5 integration calculations – Casio fx-9750G Differential/Quadratic Differential, Integration, Value User Manual
Page 10
72
3-5 Integration Calculations
To perform integration calculations, first display the function analysis menu, and then
input the values shown in the formula below.
4
(
∫
dx
)
f(x)
,
a
,
b
,
n
)
∫
(
f (x), a, b, n)
⇒
∫
a
b
f (x)dx, N = 2
n
N
number of divisions
Integration calculations are performed by applying Simpson’s Rule for the
f (x)
func-
tion you input. This method requires that the number divisions be defined as
N =
2
n
,
where the value of
n
is an integer in the range of 1 through 9. If you do not specify a
value for
n
, the calculator automatically assigns a value in accordance with the inte-
gration being performed.
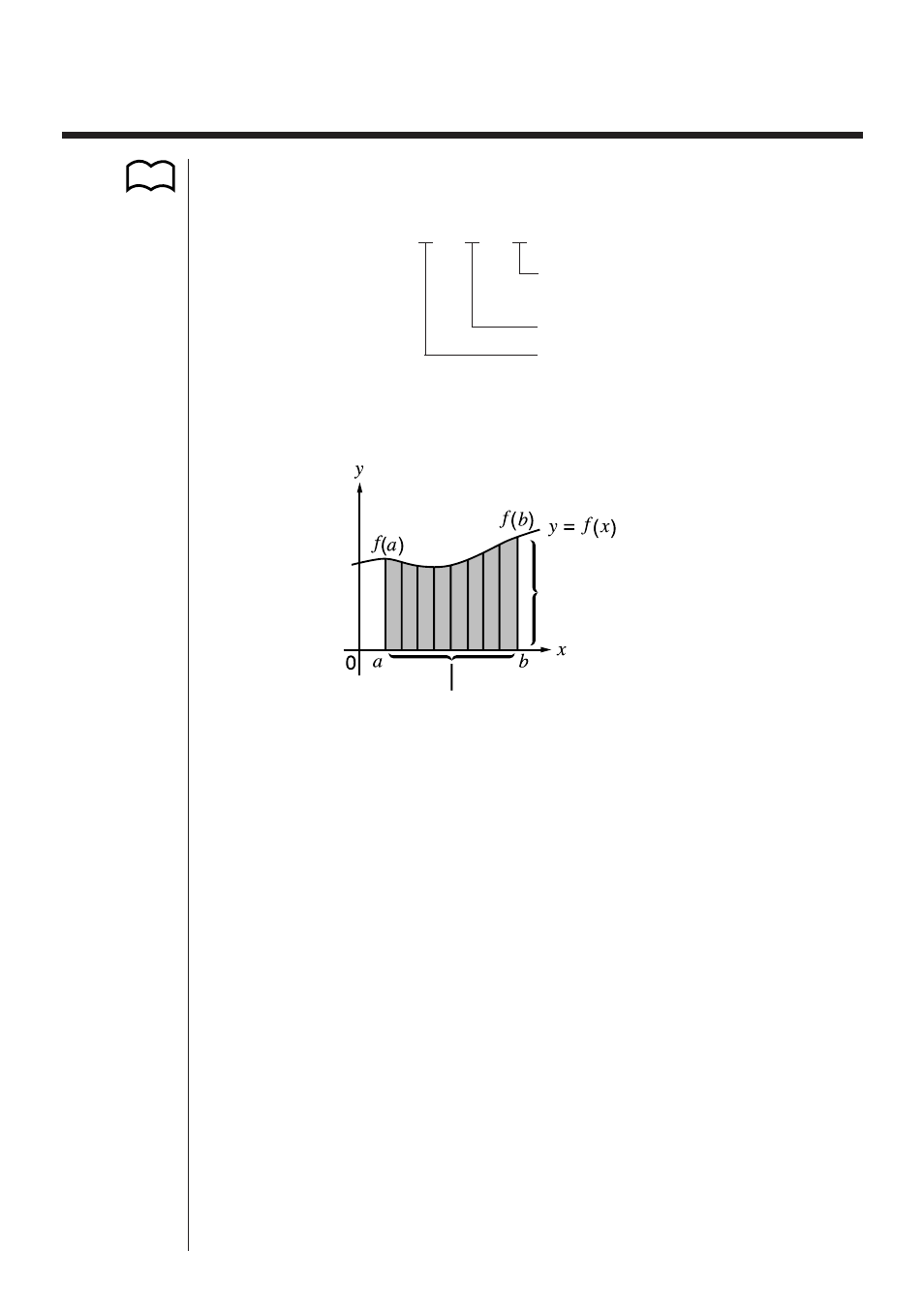
As shown in the illustration above, integration calculations are performed by calcu-
lating integral values from
a
through
b
for the function
y =
f (x)
where
a
< x < b
, and
f (x)
>
0
*. This in effect calculates the surface area of the shaded area in the illustra-
tion.
* If
f (x) <
0
where
a
< x < b
, the surface area calculation produces negative values
(surface area
×
– 1).
Number of Divisions (value for
n
in N = 2
n
,
n
is an integer from 1 through 9)
End Point
Start Point
Area of
∫
a
b
f (x)dx
is calculated
P.64
