IBM 560 User Manual
Page 41
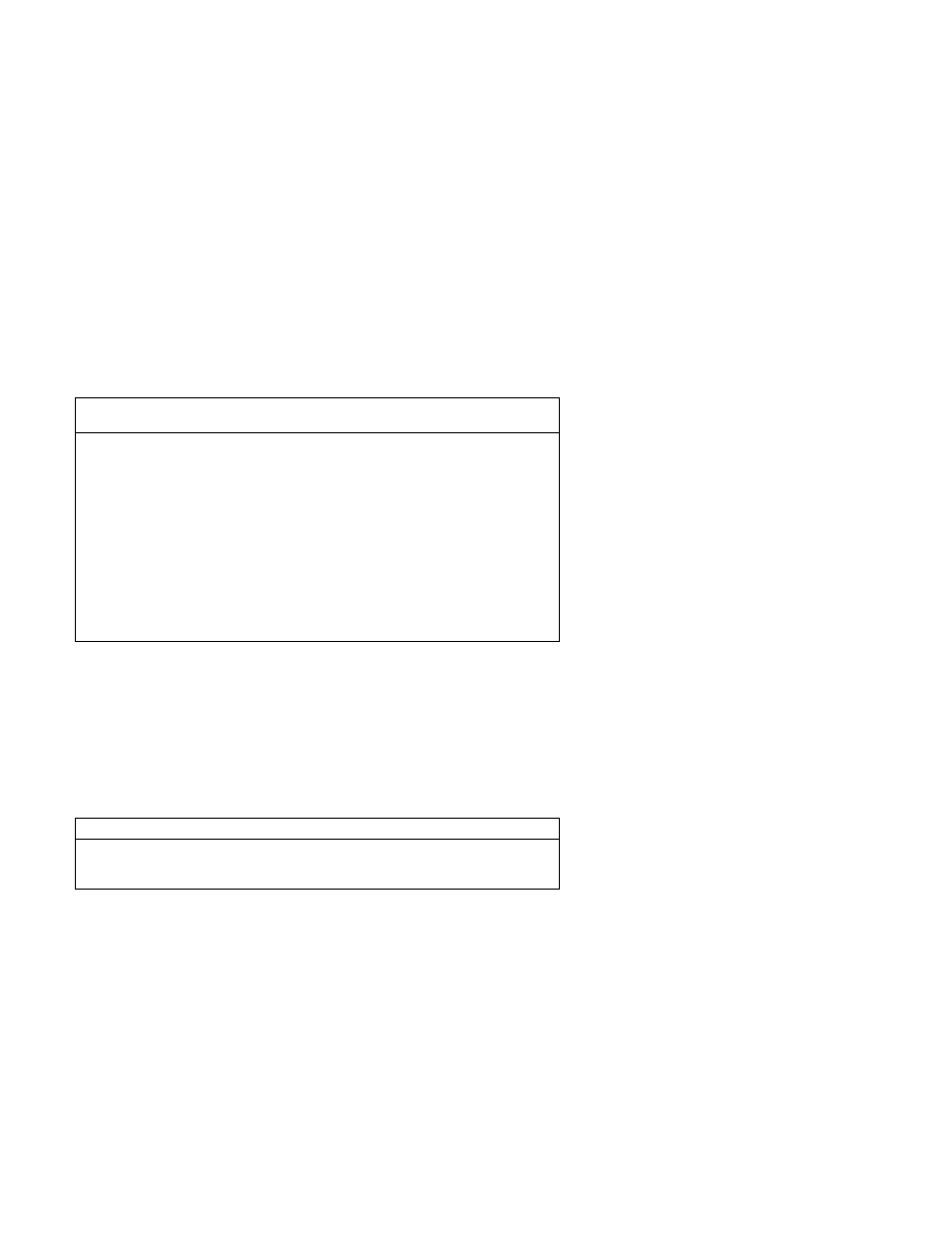
Real-Time Clock Bytes (Hex 000–00D): Bit definitions and
addresses for the real-time clock bytes are shown in Figure 2-15.
Figure
2-15. Real-Time Clock Bytes (Hex 000–00D)
Address
(Hex)
Function
Byte Number
000
Seconds
0
001
Second alarm
1
002
Minutes
2
003
Minute alarm
3
004
Hours
4
005
Hour alarm
5
006
Day of week
6
007
Date of month
7
008
Month
8
009
Year
9
00A
Status register A
10
00B
Status register B
11
00C
Status register C
12
00D
Status register D
13
Note: The Setup program initializes status registers A and B when
the time and date are set. Interrupt 1AH is the BIOS
interface to read and set the time and date; it initializes the
registers in the same way that the Setup program does.
Status Register A (Hex 00A)
Figure
2-16. Status Register A (Hex 00A)
Bit
Function
7
Update in progress
6–4
22-stage divider
3–0
Rate-selection bits
Bit 7
When set to 1, this bit indicates that the time-update
cycle is in progress. When set to 0, it indicates that the
current date and time can be read.
Bits 6–4
These bits identify which time-base frequency is being
used. The system initializes these bits to binary 010,
which selects a 32.768-kHz time base. This is the only
value supported by the system for proper timekeeping.
Bits 3–0
These bits allow the selection of a divider output
frequency. The system initializes the rate-selection bits
to a binary 0110, which selects a 1.024-kHz
ThinkPad 560/560E System Board
2-19
