Codan Radio P25 Training Guide User Manual
Page 77
P25 RADIO SYSTEMS | TRAINING GUIDE
Chapter 5: Conventional Fixed Station Interface Page 69
Internet Protocol
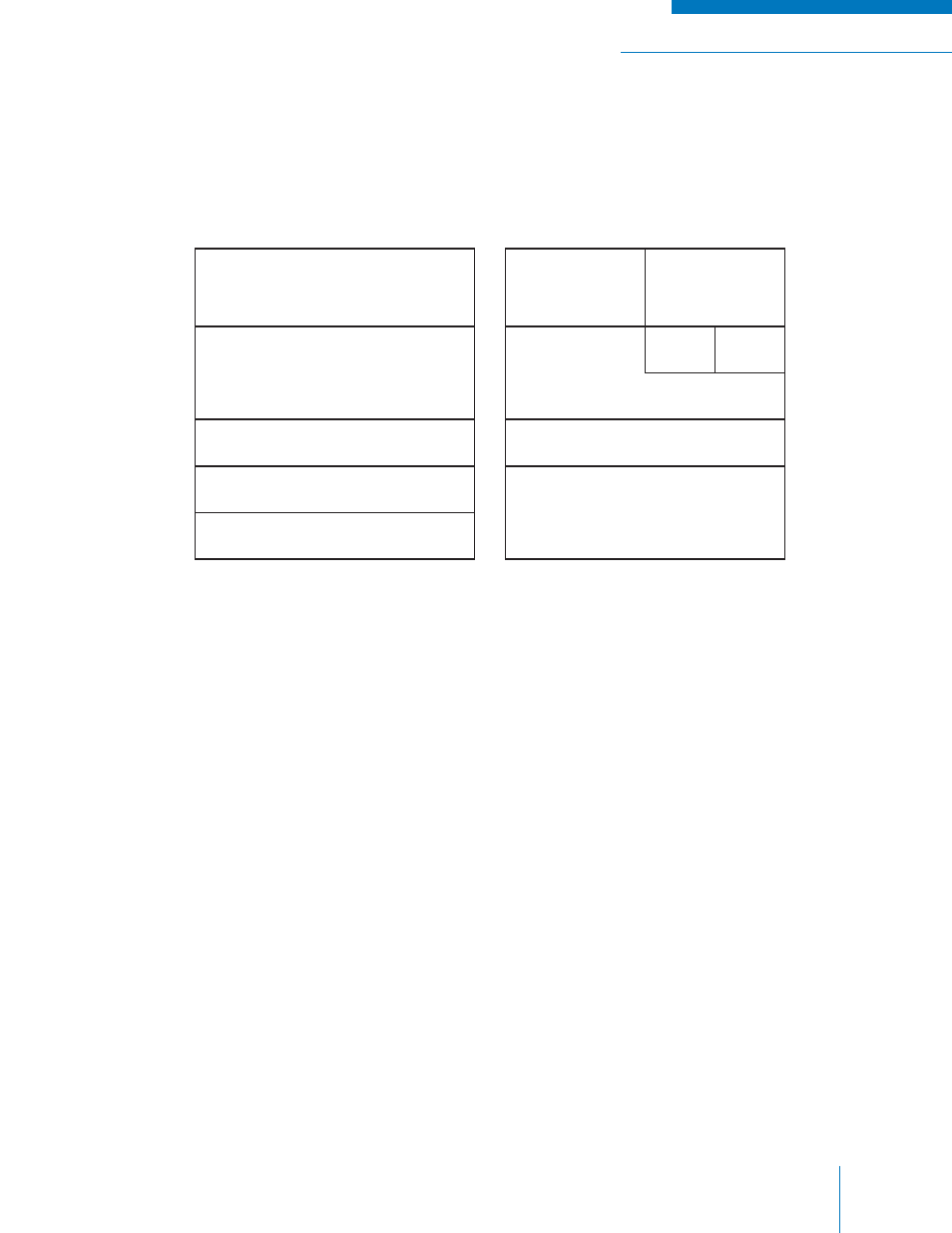
The Internet Architecture Layers are used to construct the Digital Fixed Station Interface (DFSI) protocol
suite as shown in Figure 5-5.
Figure 5-5: DFSI Internet Protocol Suite
Physical and Data Link Layers
The DFSI uses Ethernet 100 Base-T with a RJ45 connector as the physical and data link layers. In
addition to the Ethernet 100 Base-T, manufacturers may offer other industry standard physical and data
link layer protocols that support the internet protocol.
Network Layer
The DFSI uses the Internet Protocol (IP), a connectionless packet protocol. The Internet Protocol uses
unicast IP addresses to send information to a particular destination, and multicast IP addresses to send
information to a number of hosts. Host and fi xed station equipment support unicast IP addresses, and
hosts are also able to send to IP multicast addresses. The DFSI currently uses IPv4, while IPv6 is for
possible future use.
Transport Layer
The DFSI uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for its multicast capability and its ability to suit real
time applications. The Control Service transports information over UDP, and the Voice Conveyance
Service transports information over Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) on UDP for more reliable
transport. Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) may be used as well, but is not required.
Application
Link
Network
Transport
Physical
Control
Protocol
IPv4
UDP
Ethernet 100 Base-T with
an RJ-45 connector
or other industry standard
RTP
RTCP
Voice
Conveyance
Protocol
Internet Architecture Layers
DFSI Protocol Suite
