Airlink RTW026 User Manual
Page 59
Chapter 4: Web Configuration
49
Gateway:
Display the IP address of gateway.
Metric:
The number of hops (routers) to pass through to reach the remote LAN segment. The
shortest path will be used. The default value is 0.
Interface:
Displays the interface that your router is using for network connection.
Refresh
Click this button to display the table again.
Close
Click this button to return to main web page.
Configuring Other Routers on Your LAN
It is essential that all IP packets for devices that are not on the local LAN can be passed to the Router, so that they
can be forwarded to the external LAN, WAN, or Internet. To achieve this, the local LAN must be configured to use
the Router as the default route or default gateway.
Local Router
The local router is the Router installed on the same LAN segment as the Router. This router requires that the default
route is the Router itself. Typically, routers have a special entry for the default route. It should be configured as
follows.
Destination-->
Normally 0.0.0.0 but check your router documentation.
Subnet Mask-->
Normally 0.0.0.0 but check your router documentation.
Gateway-->
The IP Address of the Router.
Other Routers on the Local LAN
Other routers on the local LAN must use the Router’s Local Router as the Default Route. The entries will be the
same as the Router’s local router, with the exception of the Gateway IP Address.
For a router with a direct connection to the Router’s local Router, the Gateway IP Address is the address of the
Router’s local router.
For routers which must forward packets to another router before reaching the Router’s local router, the Gateway IP
Address is the address of the intermediate router.
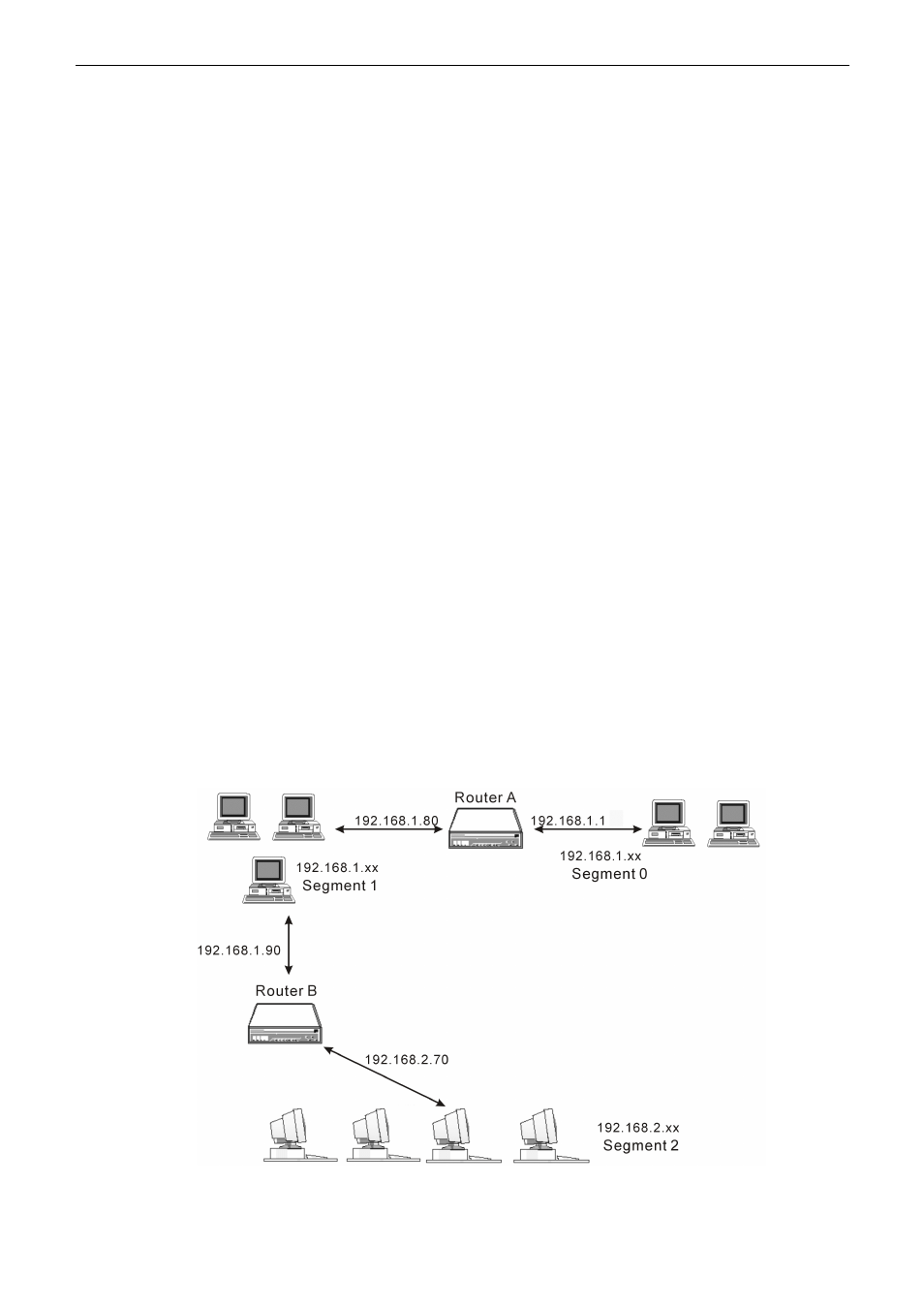
Example – Static Route
Here provides you an example of Static Route.
For the Router’s Routing Table
