Calculation priority sequence – Casio FX-82AU PLUS User Manual
Page 8
E-7
*
1
Input of the closing parenthesis is required for sin, sinh, and other functions
that include parentheses.
*
2
These multiplication symbols (
s) can be omitted. A multiplication symbol
can be omitted when it occurs immediately before an opening parenthesis,
immediately before sin or other function that includes parentheses,
immediately before the Ran# (random number) function, or immediately
before a variable (A, B, C, D, M, X, Y),
P or
e
.
*
3
The closing parenthesis immediately before the
operation can be
omitted.
Input example omitting
*
2
and
*
3
operations in the above
example.
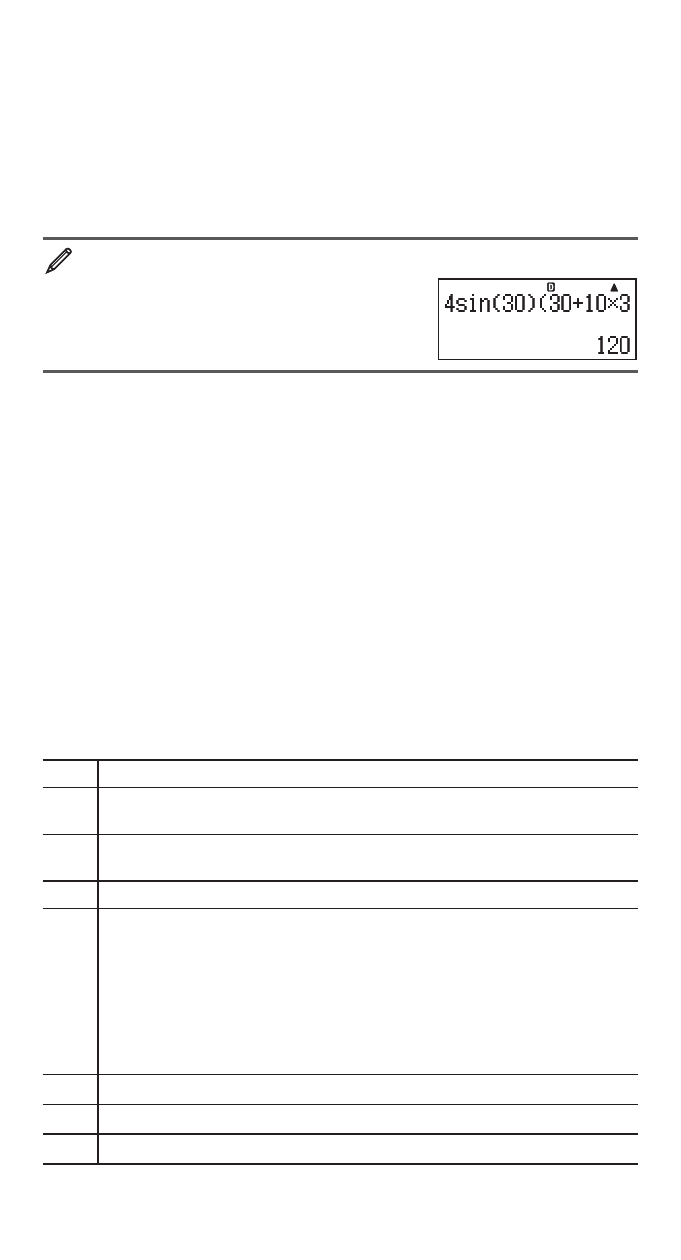
4
Q 30 30 10 3
Note: • If the calculation becomes longer than the screen width during
input, the screen will scroll automatically to the right and the
; indicator will
appear on the display. When this happens, you can scroll back to the left by
using
B and C to move the cursor. • When Linear Display is selected,
pressing
D will cause the cursor to jump to the beginning of the calculation,
while
A will jump to the end. • When Natural Display is selected, pressing
C while the cursor is at the end of the input calculation will cause it to jump
to the beginning, while pressing
B while the cursor is at the beginning will
cause it to jump to the end. • You can input up to 99 bytes for a calculation.
Each numeral, symbol, or function normally uses one byte. Some functions
require three to 13 bytes. • The cursor will change shape to
I when there are
10 bytes or less of allowed input remaining. If this happens, end calculation
input and then press
.
Calculation Priority Sequence
The priority sequence of input calculations is evaluated in accordance with the
rules below. When the priority of two expressions is the same, the calculation
is performed from left to right.
1st
Parenthetical expressions
2nd
Functions that require an argument to the right and a closing
parenthesis “)” following the argument.
3rd
Functions that come after the input value (
x
2
,
x
3
,
x
–1
,
x
!, °’ ”, °,
r
,
g
,
%), powers (
x
9), roots ()
4th
Fractions
5th
Negative sign (–)
Note: When squaring a negative value (such as –2), the value
being squared must be enclosed in parentheses (
2 7;
). Since
x
2
has a higher priority than the negative sign,
inputting
2 7 would result in the squaring of 2 and then
appending a negative sign to the result. Always keep the priority
sequence in mind, and enclose negative values in parentheses
when required.
6th
STAT Mode estimated values (
K, L, K
1
,
K
2
)
7th
Multiplication where the multiplication sign is omitted
8th
Permutation (nPr), combination (nCr)
