Great Planes Matt Chapman Eagle 580 46/EP ARF - GPMA1281 User Manual
Page 29
29
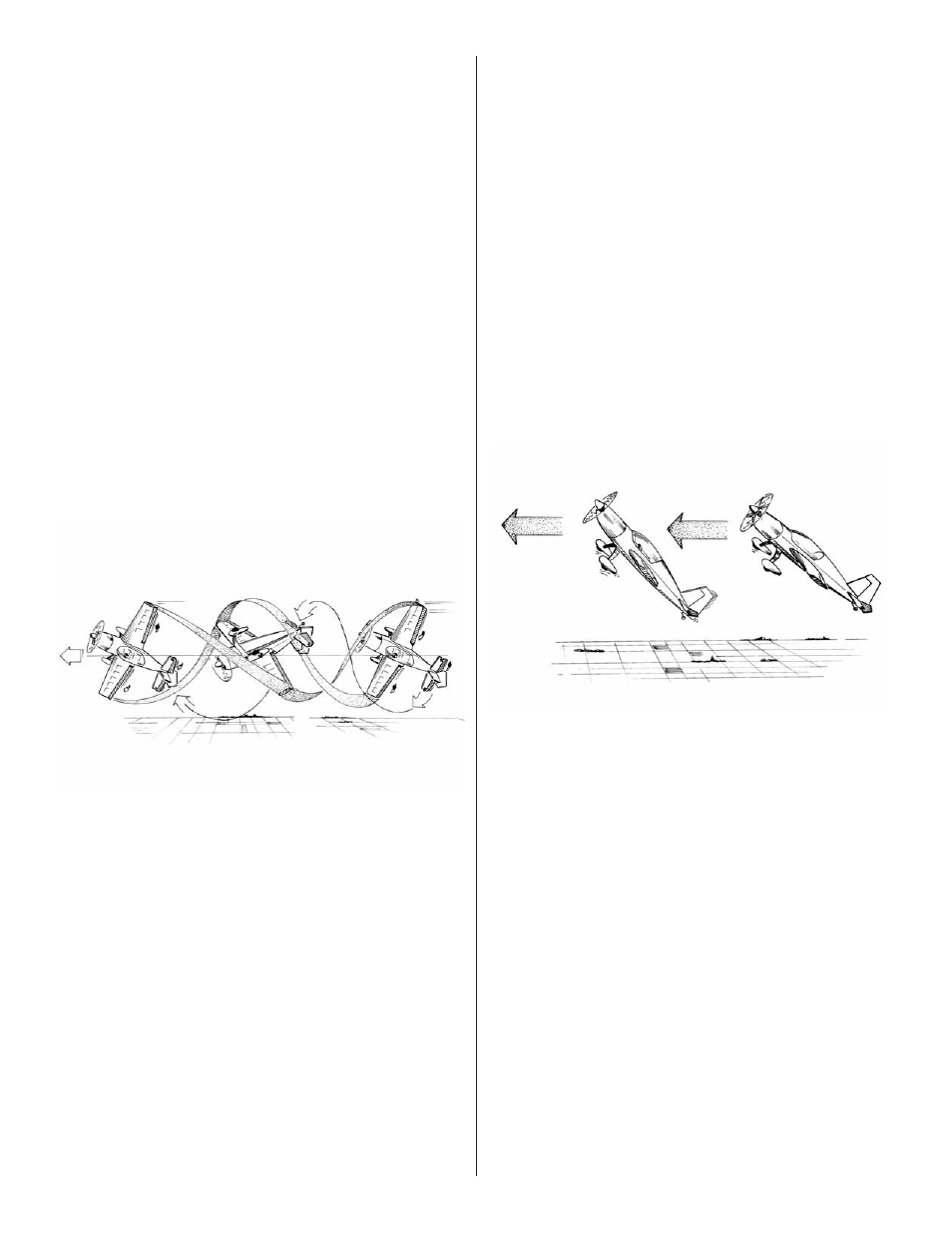
UPRIGHT FLAT SPINS
Pull the nose up slightly and slowly decrease power. As the
model slows to a few mph, slowly apply full left rudder and
power. Next, start adding up elevator as needed to keep the
model fl at in the spin. Most airplanes will require some aileron
as well to keep the wings level. This is one of the maneuvers
to experiment on; try different C.G. positions and different
amounts of throw and power to see how fl at the spin will go.
It is possible to maintain altitude in the fl at spin and in some
cases it is also possible to climb during the spin.
INVERTED FLAT SPINS
This is the same as the up-right fl at spin except most planes
like to spin in the opposite direction, for example: right rudder
and down elevator.
THE WALL
Fly straight across the fi eld at a moderate speed and simply
pull full up until vertical. Adjust the power as necessary to
maintain a hover.
KNIFE EDGE TUMBLE
This is an impressive looking maneuver that really isn’t as
diffi cult as it looks. (Before learning this maneuver you must
be able to confi dently Snap and Tumble your plane and stop
the aircraft exactly, without over rotating.) Fly the model
Knife Edge from the right at a moderate airspeed, using
just enough rudder to maintain Knife Edge, not climbing or
diving. Perform one full right negative Tumble by maintaining
your rudder setting while applying full throttle, full down
elevator, and full right aileron, releasing in time to end again
fl ying Knife Edge to the right. Note that you may need to use
some positive elevator and/or left aileron to stop the Tumble
at exactly Knife Edge. This maneuver is easier to the right
because torque helps stop the Tumble and it can be done at
varied airspeeds with proper throttle and rudder modulation.
VERTICAL HOVER
Fly a straight pass across the fi eld at 75ft high and 100ft out
and pull the model vertical. Roll the model until the top of it is
facing you and slowly begin to reduce power. As the model
begins to slow down to 10 mph or so, slowly add a little bit of
power back in. You will have to adjust the throttle as needed,
but make your adjustments smooth. Some right aileron may
be needed to keep the model from torque rolling. Use the
rudder and elevator to keep the nose pointing straight up. Be
patient as this maneuver will take a while to learn.
TORQUE ROLL
This is the same as the vertical hover but without the use of
right aileron to keep the model from rolling. If needed, you
can use a little left aileron to speed the roll up. As the model
rotates around, the controls will appear to be reversed to you
but only the orientation of the model has changed.
HARRIER
The harrier is nothing more than a high angle of attack fl ying
stall. Check the stall characteristics of your plane before
proceeding with this maneuver. Bring your plane across the
fi eld at 75ft high and 100ft out away from yourself. Slowly
pull back on the elevator while reducing throttle. The nose of
the plane should come up. Depending on the plane/setup,
you may have to make constant aileron (wing walking) and
rudder corrections for this maneuver. As the nose of the plane
comes up, start adding in a little bit of power to help maintain
airspeed. The rudder is now used to turn the model. This
maneuver will take some practice as there are a lot of small
corrections made to keep most planes in the maneuver.
This is one maneuver where less control is needed. Too
much elevator and the model goes into an uncontrollable
stall. The C.G. of the plane will have a large effect on the
stability of the model during this maneuver. Some planes
perform better with more elevator defl ection and a farther
forward C.G. while other planes prefer a further aft C.G. and
less elevator defl ection. Elevator to fl ap mixing can be used
on airplanes with marginal wing area, and some planes won’t
stall so elevator to spoileron mixing will be needed.
