IBM X3620 M3 User Manual
Page 5
A cost-optimized storage-rich alternative to traditional enterprise 2U dual-socket servers
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
5
concurrently.
Intelligent Power Capability powers individual processor elements on and off as needed, to
reduce power draw.
Execute Disable Bit functionality can help prevent certain classes of malicious buffer overflow
attacks when combined with a supporting operating system.
Intel’s
Virtualization Technology (VT) integrates hardware-level virtualization hooks that allow
operating system vendors to better utilize the hardware for virtualization workloads.
DDR3 Memory with Chipkill ECC Protection
The x3620 M3 ships with registered double data rate III (DDR3) memory and provides Active
Memory features, including advanced
Chipkill memory protection (using x4 DIMMs), for up to
16X better error correction than standard ECC memory. In addition to offering better performance
than DDR2 or fully-buffered memory, DDR3 memory also uses less energy. DDR2 memory
already offered up to 37% lower energy use than fully buffered memory. Now, a generation later,
DDR3 memory is even more efficient, using up to
15% less energy than DDR2 memory.
The x3620 M3 currently supports up to
96GB of 1.5V RDIMM (registered DIMM) memory in 12
DIMM slots. The x3620 M3 also supports either standard
1.5V DIMMs, or 1.35V DIMMs that
consume
20% less energy. Redesign in the architecture of the Xeon 5500 and 5600 Series
processors bring radical changes in the way memory works in these servers. For example, the
Xeon 5500 and 5600 Series processors
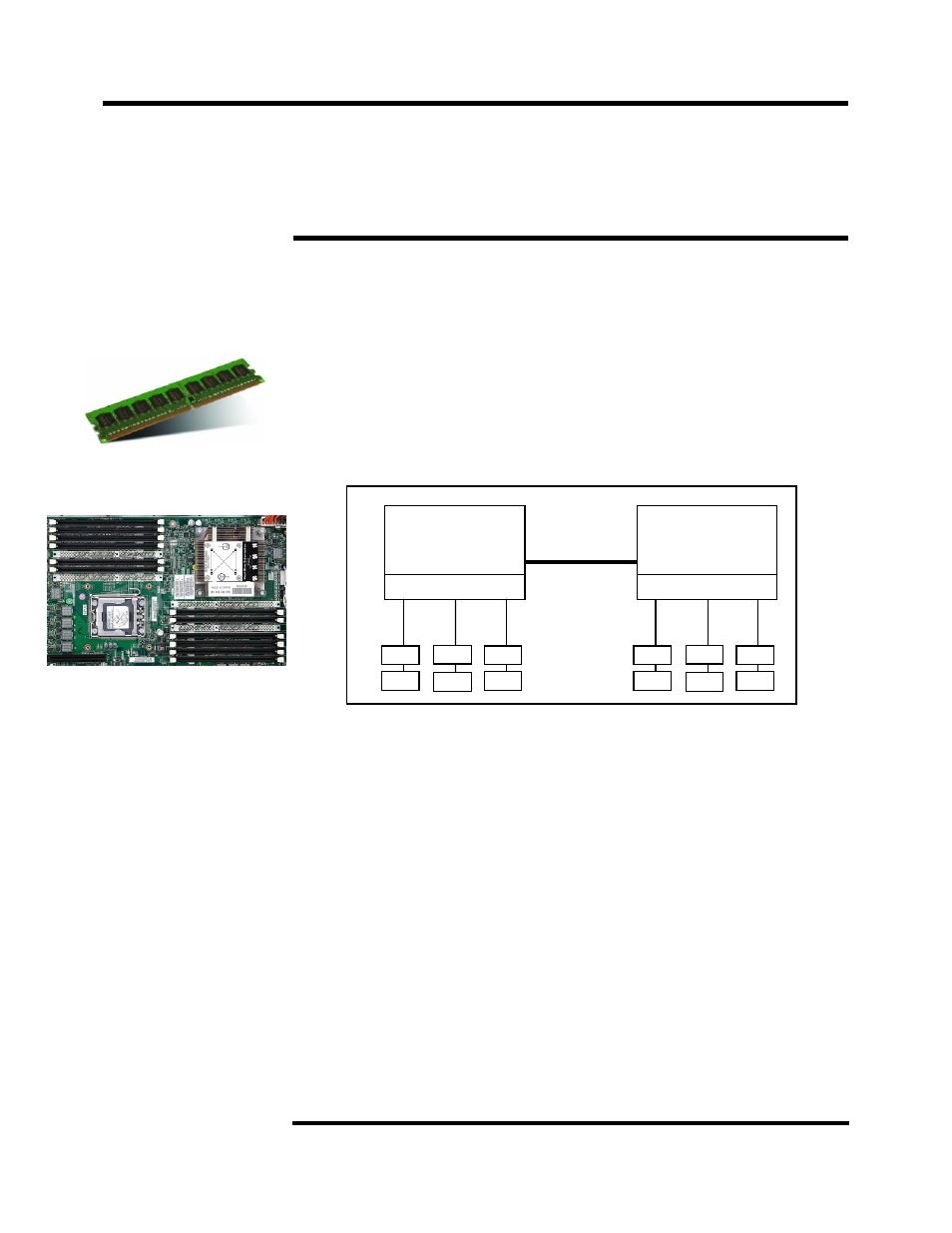
integrate the memory controller inside the
processor, resulting in two memory controllers in a 2-socket system. Each memory controller
has three memory channels. Depending on the type of memory, population of memory, and
processor model, the memory may be clocked at
1333MHz, 1066MHz or 800MHz.
Notes: Adding a second processor not only doubles the amount of memory available for use, but
also doubles the number of memory controllers, thus doubling the system memory bandwidth. If
