System grounding – Grizzly G5954 User Manual
Page 22
-20-
G5954 5HP Dust Collector
—If the CFM for your static pressure loss is
above the requirement of the woodworking
machine, then the line will most likely be
successful.
—If the CFM for your static pressure loss is
below the requirement of the machine, then
that line will not effectively collect dust. You
must modify some of the factors in that line
to reduce the static pressure loss. Some of
the ways to do this include installing larger
duct, reducing amount of flexible duct
used, increasing machine dust port size,
moving machine closer to dust collector
to eliminate duct length, and reducing 90˚
elbows or replacing them with 45˚ elbows.
Since plastic hose is abundant, relatively inexpen-
sive, easily assembled and air tight, it is a very
popular ducting material. We recommend using
flexible hose (flex-hose) to connect the wood-
working machine to the dust collector. However,
plastic flex-hose and plastic duct can create a
static electrical build up, which will build until it
discharges to a ground. If a grounding medium
is not available to prevent static electrical build
up, the electrical charge will arc to the nearest
grounded source. This electrical discharge may
cause an explosion and fire inside the system.
To protect against static electrical build up inside
a non-conducting duct, a bare copper wire should
be placed inside the duct along its length and
grounded to the dust collector. You must also
confirm that the dust collector is continuously
grounded through the electrical circuit.
If you connect the dust collector to more than one
machine by way of a non-conducting branching
duct system and blast gates, the system must
still be grounded via copper wiring as above, with
the wire attached to each grounded machine and
dust collector.
System Grounding
Be sure that you extend the bare copper wire
down all branches of the system. Do not forget
to connect the wires to each other with wire nuts
when two branches meet at a “Y” or “T” connec-
tion. If using plastic blast gates to direct air flow,
the grounding wire must be jumped (
Figure 25)
around the blast gate without interruption to the
grounding system.
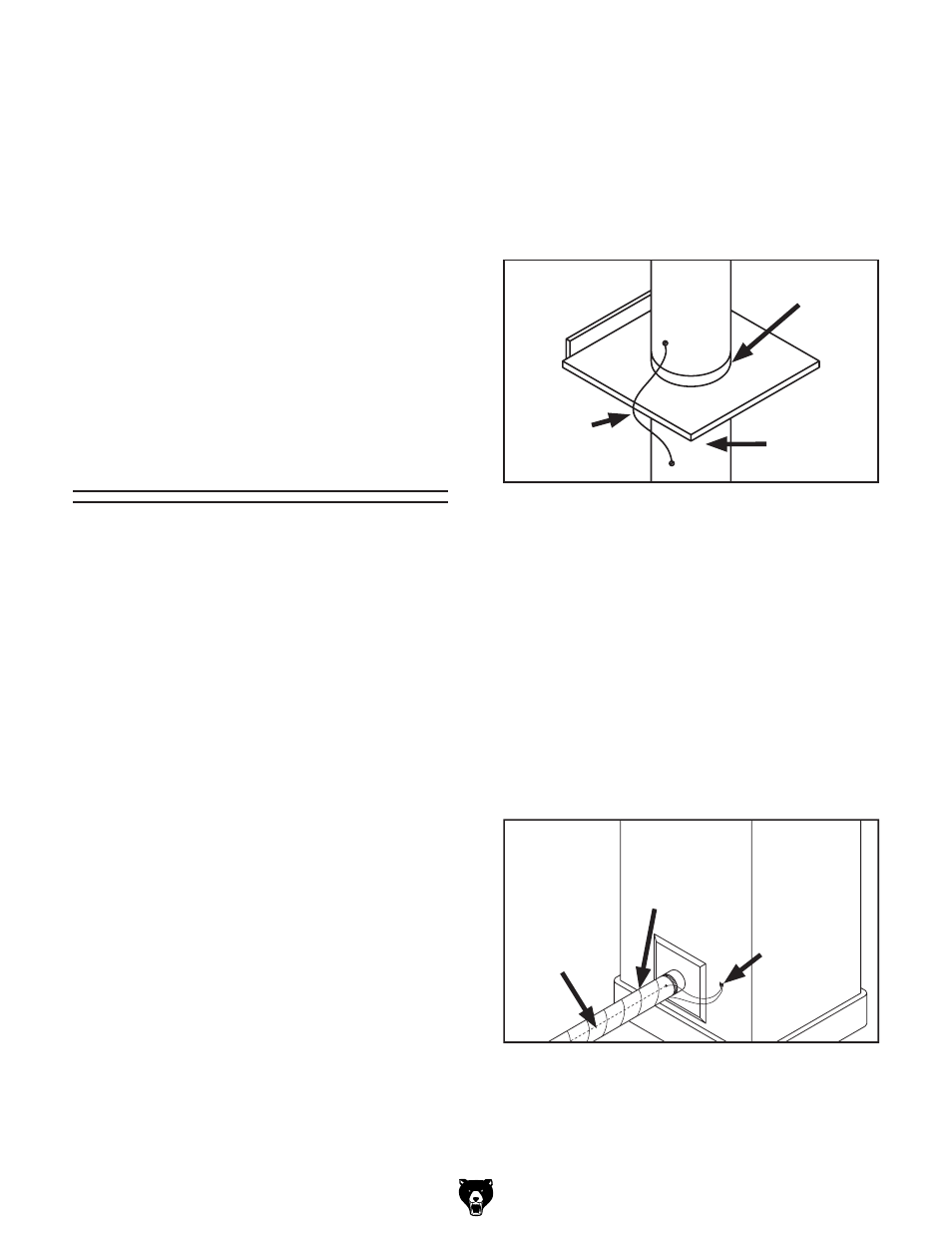
Figure 25. Ground jumper wire when using
plastic blast gates and metal duct.
Plastic
Blast
Gate
Metal Duct
Copper
Ground
Wire
Figure 26. Flex-hose grounded to machine.
Ground
Screw
Flex-Hose
Internal
Ground
Wire
External
Ground
Wire
We also recommend wrapping the outside of all
plastic ducts with bare copper wire to ground the
outside of the system against static electrical
build up. Wire connections at Y’s and T’s should
be made with wire nuts.
Attach the bare ground wire to each stationary
woodworking machine and attach to the dust
collector frame with a ground screw as shown in
Figure 26. Ensure that each machine is continu-
ously grounded to the grounding terminal in your
electric service panel.
