Retrotec Design and Evaluation for Peak Pressure and Agent Retention Time User Manual
Page 2
SP710
Page 2 of 4
rev-2010-07-14
discharged into the same test chamber at varying leakage and environmental conditions, to
accurately determine the relationship between peak pressure and other variables.
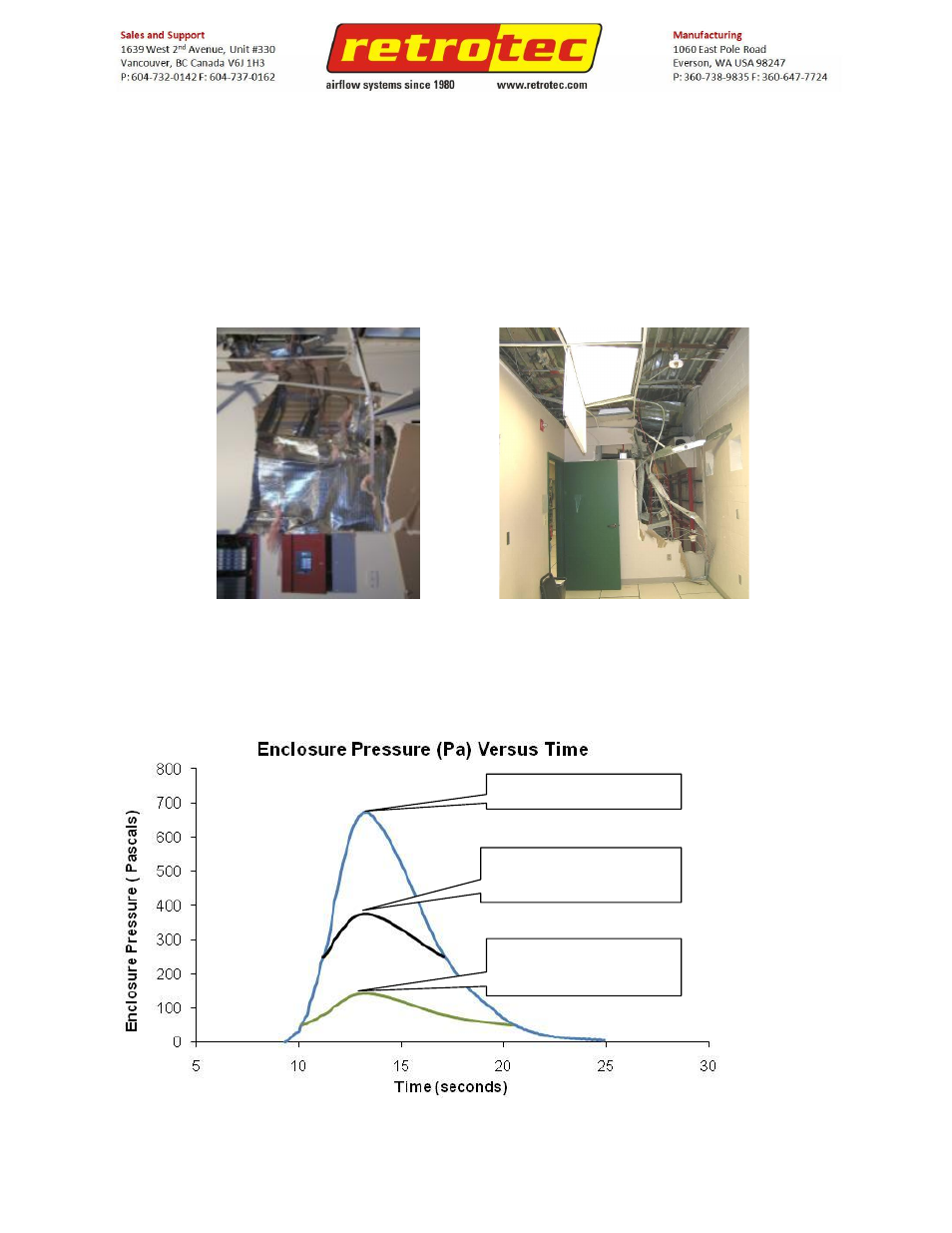
Not taking into account potential peak pressure in an enclosure can have expensive
consequences, which can be seen in the pictures below. NFPA 2001 requires a peak pressure
analysis (section 5.1.2.2(10) states that “an estimate of the maximum positive and the
maximum negative pressure, relative to ambient pressure, expected to be developed upon
discharge of agent” is required) but offers little help in determining peak pressure and relief
vent area.
Pressure Relief Vents (PRV) reduce peak pressure
In many cases, PRVs fail to open at a low enough pressure to prevent damage. If a vent starts to
open at 250 Pa, the peak pressure will rise to almost 400 Pa as shown below. Opening at 60 Pa
reduces this peak to 150 Pa while not opening at all yields 690 Pa.
No vent – 690 Pa peak
Vent opens @250 Pa –
385 Pa peak
Vent opens @60 Pa –
150 Pa peak