you add a second processor, but no additional memory for the second processor, the second
processor would have to access the memory from the first processor “remotely,” resulting in
longer latencies and lower performance. The latency to access remote memory is almost 75%
higher than local memory access. So, the goal should be to always populate both processors with
memory.
The
L5640 and X56xx processor models support up to 1333MHz memory clock speed. With new
single-rank and dual-rank RDIMMs,
L5640 and Xi56xx processors support 2 DIMMs per channel
(2DPC) at 1333MHz using 1.5V DIMMs.
The
E562x-and-up and L56xx models support a
maximum of
1066MHz clock speed (and thus memory access rate), and the E550x models
support
800MHz clock speed.
Running memory at 1333MHz (where supported) versus 1066MHz offers up to
9% better
performance, while memory running at 1066MHz produces up to
28% better performance than
memory running at 800MHz. Xeon 5500/5600 Series processors access memory with almost
50% lower latency than the earlier 5400 Series processors. That can result in faster processing
of latency-sensitive workloads.
Regardless of memory speed, the Xeon 5500/5600 platform represents a significant improvement
in memory bandwidth over the previous Xeon 5400 platform. At 1333MHz, the improvement is
almost
500% over the previous generation. This huge improvement is mainly due to the dual
integrated memory controllers and faster DDR3 1333MHz memory. Throughput at 800MHz is
25
gigabytes per second (GBps); at 1066MHz it’s 32GBps; and at 1333MHz it’s 35GBps. This
improvement translates into improved application performance and scalability.
Memory interleaving refers to how physical memory is interleaved across the physical DIMMs. A
balanced system provides the best interleaving. A Xeon 5500/5600 Series processor-based
system is balanced when all memory channels on a socket have the same amount of memory.
Ch1
Ch0
Xeon 5600 / 5500
Processor 1
Memory Controller
2
3
Ch2
7
8
5
6
Xeon 5600 / 5500
Processor 2
Ch0
10
11
Ch2
15
16
Ch1
13
14
QPI
Memory Controller
