Design, function & operation, Figure 1 - typical tank installation – Groth 1721B User Manual
Page 3
Page 3 of 18
DESIGN, FUNCTION & OPERATION
Pressure Relief: As the pressure in the storage tank
increases the vacuum pallet is held shut. When the
set pressure is reached the pressure pallet lifts and
relieves to the outlet pipe.
Vacuum Relief: As a vacuum is drawn on the
storage tank (for example, when fluid is being
pumped out), the pressure pallet is held shut by tank
vacuum. When the vacuum setting is reached, the
pallet lifts and air is drawn in from the atmosphere
and flows into the tank.
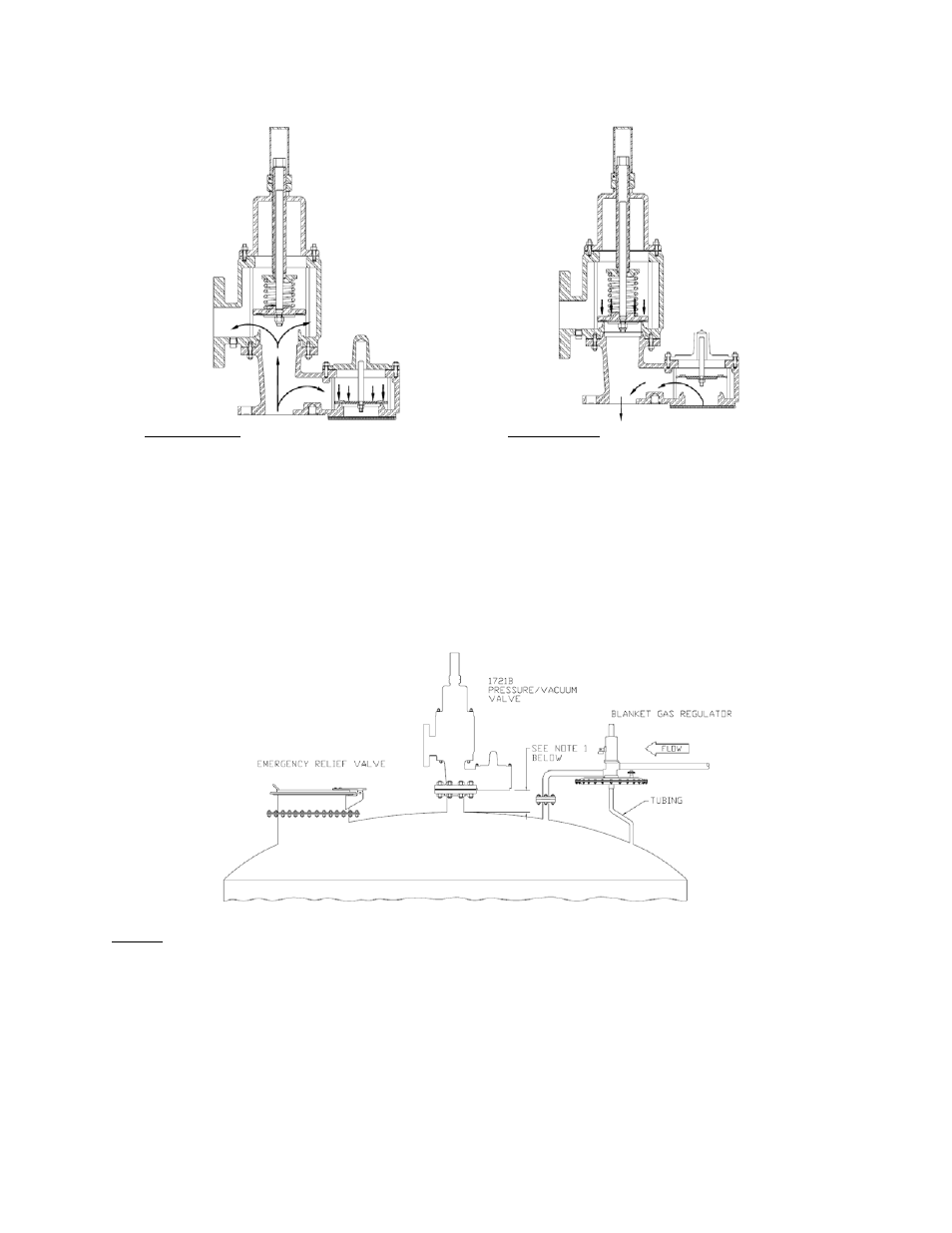
Typical valve installation on a tank or vessel is illustrated in Fig.1 on the next page using a Model 1221A
Pressure/Vacuum Relief Valve. Most tanks will have provision for an operating relief valve, an emergency relief valve,
and a blanketing regulator that maintains a positive gas pressure in the tank.
The combination of these valves and regulator are designed to ensure that the tank is protected from both excess
vacuum and pressure conditions.
Figure 1 - Typical Tank Installation
NOTE 1: Minimum recommended clearance between vacuum inlet port and tank roof is nominal flange bore of valve.
Tank protection equipment typically includes an operating valve which is designed to provide pressure/vacuum relief
under normal pump in/out and thermal breathing conditions. An emergency relief valve can also provide both
pressure and vacuum relief, normally sized to provide pressure relief if there is a fire in the immediate vicinity of the
tank. It may also be sized by the tank designer to provide protection in the event of equipment failure (such as the
rupture of a process steam line or an inert gas blanketing system failing “wide open”) or operator error.
A typical tank installation is shown in Figure 1. The following Installation Notes are recommended:
1. Minimum clearance between tank roof and vacuum inlet port must be at least equal to the valve’s nominal
flange bore.
2. Tank nozzle bore must be > or = valve inlet flange bore.
3. Inlet and outlet piping loads must be supported by appropriate structural supports, NOT by the valve body.
