Monitoring k2 lx0 raid trends – Grass Valley K2 Lx0 RAID User Manual
Page 10
10
Monitoring the K2 Lx0 RAID with NetCentral
September 7, 2007
Monitoring the K2 Lx0 RAID with NetCentral
Monitoring K2 Lx0 RAID Trends
Click the
Trends
button to see the Trends view. The Trends view pulls specific device
parameters and provides you with a daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly view of
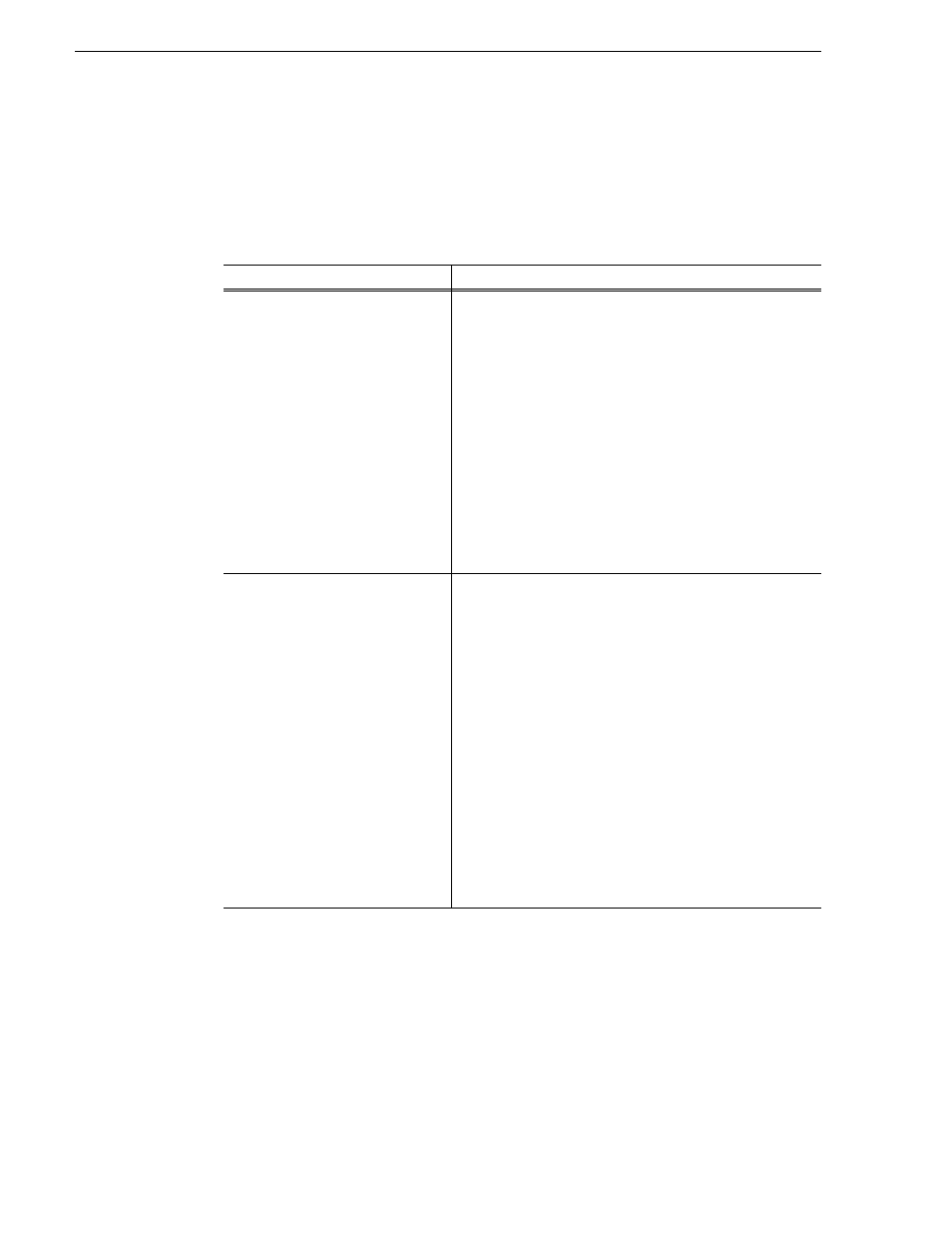
selected parameters. The following table lists the Trends view graphs for the K2 Lx0
RAID and provides explanations:
Name of Trend graph
Explanation of Trend graph
System\
Up Time
Up time essentially is an ever incrementing value that indicates
the system is up and running and is measured as an absolute
value in minutes; given that the polling rate is more than a
minute.
Though the value itself is of less significance, it is the ramp
graph obtained by plotting these values that proves significant
where a downward edge on the ramp indicates a device going
offline and a flat line at zero indicating the device downtime.
Multiple ramps indicate how often the device was taken down
for activities like maintenance or servicing, or simply how
many times it was restarted to handle a complete device failure.
If the ramps do not coincide when the device was taken down,
it could indicate conditions like automatic restarts, and the
device may need attention.
Storage\Disk Block Reassigns
Block Reassigns is the count of inaccessible disk blocks
reassigned by the controller to another accessible block on the
physical disk.
When the controller cannot access a particular disk block with
a specific number of retry attempts, it reassigns the
“inaccessible” block to another block on the physical disk.
When the controller performs such a disk block reassignment,
all disk access requests made for that block are henceforth
redirected to the reassigned block.
The controller can only allow a finite number of block
reassignments on a physical disk before it disables the physical
disk. However the number itself depends on the particular kind
of drive, controller hardware or firmware.
Typically this should be a zero value. Disks with an increasing
number of block reassignments will tend to project disk IO
latencies and is typically indicative of disk replacement.
