Maximum pressure limitations, Instruction manual, Warning – Emerson Process Management 667 User Manual
Page 3
Instruction Manual
D100311X012
667 Size 80 and 100 Actuators
May 2011
3
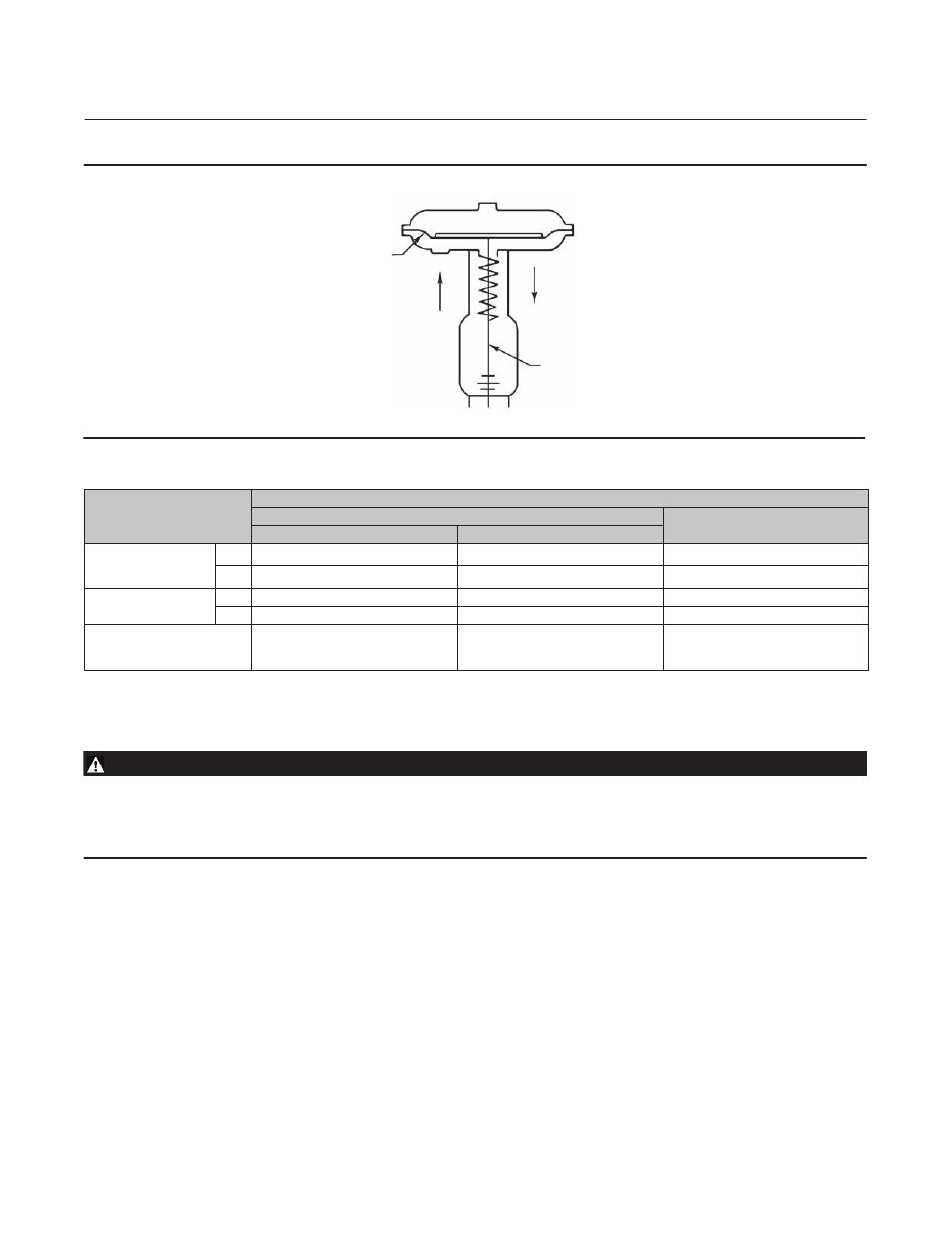
Figure 2. Schematic Representation of Fisher 667 Actuator
DIAPHRAGM
AIR
LIFTS
SPRING
PUSHES
DOWN
ACTUATOR
STEM
667 REVERSE‐ACTING DIAPHRAGM ACTUATOR
AF3833‐A
A6127
Table 2. Maximum Pressure Limitations
PRESSURE LIMITATIONS
ACTUATOR SIZE
80
100
Standard Cast Iron Construction
All Steel Construction
Maximum Casing
Pressure for Actuator
Sizing
bar
3.4
4.9
6.9
psig
50
70
100
Maximum Excess
Diaphragm Pressure
bar
1.4
1.4
1.7
psig
20
20
25
Maximum Diaphragm Casing
Pressure
Upper bench set plus Maximum
Excess Diaphragm Pressure or 4.1 bar
(60 psig), whichever is less.
Upper bench set plus Maximum
Excess Diaphragm Pressure or 5.5 bar
(80 psig), whichever is less.
Upper bench set plus Maximum
Excess Diaphragm Pressure or 7.9 bar
(115 psig), whichever is less.
Maximum Pressure Limitations
WARNING
To avoid personal injury or parts damage, do not exceed the Maximum Pressures listed in table 2. Exceeding any of the
maximum pressures can result in uncontrolled movement of parts, damage to actuator parts and the control valve, and
loss of control of the process. Use pressure‐limiting or pressure‐relieving devices to prevent casing pressure from
exceeding these limits.
The casing and diaphragm of 667 actuators are pressure operated. This air pressure provides force to compress the
spring and stroke the actuator. The following explanations describe the maximum pressure limits for 667 actuators.
Refer to the nameplate, warning tag, and table 2 for maximum values.
D Maximum Casing Pressure for Actuator Sizing: This is the maximum pressure that can be applied to provide full
travel of the actuator. If this stroking pressure is exceeded before the upper diaphragm plate contacts the travel
stop, damage to the stem or other parts might result. The Maximum Diaphragm Casing Pressure for a specific
actuator construction may be less than the Maximum Casing Pressure for Actuator Sizing. See table 2.
D Maximum Excess Diaphragm Pressure: This is the additional pressure that may be added when the actuator is at full
travel. If the Maximum Excess Diaphragm Pressure is exceeded once the actuator has reached full travel, damage to
the diaphragm or diaphragm casing might result.
