Failure – BECKHOFF DK9222-0810-0040 User Manual
Page 5
I/O
I/O, Building Automation
Application Note DK9222-0810-0040
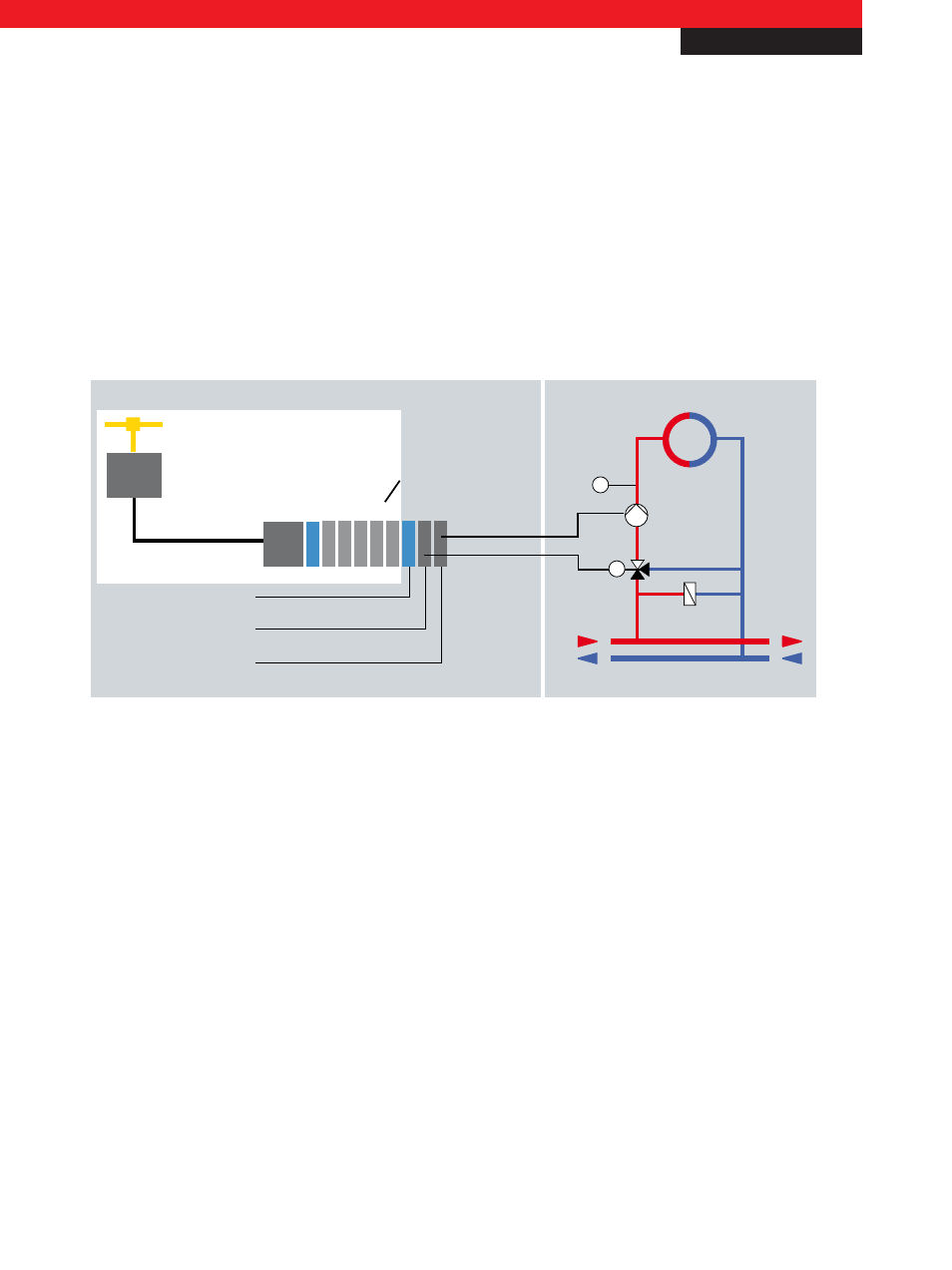
5. Practical example for local override operation: activation of a heating circuit
Since the focus in the event of malfunctions/failures is more on finding the source of error than on permanent availability,
targeted, limited operation of important building functions through manual interventions is required. This is where local
override operation comes in, explained here using the example of a heating circuit:
Fig. 5 In the event of a failure of the communication, the controller or the power at the Bus Coupler, local override operation can
occur through the separate power supply of the manual operating terminals.
Despite failure of the communication to the building management system or the automation device, failure of the controller
or a power failure at the Bus Coupler, the configuration shown in Fig. 5 enables local override operation through the separate
power supply of the manual operating terminals. The KM2652 relay terminal activates the pump for the heating circuit. The
analog value specification of the KM4602 specifies the valve position. Since the terminal switch positions are submitted to
the controller (and therefore the building management system), the status of the switches can be queried once the fault has
been rectified. In the event of a failure of the 230 V AC power supply within the heating circuit, local override operation can no
longer be ensured.
New Automation Technology
Beckhoff
5
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Substation (any automation device)
any fieldbus
KL9400
Power supply unit terminal for the K-bus
KM4602
manual operation, analog output 0...10 V
KM2652
manual operation, relay 230 V AC, 6 A
Power supply
Bus Coupler
Power supply
local override
=
Connection to BACS (Ethernet)
T
M
heating circuit
System controller
Failure
Bus Couplers and Terminals
