Functional block diagram, Supported audio and video formats, Input and output video – Sierra Video ADC-142 User Manual
Page 8: Analog audio, Discrete aes audio input, Adc-142 block diagram
Page 8 of 29
ADC-142 Owner’s Manual •••• (V 2.1)
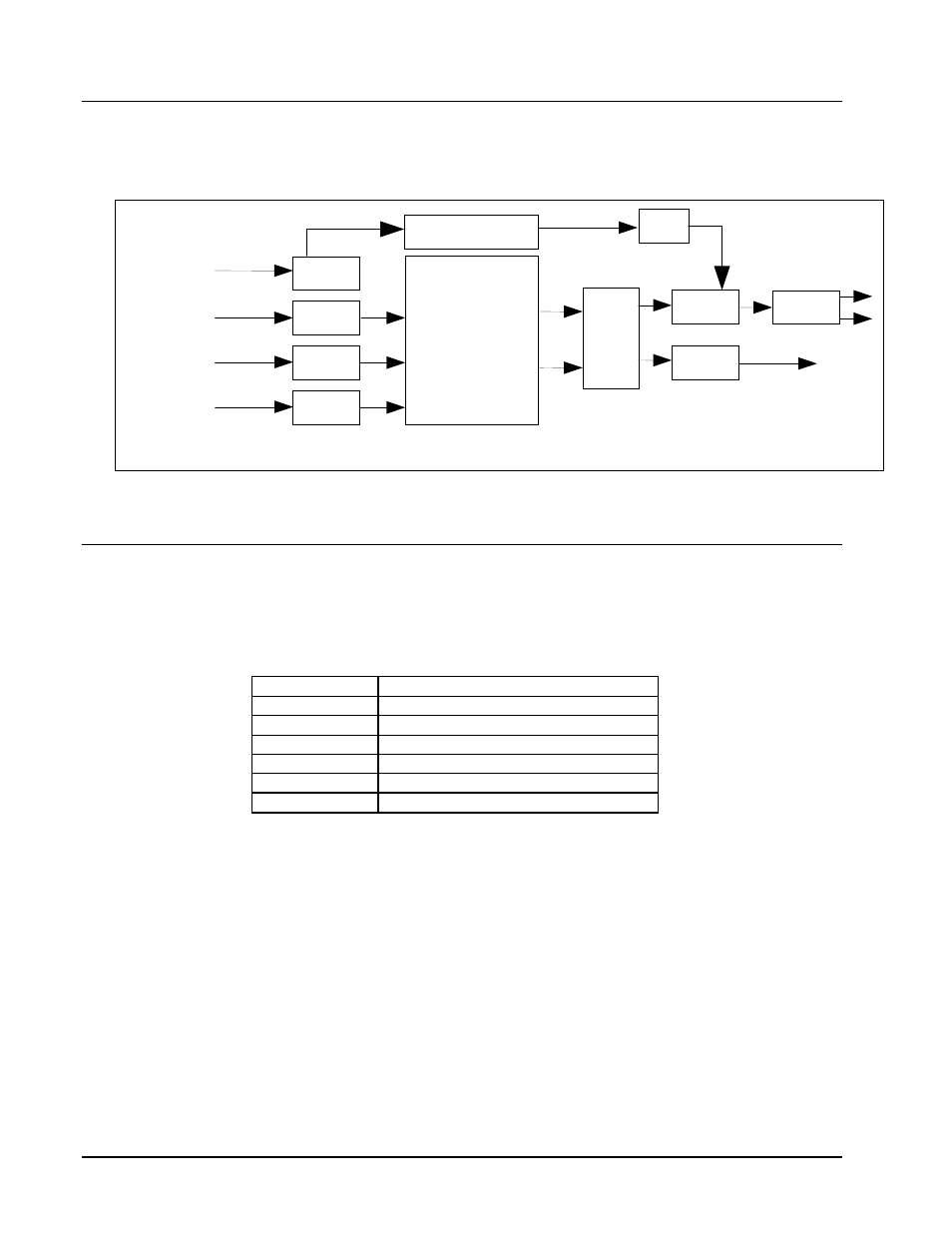
Functional Block Diagram
The ADC-142 has a very flexible signal flow path and feature set that combines several products into
one compact package. This section diagrams the basic signal flow of your ADC-142 product.
Figure 1. Simplified Block Diagram of ADC-142 Functions
Supported Audio and Video Formats
Input and Output Video
The ADC-142 supports the complete range of modern SMPTE standard SD and HD video formats.
Raster structure Frame Rate
1080psF
23.98, 24
1080p
23.98, 24
1080i
1
25, 29.97, 30
720p
25, 29.97, 30, 50, 59.94, 60
486i
1
29.97
575i
1
25
Notes:
1. All rates displayed as frame rates, interlaced (“i”) field rates are two times the number shown.
Analog Audio
The ADC-142 supports 8 channels differential analog audio. The analog audio is converted in such a
way as to make +24 dBu (analog) equivalent to 0 dBFS (digital).
Discrete AES Audio Input
The ADC-142 can accept 16 channels (8 pairs) of discrete AES audio on 75 ohm BNC connections.
The AES must have a nominal rate of approximately 48 kHz. Sample rate conversion is employed to
account for minor clock rate differences in the input AES stream and the input video stream. However,
the card does not support AES input at 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz or 192 kHz rates.
Analog
Video Input
ADC-142 Block Diagram
Audio Control:
Routing
Gain
Polarity
Diff. Analog
Audio A/D
AES
Decode
and SRC
Dolby E
Decode
and SRC
From AES or
Embedded Audio
8 pairs
16 channels
8 channels
Analog
Video A/D
Audio
Embed
AES
Encode
Video Proc:
Gain, Lift, Saturation, Phase
Video
Video
Serializer
and Cable
Driver
8 pairs
16 channels
Frame
Sync
FS
Tracking
Delay +
User
Offset
