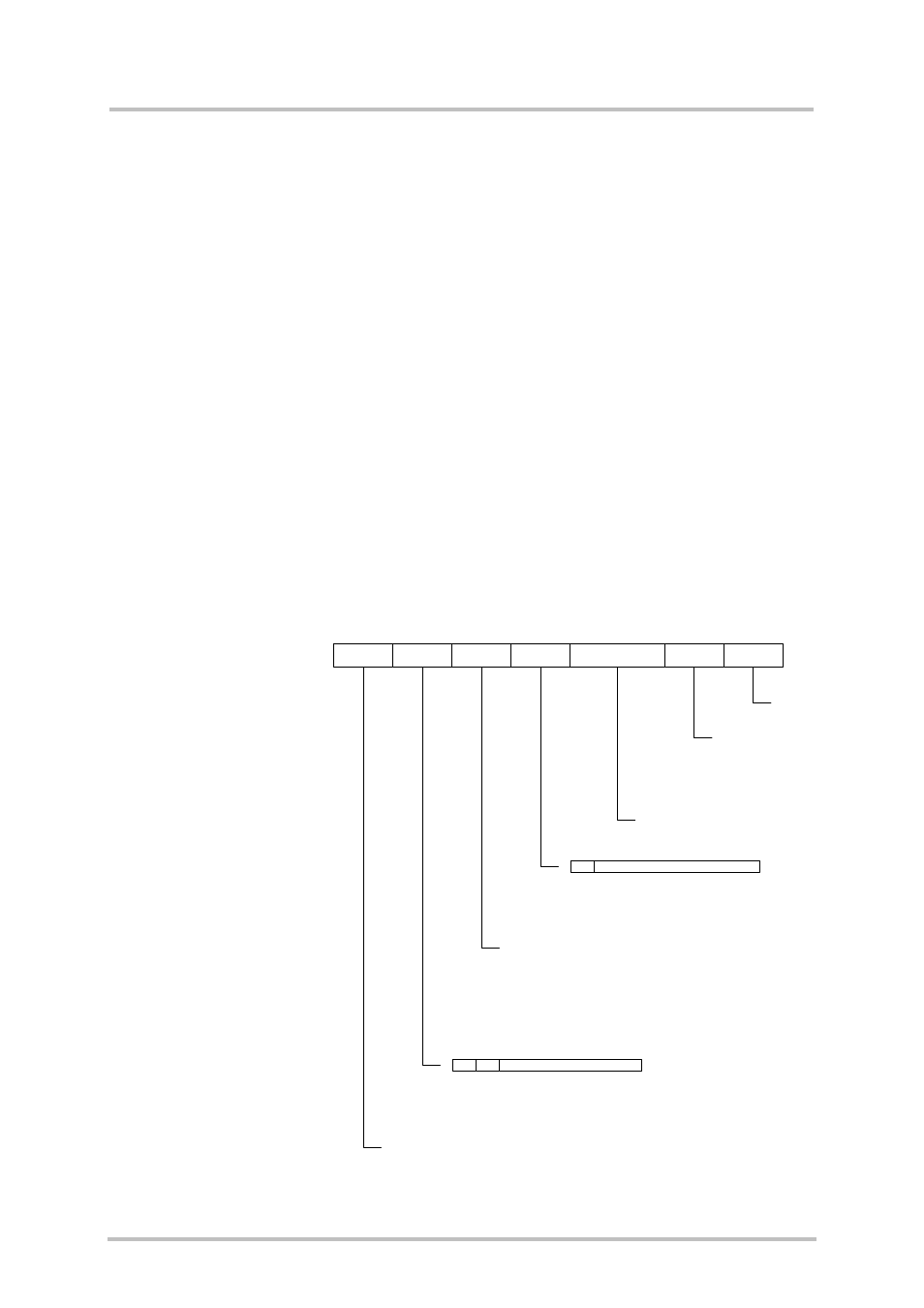
Address
1 Octet
Control
1 Octet
Flag
1 Octet
0xF9
DLCI
DLCI: Data Link Connection Identifier
C/R:
Command / Response
EA:
extension bit; EA = 1
Frame type:
SABM Set Asynchronous Balanced Mode
UA
Unnumbered Acknowledgement
DM
Disconnected Mode
DISC
Disconnect
UIH
Unnumbered Information with Header check
UI
Unnumbered Information
P/F-Bit Poll- /Final - Bit
Length
1 or 2 Octets
Information
n Octets
FCS
1 Octet
Flag
1 Octet
0xF9
Checksum for address,
control and length
fields, also for the
information field in the
case of UI frames FCS.
Length
EA
Length: Length Information
EA:
extension bit;
EA = 1 -> 1 octet length information
EA = 0 -> >2 octets length information
EA
C/R
4 Structure of the multiplexer protocol
4.1 Introduction of the multiplexer protocol
The supported multiplexer protocol conforms to the GSM 07.10 Multiplexer Protocol. The
non-error recovery mode was implemented with the basic option.
The frames have a start and a stop byte. A checksum is calculated to protect the transferred
data. Frame repetition is not enabled.
Data and fax calls are transferred in the logical channel DLCI = 1 (DLCI: Data Link
Connection Identifier). The remaining DLCIs are in AT command mode; two GPRS
connections can be established simultaneously on every channel.
The multiplexer protocol must be started and the logical channels opened in compliance with
specified procedures.
This chapter also discusses the following issues:
• Opening logical channels without parameter negotiation
• Opening logical channels with parameter negotiation
• Closing of logical channels
4.2 Data link layer
The following sections
show the detailed structure
of
a data link frame.
Figure 3: Data link layer
